Related Research Articles
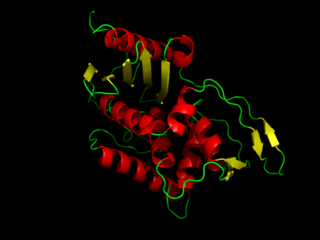
DD-transpeptidase is a bacterial enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of the R-L-αα-D-alanyl moiety of R-L-αα-D-alanyl-D-alanine carbonyl donors to the γ-OH of their active-site serine and from this to a final acceptor. It is involved in bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, namely, the transpeptidation that crosslinks the peptide side chains of peptidoglycan strands.
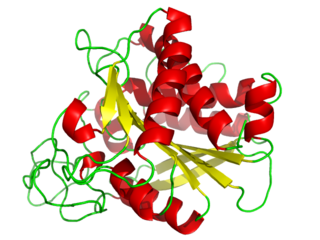
A carboxypeptidase is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes (cleaves) a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) end of a protein or peptide. This is in contrast to an aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at the N-terminus of proteins. Humans, animals, bacteria and plants contain several types of carboxypeptidases that have diverse functions ranging from catabolism to protein maturation. At least two mechanisms have been discussed.

Carboxypeptidase A usually refers to the pancreatic exopeptidase that hydrolyzes peptide bonds of C-terminal residues with aromatic or aliphatic side-chains. Most scientists in the field now refer to this enzyme as CPA1, and to a related pancreatic carboxypeptidase as CPA2.

Glutamate carboxypeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Butyrate—CoA ligase, also known as xenobiotic/medium-chain fatty acid-ligase (XM-ligase), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, an acyl-lysine deacylase (EC 3.5.1.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aminoacylase (EC 3.5.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-ureidopropionase (EC 3.5.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a long-chain-fatty-acyl-glutamate deacylase (EC 3.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
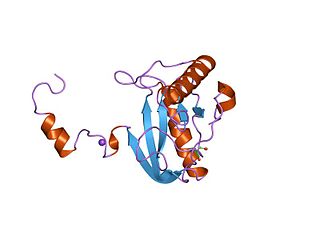
In enzymology, a N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase is an enzyme that catalyzes a chemical reaction that cleaves the link between N-acetylmuramoyl residues and L-amino acid residues in certain cell-wall glycopeptides.
In enzymology, a N-acyl-D-glutamate deacylase (EC 3.5.1.82) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-(long-chain-acyl)ethanolamine deacylase (EC 3.5.1.60) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycine N-acyltransferase (GLYAT), also known as acyl-CoA:glycine N-acyltransferase (ACGNAT), is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Glycine-N-acyltransferase, also known as GLYAT, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the GLYAT gene.
Muramoylpentapeptide carboxypeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction.
Muramoyltetrapeptide carboxypeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Zinc D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase (EC 3.4.17.14, Zn2+ G peptidase, D-alanyl-D-alanine hydrolase, D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving carboxypeptidase, DD-carboxypeptidase, G enzyme, DD-carboxypeptidase-transpeptidase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Acyl-homoserine-lactone acylase (EC 3.5.1.97, acyl-homoserine lactone acylase, AHL-acylase, AiiD, N-acyl-homoserine lactone acylase, PA2385 protein, quorum-quenching AHL acylase, quorum-quenching enzyme, PvdQ, QuiP) is an enzyme with systematic name N-acyl-L-homoserine-lactone amidohydrolase. This enzyme functions as a quorum quencher by catalysing the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Levy CC, Goldman P (August 1969). "Bacterial peptidases. 3. An enzyme specific for N-acyl linkages to alanine". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 244 (16): 4467–72. PMID 5806587.
- ↑ Miyagawa, E.; Takahiro, H.; Yoshinobu, M. (1986). "Purification and properties of N-benzoyl-L-alanine amidohydrolase from Corynebacterium equii". Agric. Biol. Chem. 50: 1527–1531. doi:10.1080/00021369.1986.10867595.