
The African National Congress (ANC) is a political party in South Africa. It originated as a liberation movement known for its opposition to apartheid and has governed the country since 1994, when the first post-apartheid election resulted in Nelson Mandela being elected as President of South Africa. Cyril Ramaphosa, the incumbent national President, has served as President of the ANC since 18 December 2017.

The Inkatha Freedom Party is a conservative political party in South Africa, which is a part of the current South African government of national unity together with the African National Congress (ANC). Although registered as a national party, it has had only minor electoral success outside its home province of KwaZulu-Natal. Mangosuthu Buthelezi, who served as chief minister of KwaZulu during the Apartheid period, founded the party in 1975 and led it until 2019. He was succeeded as party president in 2019 by Velenkosini Hlabisa.

The Democratic Alliance is a South African political party which is a part of the current South African Government of National Unity (GNU) together with the African National Congress (ANC), Inkatha Freedom Party (IFP), and several others. The party has been the second-largest in South Africa since its foundation in 2000. The party is broadly centrist, and has been attributed both centre-left and centre-right policies. It is a member of Liberal International and the Africa Liberal Network. The DA traces its roots to the founding of the anti-apartheid Progressive Party in 1959, with many mergers and name changes between that time and the present. The DA has a variety of ideologically liberal tendencies, including neoliberalism, social liberalism, classical liberalism, and conservative liberalism.

The United Democratic Movement (UDM) is a centre-left, social-democratic, South African political party, formed by a prominent former National Party leader, Roelf Meyer, a former African National Congress and Transkei homeland leader, General Bantu Holomisa, and a former ANC Executive Committee member, John Taylor. It has an anti-separatist, pro-diversity platform; and supports an individualist South Africa with a strong moral sense, in both social and economic senses.

The Defiance Campaign against Unjust Laws was presented by the African National Congress (ANC) at a conference held in Bloemfontein, South Africa in December 1951. The Campaign had roots in events leading up the conference. The demonstrations, taking place in 1952, were the first "large-scale, multi-racial political mobilization against apartheid laws under a common leadership."

The Anti-Apartheid Movement (AAM) was a British organisation that was at the centre of the international movement opposing the South African apartheid system and supporting South Africa's non-white population who were oppressed by the policies of apartheid. The AAM changed its name to ACTSA: Action for Southern Africa in 1994, when South Africa achieved majority rule through free and fair elections, in which all races could vote.

Internal resistance to apartheid in South Africa originated from several independent sectors of South African society and took forms ranging from social movements and passive resistance to guerrilla warfare. Mass action against the ruling National Party (NP) government, coupled with South Africa's growing international isolation and economic sanctions, were instrumental in leading to negotiations to end apartheid, which began formally in 1990 and ended with South Africa's first multiracial elections under a universal franchise in 1994.

The Congress of the People (COPE) is a South African political party formed in 2008 by former members of the African National Congress (ANC). The party was founded by former ANC members Mosiuoa Lekota, Mbhazima Shilowa and Mluleki George to contest the 2009 general election. The party was announced following a national convention held in Sandton on 1 November 2008, and was founded at a congress held in Bloemfontein on 16 December 2008. The name echoes the 1955 Congress of the People at which the Freedom Charter was adopted by the ANC and other parties, a name strongly contested by the ANC in a legal move dismissed by the Pretoria High Court.
This article covers the history of the Pan Africanist Congress of Azania, once a South African liberation movement and now a minor political party.
No Land! No House! No Vote! is the name of a campaign by a number of poor people's movements in South Africa that calls for the boycotting of the vote and a general rejection of party politics and vote banking. The name is meant to imply that if government does not deliver on issues important to affected communities these movements will not vote.
The Institute for Democratic Alternatives in South Africa (IDASA) later known as the Institute for Democracy in South Africa was a South African-based think-tank organisation that was formed in 1986 by Frederik van Zyl Slabbert and Alex Boraine. Its initial focus from 1987 was creating an environment for white South Africans to talk to the banned liberation movement in-exile, the African National Congress (ANC) prior to its unbanning in 1990 by the President F. W. de Klerk. After the South African election in 1994, its focus was on ensuing the establishment of democratic institutions in the country, political transparency and good governance. Caught up in a funding crisis after the Great Recession, it closed in 2013.
Kopeng Obed Bapela is a South African politician who is currently serving as the Deputy Minister of Public Enterprises since 6 March 2023. Before that, he was Deputy Minister of Cooperative Governance and Traditional Affairs from 2014 to 2023. A member of the African National Congress (ANC), he has been a member of the National Assembly since 2002 and a deputy minister since 2010.
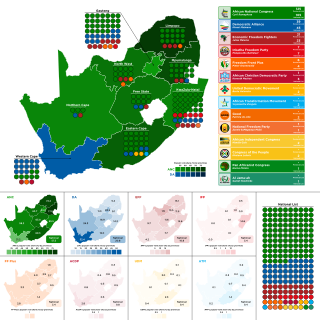
General elections were held in South Africa on 8 May 2019 to elect a new President, National Assembly and provincial legislatures in each province. These were the sixth elections held since the end of apartheid in 1994 and determined who would become the next President of South Africa.
Nosipho Dastile (1938–2009) was a community and anti-Apartheid activist in the small town of Uitenhage, just outside Port Elizabeth, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. She was elected councillor under the banner of what was then the new democratically constituted Uitenhage Transitional Local Council from 1994 to 1999.
Florence Matomela OLG (1910–1969) was a South African anti-pass law activist, communist, civil rights campaigner, ANC veteran, teacher and mother who dedicated her life to fighting against Apartheid laws in South Africa. Matomela was the provincial organiser of the African National Congress Women's League (ANCWL) and vice-president of the Federation of South African Women (FEDSAW) in the mid 1950s.
Bicks Ndoni was a South African politician who served as chief whip of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality from August 2018 until his death in January 2020. He was previously the deputy mayor of Nelson Mandela Bay under the mayoralty of Danny Jordaan. Ndoni served as the mayor of Uitenhage transitional council in the 1990s. He was an African National Congress (ANC) politician.
Mohammed Haniff Hoosen is a South African politician who served as a Member for the National Assembly for the Independent Democrats (ID) (2007–2014) and for the Democratic Alliance (DA) (2014–2024). Within the Official Opposition Shadow Cabinet, he was the Shadow Minister of Home Affairs from 2014 to 2019, the Shadow Minister of Cooperative Governance and Traditional Affairs from 2019 to 2020 and the DA's spokesperson on the Standing Committee on the Auditor-General from 2020 until his resignation in 2024.

Leon Amos Schreiber is a South African writer and politician who is currently serving as Minister of Home Affairs since 3 July 2024. A member of the Democratic Alliance (DA), he has been a Member of the National Assembly of South Africa since May 2019.
Mkhangeli Manford Matomela is a South African politician who represented the African National Congress (ANC) in the Eastern Cape Provincial Legislature until August 2013, when he left the legislature and the party to found the breakaway Kingdom Governance Movement. He was formerly the Speaker of the Eastern Cape Provincial Legislature from 2004 to 2009 and the Eastern Cape's Member of the Executive Council (MEC) for Education from 2004 to 2007. Matomela contested the 2014 general election as a candidate for the Kingdom Governance Movement, but the party did not win any seats.










