
The Borchaly uezd was a county (uezd) of the Tiflis Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, and later of the independent and Soviet republics of Georgia. Its administrative center was the town of Shulavery. The area of the county roughly corresponded to the contemporary Lori Province of Armenia and the Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia.

The Elizavetpol uezd, also known as the Ganja uezd after 1918, was a county (uezd) of the Elizavetpol Governorate of the Russian Empire, and later of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and Azerbaijan SSR until its formal abolition in 1929. The area of the Elizavetpol uezd corresponds to the modern-day Gadabay, Shamkir, Dashkasan, Goygol, and Samukh districts of Azerbaijan.

The Erivan uezd was a county (uezd) of the Erivan Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Etchmiadzin and Surmalu uezds to the west, the Nor Bayazet uezd to the east, the Sharur-Daralayaz uezd to the south, and Iran to the southwest. It included most of the Ararat Province and southern parts of the Kotayk Province of central Armenia, the Sadarak District of the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, and the Aras corridor of the Aralık District of the Iğdır Province of Turkey. The administrative centre of the county was the city of Erivan.

The Sharur-Daralayaz uezd was a county (uezd) of the Erivan Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. It bordered the governorate's Erivan and Nor Bayazet uezds to the north, the Nakhichevan uezd to the south, the Zangezur and Jevanshir uezds of the Elizavetpol Governorate to the east, and Persia to the southwest. It included most of the Vayots Dzor Province of present-day Armenia and the Sharur District of the Nakhchivan exclave of present-day Azerbaijan. The administrative centre of the county was Bashnorashen.

The Dagestan Oblast was a province (oblast) of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. It roughly corresponded to most of present-day southeastern Dagestan within the Russian Federation. The Dagestan oblast was created in 1860 out of the territories of the former Caucasian Imamate, bordering the Terek Oblast to the north, the Tiflis Governorate and Zakatal Okrug to the west, the Elizavetpol Governorate to the south, and Baku Governorate to the east. The administrative center of the oblast was Temir-Khan-Shura.

The Surmalu uezd was a county (uezd) of the Erivan Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. It bordered the governorate's Etchmiadzin and Erivan uezds to the north, the Kars Oblast to the west, Persia to the east, and the Ottoman Empire to the south. The district made up most of the Iğdır Province of present-day Turkey. As part of the Russian Transcaucasus, the Surmalu uezd possessed economical importance for its abundantly rich salt mines in Kulp (Tuzluca), and spiritual importance to Armenians as the location of the culturally significant Mount Ararat. The administrative centre of the county was Igdyr.

The Nor Bayazet or Novobayazet uezd was a county (uezd) of the Erivan Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Alexandropol uezd to the north, the Etchmiadzin and Erivan uezds to the west, the Sharur-Daralayaz uezd to the south, and the Kazakh, Elizavetpol, and Jevanshir uezds of the Elizavetpol Governorate to the east. Centered on Lake Sevan, the Nor Bayazet uezd included most of the contemporary province of Gegharkunik and northern parts of the Kotayk Province of Armenia. The administrative center of the uezd was the city Novobayazet for which the district was eponymously named.
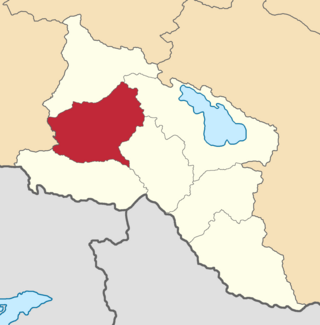
The Etchmiadzin uezd was a county (uezd) of the Erivan Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. The uezd bordered the Alexandropol uezd to the north, the Nor Bayazet uezd to the east, Erivan uezd to the north, the Surmalu uezd to the south, and the Kars Oblast to the west. It included all of the Armavir Province and most of the Aragatsotn Province of present-day Armenia. The administrative centre of the county was Vagorshapat (Vagharshapat), also referred to as Etchmiadzin—the administrative capital of the Armenian Apostolic Church.

The Zugdidi uezd was a county (uezd) of the Kutaisi Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire. It bordered the Sukhumi Okrug to the north, the Lechkhumi uezd to the east, the Senaki uezd to the south, and the Black Sea to the west. The area of the Zugdidi uezd corresponded to most of the contemporary Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti region of Georgia. The county was eponymously named for its administrative center, Zugdidi.

