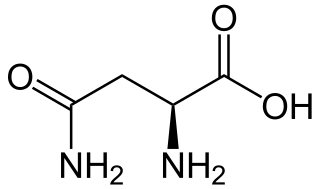
Asparagine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar, aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is encoded by the codons AAU and AAC.
In molecular biology, biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism.

Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease enzyme present in papaya and mountain papaya. It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.
Aminopeptidases are enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of amino acids from the amino terminus (N-terminus) of proteins or peptides (exopeptidases). They are widely distributed throughout the animal and plant kingdoms and are found in many subcellular organelles, in cytosol, and as membrane components. Aminopeptidases are used in essential cellular functions. Many, but not all, of these peptidases are zinc metalloenzymes.
Cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme.

Aspartoacylase is a hydrolytic enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ASPA gene. ASPA catalyzes the deacylation of N-acetyl-l-aspartate (N-acetylaspartate) into aspartate and acetate. It is a zinc-dependent hydrolase that promotes the deprotonation of water to use as a nucleophile in a mechanism analogous to many other zinc-dependent hydrolases. It is most commonly found in the brain, where it controls the levels of N-acetyl-l-aspartate. Mutations that result in loss of aspartoacylase activity are associated with Canavan disease, a rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease.
N4-(beta-N-acetylglucosaminyl)-L-asparaginase (EC 3.5.1.26, aspartylglucosylamine deaspartylase, aspartylglucosylaminase, aspartylglucosaminidase, aspartylglycosylamine amidohydrolase, N-aspartyl-beta-glucosaminidase, glucosylamidase, beta-aspartylglucosylamine amidohydrolase, 4-N-(beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine amidohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name N4-(beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine amidohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin.
Protein L-isoaspartyl methyltransferase , also called S-adenosyl-L-methionine:protein-L-isoaspartate O-methyltransferase, is an enzyme which recognizes and catalyzes the repair of damaged L-isoaspartyl and D-aspartyl groups in proteins. It is a highly conserved enzyme which is present in nearly all eukaryotes, archaebacteria, and Gram-negative eubacteria.

N-Acetylaspartylglutamic acid is a peptide neurotransmitter and the third-most-prevalent neurotransmitter in the mammalian nervous system. NAAG consists of N-acetylaspartic acid (NAA) and glutamic acid coupled via a peptide bond.
Glutamyl aminopeptidase (EC 3.4.11.7, aminopeptidase A, aspartate aminopeptidase, angiotensinase A, glutamyl peptidase, Ca2+-activated glutamate aminopeptidase, membrane aminopeptidase II, antigen BP-1/6C3 of mouse B lymphocytes, L-aspartate aminopeptidase, angiotensinase A2) is an enzyme encoded by the ENPEP gene. Glutamyl aminopeptidase has also recently been designated CD249 (cluster of differentiation 249).

Leucyl aminopeptidases are enzymes that preferentially catalyze the hydrolysis of leucine residues at the N-terminus of peptides and proteins. Other N-terminal residues can also be cleaved, however. LAPs have been found across superkingdoms. Identified LAPs include human LAP, bovine lens LAP, porcine LAP, Escherichia coli LAP, and the solanaceous-specific acidic LAP (LAP-A) in tomato.

In enzymology, an aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that is very important in the biosynthesis of amino acids in prokaryotes, fungi, and some higher plants. It forms an early branch point in the metabolic pathway forming lysine, methionine, leucine and isoleucine from aspartate. This pathway also produces diaminopimelate which plays an essential role in bacterial cell wall formation. There is particular interest in ASADH as disabling this enzyme proves fatal to the organism giving rise to the possibility of a new class of antibiotics, fungicides, and herbicides aimed at inhibiting it.
Aspartate—tRNAAsn ligase is an enzyme with systematic name L-aspartate:tRNAAsx ligase (AMP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aspartate—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Aspartyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DNPEP gene.

Chromosome 9 open reading frame 3 (C9ORF3) also known as aminopeptidase O (APO) is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the C9ORF3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is an aminopeptidase which is most closely related in sequence to leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H). APO is a member of the M1 metalloproteinase family.
Beta-peptidyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pyroglutamyl-peptidase II is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

L-Aspartic-4-semialdehyde is an α-amino acid derivative of aspartate. It is an important intermediate in the aspartate pathway, which is a metabolic pathway present in bacteria and plants. The aspartate pathway leads to the biosynthesis of a variety of amino acids from aspartate, including lysine, methionine, and threonine.












