| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | South Pacific Ocean |
| Archipelago | Solomon Islands |
| Administration | |
| Province | |
Anuta Paina is an island in Malaita Province, Solomon Islands. [1] [2] It is located off the east coast of Malaita Island. [3]
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | South Pacific Ocean |
| Archipelago | Solomon Islands |
| Administration | |
| Province | |
Anuta Paina is an island in Malaita Province, Solomon Islands. [1] [2] It is located off the east coast of Malaita Island. [3]

Solomon Islands is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean, that lies east of Papua New Guinea.

Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons, is a country consisting of 21 major islands Guadalcanal, Malaita, Makira, Santa Isabel, Choiseul, New Georgia, Kolombangara, Rennell, Vella Lavella, Vangunu, Nendo, Maramasike, Rendova, Shortland, San Jorge, Banie, Ranongga, Pavuvu, Nggela Pile and Nggela Sule, Tetepare, and over 900 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Papua New Guinea to the west, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, and Tuvalu to the east, and Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 28,896 square kilometres, and a population of 734,887 according to the official estimates for mid 2023. Its capital and largest city, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands.

Fatutaka, Fatu Taka or Patu Taka is a small volcanic island in Temotu Province, in the nation of Solomon Islands, south-west Pacific Ocean. The easternmost island in Solomon Islands, Fatutaka is located c. 32 km (20 mi) southeast of Anuta and can be seen from there in clear weather. Fatutaka and Anuta were discovered for Europeans by Admiral Edward Edwards in 1791.
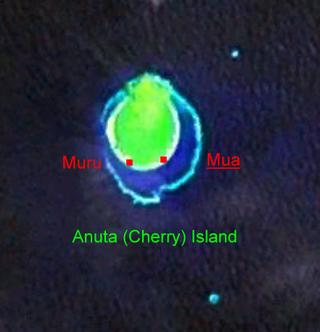
Anuta is a small volcanic island in the province of Temotu in the southeastern part of Solomon Islands. It is one of the smallest permanently inhabited Polynesian islands. It is one of the Polynesian Outlier communities in Melanesia.

Malaita Province is the most populous and one of the largest of the nine provinces of Solomon Islands. The population of the province is 122,620 (1999). The area of the province is 4,225 km2 (1,631 sq mi).

South Malaita Island is the island at the southern tip of the larger island of Malaita in the eastern part of Solomon Islands. It is also known as Small Malaita and Maramasike for Areare speakers and Malamweimwei for more than 80% of the islanders. The island is referred to as Iola Raha. It is called "small" to distinguish it from the much larger sibling. It is part of Malaita Province. South Malaita came under effective control of the colonial administration after the Solomon Islands was declared a British Protectorate in 1893. During the colonial days, the island was divided by the colonial government and missionary establishments into the Asimeuri, Asimae, and Raroisu'u districts.
Oroha, categorized as an Austronesian language, is one of many languages spoken by Melanesian people in the Solomon Islands. It is also known as Maramasike, Mara Ma-Siki, Oraha, and Oloha, and is used primarily in the southern part of Malaita Island within the Malaita Province. Little Mala is composed of three indigenous languages of the 'Tolo' people which are Na’oni, Pau, and Oroha. They are all slightly different, yet come from the same origin. The three languages may be thought of as different dialects of the same language. The three Tolo villages now harbor schools under the Melanesian Mission.

Ulawa Island is an island in Solomon Islands. It is located near Malaita Island and belongs to Makira-Ulawa Province. The island has an area of 65.92 square kilometres.

The Maramasike Passage is a narrow passage which separates the two main islands of Malaita Province in the Solomon Islands, the larger Malaita and the smaller South Malaita Island, also known as Maramasike. A similar passage is found between the Nggela Islands. The channel is the result of volcanic activity. The northern mouth leads to Raroi Su'u Lagoon, a sheltered bay.

Raraka, or Te Marie, is an atoll in the west of the Tuamotu group in French Polynesia. It lies 17 km to the southeast of Kauehi Atoll.

Pio Island is an island in Solomon Islands province of Makira-Ulawa. It is situated 4 km north-west of Ugi Island. It is 2.7 km long and 1.5 km wide. The estimated terrain elevation above sea level is some 227 metres. The island has no villages. Coral reef surrounds the island, which is largest in the west and south of the island.
The Tikopia language is a Polynesian Outlier language from the island of Tikopia in the Solomon Islands. It is closely related to the Anuta language of the neighboring island of Anuta. Tikopian is also spoken by the Polynesian minority on Vanikoro, who long ago migrated from Tikopia.
Fenualoa is the second largest island in the Reef Islands, in Temotu Province, in the nation of Solomon Islands.
Patteson Shoal is an outer reef in the Reef Islands, in Temotu Province, in the independent nation of Solomon Islands. It is located about 50 km northeast of Nupani. The shoal is named for John Coleridge Patteson.
Mbasakana is an island in Malaita Province, Solomon Islands.

Ndai, formerly known as Gower Island, is an island in Malaita Province, Solomon Islands. It is located to the north of Malaita Island.
Furona Island is a small island off the coast of Santa Isabel in Solomon Islands.
The Diocese of Malaita is one of the nine current dioceses of the Anglican Church of Melanesia. One of the four original ACOM dioceses, Malaita diocese was erected in January 1975; it is currently subdivided into six regions of 46 parishes.

The Bass Islands are a subordinate group in the south of the Duff Islands of the nation of Solomon Islands in the Pacific Ocean. Alternatively they are known as Basses Islands or Ile de Bass. The estimated terrain elevation above sea level is some 15 metres.
Tahua is one of the Duff Islands, of Temotu Province, in the independent nation of Solomon Islands. The estimated terrain elevation above sea level is some 23 metres. The island is inhabited.