Related Research Articles
E2F is a group of genes that encodes a family of transcription factors (TF) in higher eukaryotes. Three of them are activators: E2F1, 2 and E2F3a. Six others act as suppressors: E2F3b, E2F4-8. All of them are involved in the cell cycle regulation and synthesis of DNA in mammalian cells. E2Fs as TFs bind to the TTTCCCGC consensus binding site in the target promoter sequence.

The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a general transcription factor that binds specifically to a DNA sequence called the TATA box. This DNA sequence is found about 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site in some eukaryotic gene promoters.
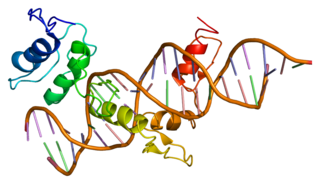
Zinc finger protein GLI1 also known as glioma-associated oncogene is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLI1 gene. It was originally isolated from human glioblastoma cells.

Transcription factor Sp1, also known as specificity protein 1* is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SP1 gene.
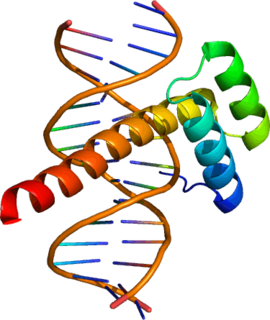
Ultrabithorax (Ubx) is a homeobox gene found in insects, and is used in the regulation of patterning in morphogenesis. There are many possible products of this gene, which function as transcription factors. Ubx is used in the specification of serially homologous structures, and is used at many levels of developmental hierarchies. In Drosophila melanogaster it is expressed in the third thoracic (T3) and first abdominal (A1) segments and represses wing formation. The Ubx gene regulates the decisions regarding the number of wings and legs the adult flies will have. The developmental role of the Ubx gene is determined by the splicing of its product, which takes place after translation of the gene. The specific splice factors of a particular cell allow the specific regulation of the developmental fate of that cell, by making different splice variants of transcription factors. In D. melanogaster, at least six different isoforms of Ubx exist.
Position-effect variegation (PEV) is a variegation caused by the silencing of a gene in some cells through its abnormal juxtaposition with heterochromatin via rearrangement or transposition. It is also associated with changes in chromatin conformation.

Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains.

Myb-related protein B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYBL2 gene.
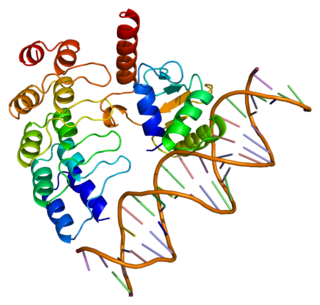
GA-binding protein alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABPA gene.

NK2 homeobox 1 (NKX2-1), also known as thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NKX2-1 gene.

Staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing protein 1 also known as 100 kDa coactivator or Tudor domain-containing protein 11 (TDRD11) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SND1 gene. SND1 is a main component of RISC complex and plays an important role in miRNA function. SND1 is Tudor domain containing protein and Tudor Proteins are highly conserved proteins and even present in Drosophila melanogaster. SND1 is also involved in Autism.

Serine/threonine protein kinase NLK is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NLK gene. Its name is an abbreviation for Nemo-Like Kinase, Nemo (nmo) being the Drosophila ortholog of the mammalian NLK gene. This enzyme is a member of the Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, although not explicitly designated as such. It is a highly divergent, atypical member of the MAPK group, lacking most features so characteristic of most mitogen-activated protein kinases. Its activation mechanism and downstream targets are still not well characterized.

Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED7 gene.

LIM homeobox transcription factor 1, alpha, also known as LMX1A, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the LMX1A gene.

snRNA-activating protein complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNAPC2 gene.

Transcription factor AP-4 , also known as TFAP4, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TFAP4 gene.

General transcription factor IIF subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2F1 gene.

Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 27 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED27 gene. It forms part of the Mediator complex.

Selective factor 1 is a transcription factor that binds to the promoter of genes and recruits a preinitiation complex to which RNA polymerase I will bind to and begin the transcription of ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
The transactivation domain or trans-activating domain (TAD) is a transcription factor scaffold domain which contains binding sites for other proteins such as transcription coregulators. These binding sites are frequently referred to as activation functions (AFs). TADs are named after their amino acid composition. These amino acids are either essential for the activity or simply the most abundant in the TAD. Transactivation by the Gal4 transcription factor is mediated by acidic amino acids, whereas hydrophobic residues in Gcn4 play a similar role. Hence, the TADs in Gal4 and Gcn4 are referred to as acidic or hydrophobic, respectively.
References
- ↑ Zhao K, Hart CM, Laemmli UK (June 1995). "Visualization of chromosomal domains with boundary element-associated factor BEAF-32". Cell. 81 (6): 879–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90008-X . PMID 7781065. S2CID 18999226.
- ↑ Reuter G, Giarre M, Farah J, Gausz J, Spierer A, Spierer P (March 1990). "Dependence of position-effect variegation in Drosophila on dose of a gene encoding an unusual zinc-finger protein". Nature. 344 (6263): 219–23. Bibcode:1990Natur.344..219R. doi:10.1038/344219a0. PMID 2107402. S2CID 4321455.
- ↑ Clark KA, McKearin DM (March 1996). "The Drosophila stonewall gene encodes a putative transcription factor essential for germ cell development". Development. 122 (3): 937–50. doi:10.1242/dev.122.3.937. PMID 8631271.
- 1 2 England BP, Admon A, Tjian R (January 1992). "Cloning of Drosophila transcription factor Adf-1 reveals homology to Myb oncoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (2): 683–7. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89..683E. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.683 . PMC 48303 . PMID 1731341.
- 1 2 Cutler G, Perry KM, Tjian R (April 1998). "Adf-1 is a nonmodular transcription factor that contains a TAF-binding Myb-like motif". Mol. Cell. Biol. 18 (4): 2252–61. doi:10.1128/MCB.18.4.2252. PMC 121473 . PMID 9528796.
- ↑ Bhaskar V, Courey AJ (October 2002). "The MADF-BESS domain factor Dip3 potentiates synergistic activation by Dorsal and Twist". Gene. 299 (1–2): 173–84. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(02)01058-2. PMID 12459265.
- ↑ Delattre M, Spierer A, Hulo N, Spierer P (January 2002). "A new gene in Drosophila melanogaster, Ravus, the phantom of the modifier of position-effect variegation Su(var)3-7". Int. J. Dev. Biol. 46 (1): 167–71. PMID 11902679.