In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades.
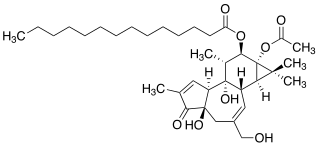
12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also commonly known as tetradecanoylphorbol acetate, tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate, and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) is a diester of phorbol. It is a potent tumor promoter often employed in biomedical research to activate the signal transduction enzyme protein kinase C (PKC). The effects of TPA on PKC result from its similarity to one of the natural activators of classic PKC isoforms, diacylglycerol. TPA is a small molecule drug.

Phosphoinositide phospholipase C is a family of eukaryotic intracellular enzymes that play an important role in signal transduction processes. These enzymes belong to a larger superfamily of Phospholipase C. Other families of phospholipase C enzymes have been identified in bacteria and trypanosomes. Phospholipases C are phosphodiesterases.

Pleckstrin homology domain or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton.

Phorbol is a natural, plant-derived organic compound. It is a member of the tigliane family of diterpenes. Phorbol was first isolated in 1934 as the hydrolysis product of croton oil, which is derived from the seeds of the purging croton, Croton tiglium. The structure of phorbol was determined in 1967. Various esters of phorbol have important biological properties, the most notable of which is the capacity to act as tumor promoters through activation of protein kinase C. They mimic diacylglycerols, glycerol derivatives in which two hydroxyl groups have reacted with fatty acids to form esters. The most common and potent phorbol ester is 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also called phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), which is used as a biomedical research tool in contexts such as models of carcinogenesis.
Diacylglycerol kinase is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the conversion of diacylglycerol (DAG) to phosphatidic acid (PA), utilizing ATP as a source of the phosphate. In non-stimulated cells, DGK activity is low, allowing DAG to be used for glycerophospholipid biosynthesis, but on receptor activation of the phosphoinositide pathway, DGK activity increases, driving the conversion of DAG to PA. As both lipids are thought to function as bioactive lipid signaling molecules with distinct cellular targets, DGK therefore occupies an important position, effectively serving as a switch by terminating the signalling of one lipid while simultaneously activating signalling by another.
Chimerin 1 (CHN1), also known as alpha-1-chimerin, n-chimerin, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CHN1 gene.

A C2 domain is a protein structural domain involved in targeting proteins to cell membranes. The typical version (PKC-C2) has a beta-sandwich composed of 8 β-strands that co-ordinates two or three calcium ions, which bind in a cavity formed by the first and final loops of the domain, on the membrane binding face. Many other C2 domain families don't have calcium binding activity.

Protein kinase C alpha (PKCα) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCA gene.

Protein kinase C delta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCD gene.

Protein kinase C beta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCB gene.

Protein kinase C iota type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCI gene.

Protein kinase C eta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCH gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase D3 (PKD3) or PKC-nu is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKD3 gene.

Chimerin 2 (beta-chimaerin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHN2 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase D2 or PKD2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKD2 gene.

RAS guanyl-releasing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASGRP2 gene.
Chimerin is a type of nerve tissue protein.

A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009.

Mezerein is a toxic diterpene ester found in the sap of Daphne mezereum and related plants. Plants of the genera Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae possess a wide variety of different phorbol esters, which share the capacity of mimicking diacylglycerol (DAG) and thus activating different isoforms of protein kinase C. Mezerein was first isolated in 1975. It has antileukemic properties in mice, but it is also defined as a weak promoter of skin cancers in the same species. All parts of the plants contain an acrid and irritant sap that contains mezerein, thought to be the principal poison. The sap is especially prevalent in the bark and berries.


















