
QwaQwa was a bantustan ("homeland") in the central eastern part of South Africa. It encompassed a very small region of 655 square kilometres (253 sq mi) in the east of the former South African province of Orange Free State, bordering Lesotho. Its capital was Witsieshoek. It was the designated homeland of more than 180,000 Sesotho-speaking Basotho people.

The Freedom Front Plus is a right-wing political party in South Africa that was formed in 1994. It is led by Pieter Groenewald. Since 2024, it is a part of the current South African government of national unity together with the African National Congress (ANC), the Democratic Alliance and other parties.

Dikwankwetla Party of South Africa is a political party in the Free State province, South Africa. The party was founded by Kenneth Mopeli in 1975. The party governed the bantustan state of QwaQwa from 1975 to 1994.

The Congress of the People (COPE) is a South African political party formed in 2008 by former members of the African National Congress (ANC). The party was founded by former ANC members Mosiuoa Lekota, Mbhazima Shilowa and Mluleki George to contest the 2009 general election. The party was announced following a national convention held in Sandton on 1 November 2008, and was founded at a congress held in Bloemfontein on 16 December 2008. The name echoes the 1955 Congress of the People at which the Freedom Charter was adopted by the ANC and other parties, a name strongly contested by the ANC in a legal move dismissed by the Pretoria High Court.

Al Jama-ah is a South African political party. It was formed in 2007 by present leader Ganief Hendricks and contested the 2009, 2014, 2019 and 2024 national elections.

The Cape Independence Party (CAPEXIT), previously called the Cape Party, is a political party in South Africa which seeks to use all constitutional and legal means to bring about Cape independence, which includes the entire Western Cape, Northern Cape, six municipalities in the Eastern Cape, and one municipality in the Free State. The area includes all municipalities in those provinces with an Afrikaans-speaking majority. In 2009, it was claimed to have had a membership of approximately 1,000 people across South Africa, but official membership figures are not made public. The party currently holds two seats on the Cape Town City Council.

Maluti-a-Phofung Municipality is a local municipality within the Thabo Mofutsanyane District Municipality, in the Free State province of South Africa. It encompasses substantially all of the former bantustan of QwaQwa, except for the small enclave at Botshabelo. The population is almost entirely Basotho. The municipality is named after the Drakensberg mountains. The peak is known as the Sentinel, which is called Phofung in Sesotho.

The Patriotic Alliance (PA) is a right-wing political party in South Africa, formed in November 2013 by, among others, businessmen Gayton McKenzie and Kenny Kunene. Since 2024, it is a part of the current South African government of national unity together with the African National Congress (ANC), the Democratic Alliance and other parties.
Azwihangwisi Faith Muthambi is a South African politician who represents the African National Congress (ANC) in the National Assembly of South Africa. She was formerly the Minister of Public Service and Administration and Minister of Communications under President Jacob Zuma. She returned to the National Assembly in June 2024 after serving a prior stint in her seat between 2009 and 2022.
Hlaudi Motsoeneng is the leader of African Content Movement (ACM) who served as the acting Chief operating officer of the South African Broadcasting Corporation (SABC) from 2011 to 2013. Motsoeneng was removed from his position as Chief operating officer after it had been found that he lied about his qualifications. After being removed as acting Chief operating officer it was announced that Motsoeneng would move back to his previous position as Group Executive Editor of Provinces and Corporate Affairs of the SABC. In December 2016, the Western Cape High Court ruled that Motsoeneng's appointment as Group Executive was illegal and that he was "not entitled to occupy any position at the SABC". In June 2022 the state capture commission proposed criminal investigations into possible contraventions of the Public Finance Management Act when group CEO Lulama Mokhobo and COO Motsoeneng concluded an SABC agreement with the Gupta owned TNA newspaper. In July 2022 the High Court dismissed Motsoeneng's bid to appeal the repayment, with interest, of R11.5 million obtained unlawfully when the SABC concluded a deal with MultiChoice.
General elections were held in South Africa on 8 May 2019 to elect a new President, National Assembly and provincial legislatures in each province. These were the sixth elections held since the end of apartheid in 1994 and determined who would become the next President of South Africa.

Good is a South African political party that was formed in December 2018. It is led by its founder Patricia de Lille, current Minister of Tourism and former mayor of Cape Town, who is also the party's sole member in the National Assembly. The party's stronghold is the Western Cape and mainly draws support from the Coloured community.

The African Transformation Movement (ATM) is a political party in South Africa. It is led by Vuyolwethu Zungula, leader and party president. It was formed with the backing of the South African Council of Messianic Churches in Christ (SACMCC), which together are supported by millions of congregants.

African Democratic Change (ADeC) is a South African political party. It was launched on 1 December 2017 by former African National Congress Member of Parliament, Makhosi Khoza. Khoza resigned from the party in April 2018. The party is currently led by Visvin Reddy.

The Electoral Commission of South Africa (IEC) announced on 20 March 2019 that a record number of 48 parties had registered candidates for the national parliamentary election. This is 19 more parties that contested the 2014 national elections. In the provincial legislature elections, the total number of parties registering candidates were:

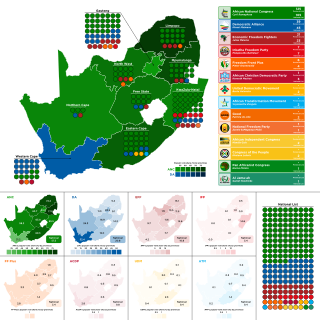
General elections were held in South Africa on 29 May 2024 to elect a new National Assembly as well as the provincial legislature in each of the nine provinces. This was the 7th general election held under the conditions of universal adult suffrage since the end of the apartheid era in 1994. The new National Council of Provinces (NCOP) will be elected at the first sitting of each provincial legislature.

ActionSA is a centre-right political party in South Africa established in 2020 by Herman Mashaba, a former mayor of Johannesburg, shortly after he left the Democratic Alliance (DA).
The MAP16 Civic Movement (MAP16) is a minor South African political party. It was formed after sixteen African National Congress (ANC) local councillors from the Maluti-a-Phofung Local Municipality were expelled by the ANC for voting to unseat the ANC mayor Vusi Tshabalala, who faced a number of corruption charges.
Vusimusi William Tshabalala is a South African politician who has represented the African National Congress (ANC) in the Free State Provincial Legislature since 2019. He was also the Majority Chief Whip in the legislature until October 2021, when he was replaced after the ANC suspended him while he faced internal disciplinary charges. He is also known for his controversial tenure in the Free State's Maluti-a-Phofung Local Municipality, where he was Mayor between 2013 and 2018.

uMkhonto weSizwe, abbreviated as MK, and often referred to as the MK Party, is a nominally left-wing populist South African political party, founded in December 2023. The party is named after uMkhonto weSizwe, the paramilitary wing of the African National Congress (ANC) which was active during the apartheid regime in South Africa. However, the ANC has threatened legal action over the usage of the name, and the formation has been criticised by original MK veterans.

