The Lenkoran uezd or Talysh uezd was a county (uezd) within the Baku Governorate of the Russian Empire, and then of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and the Azerbaijan SSR until its formal abolishment in 1929. The county was located on the southern part of the governorate, bordering Caspian Sea to the east, Javad uezd to the north, and Iran to the southwest. The administrative centre of the county was the city of Lenkoran.

The Shemakha uezd was a county (uezd) within the Baku Governorate of the Russian Empire, and then of Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and Azerbaijan SSR until its formal abolishment in 1929. The county was located in the central part of the Baku Governorate, bordering the Javad uezd to the south, Baku uezd to the east, Geokchay uezd to the west and Kuba uezd to the north. The administrative centre of the county was the city of Shemakha.

The Kars okrug was a district (okrug) of the Kars Oblast of the Russian Empire between 1878 and 1918. Its capital was the city of Kars, presently part of the Kars Province of Turkey and the Amasia District of Armenia. The okrug bordered with the Ardahan okrug in the north, the Kagizman okrug in the south, the Olti okrug in the west, and the Erivan Governorate to its east.

The Kagizman okrug was a district (okrug) of the Kars Oblast of the Russian Empire, existing between 1878 and 1918. Its capital was the town of Kagyzman, presently in the Kars Province of Turkey. The okrug bordered with the Kars okrug to the north, the Olti okrug to the northwest, the Erivan Governorate to the east, and the Erzurum Vilayet of the Ottoman Empire to the west.

The Geokchay uezd was a county (uezd) of the Baku Governorate of the Russian Empire and then of the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic and Azerbaijan SSR until its formal abolishment in 1929. The uezd was located in the central part of the governorate, bordering the Kuba uezd to the north, the Shemakha uezd to the east, the Javad uezd to the south and the Elizavetpol Governorate to the west. The administrative center of the uezd was the city of Geokchay.
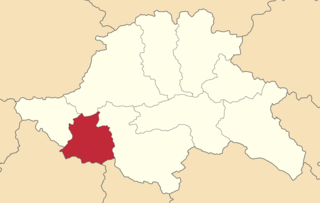
The Akhalkalaki uezd was a county (uezd) of the Tiflis Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, and then of Democratic Republic of Georgia, with its administrative centre in Akhalkalak. The county bordered the Gori uezd to the north, the Borchaly uezd to the east, the Alexandropol uezd of the Erivan Governorate and the Kars and Ardahan okrugs of the Kars Oblast to the south, and the Akhaltsikhe uezd to the west. The area of the county corresponded to part of the contemporary Samtskhe–Javakheti region of Georgia.

The Akhaltsikhe uezd was a county (uezd) of the Tiflis Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, and then of Democratic Republic of Georgia, with its administrative center in Akhaltsikh. The uezd bordered the Gori uezd and the Kutaisi Governorate to the north, the Akhalkalaki uezd to the east, the Ardahan Okrug of the Kars Oblast to the south, and the Batum Okrug of the Batum Oblast to the west. The area of the uezd corresponded to part of the contemporary Samtskhe-Javakheti region of Georgia.

The Dusheti uezd was a county (uezd) of the Tiflis Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, and then of Democratic Republic of Georgia, with its administrative centre in Dushet. The area of the uezd roughly corresponded to the contemporary Mtskheta-Mtianeti region of Georgia.

The Telavi uezd was a county (uezd) of the Tiflis Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, and then of Democratic Republic of Georgia, with its administrative center in Telavi. The area of the county corresponded to part of the contemporary Kakheti region of Georgia.

The Tiflis uezd was a county (uezd) of the Tiflis Governorate of the Caucasus Viceroyalty of the Russian Empire, and then of Democratic Republic of Georgia, with its administrative centre in Tiflis. The area of the uezd roughly corresponded to the contemporary Kvemo Kartli region of Georgia. The district bordered the Telavi uezd to the northeast, the Tionety and Dusheti uezds to the north, the Gori uezd to the northwest, the Borchaly uezd to the west, the Kazakh uezd of the Elizavetpol Governorate to the south, and the Signakh uezd to the east.

The Artvin okrug was a district (okrug) of the Batum Oblast of the Russian Empire, existing between 1878 and 1918. The district was eponymously named for its administrative centre, Artvin, presently part of the Artvin Province of Turkey. The district bordered with the Olti okrug to the south, the Ardahan okrug to the east, the Batumi okrug to the north, and the Ottoman Empire to the west. Between 1883 and 1903, the Artvin okrug formed a part of the Kutaisi Governorate.





















