Related Research Articles

The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many macromolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites. The term comes from the Latin word cellula meaning 'small room'.

The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes (endomembranes) that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. In eukaryotes the organelles of the endomembrane system include: the nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, endosomes, and plasma (cell) membrane among others. The system is defined more accurately as the set of membranes that forms a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport. Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of plastids or mitochondria, but might have evolved partially from the actions of the latter.

Lamins, also known as nuclear lamins are fibrous proteins in type V intermediate filaments, providing structural function and transcriptional regulation in the cell nucleus. Nuclear lamins interact with inner nuclear membrane proteins to form the nuclear lamina on the interior of the nuclear envelope. Lamins have elastic and mechanosensitive properties, and can alter gene regulation in a feedback response to mechanical cues. Lamins are present in all animals but are not found in microorganisms, plants or fungi. Lamin proteins are involved in the disassembling and reforming of the nuclear envelope during mitosis, the positioning of nuclear pores, and programmed cell death. Mutations in lamin genes can result in several genetic laminopathies, which may be life-threatening.
A nuclear localization signalorsequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
KASH domains are conserved C-terminal protein regions less than ~30 amino acids. KASH is an acronym for Klarsicht, ANC-1, Syne Homology. KASH domains always follow a transmembrane domain. Most proteins containing KASH domains are thought to be involved in the positioning of the nucleus in the cell. KASH domains interact with proteins containing SUN domains in the space between the outer and inner nuclear membranes to bridge the nuclear envelope, and may transfer force from the nucleoskeleton to the cytoplasmic cytoskeleton and enable mechanosensory roles in cells. KASH proteins are thought to largely localize to the outer nuclear membrane, although there are reports of inner nuclear membrane localization of some KASH protein isoforms.
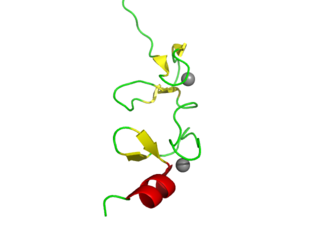
LIM domains are protein structural domains, composed of two contiguous zinc fingers, separated by a two-amino acid residue hydrophobic linker. The domain name is an acronym of the three genes in which it was first identified. LIM is a protein interaction domain that is involved in binding to many structurally and functionally diverse partners. The LIM domain appeared in eukaryotes sometime prior to the most recent common ancestor of plants, fungi, amoeba and animals. In animal cells, LIM domain-containing proteins often shuttle between the cell nucleus where they can regulate gene expression, and the cytoplasm where they are usually associated with actin cytoskeletal structures involved in connecting cells together and to the surrounding matrix, such as stress fibers, focal adhesions and adherens junctions.
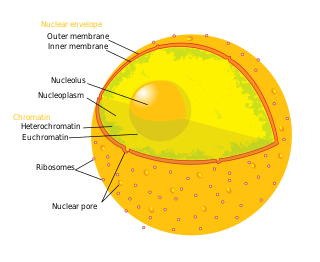
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material.

Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membranes fuse, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nuclear pores enable the passive and facilitated transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. Nucleoporins, a family of around 30 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. Nucleoporin 62 is the most abundant member of this family. Nucleoporins are able to transport molecules across the nuclear envelope at a very high rate. A single NPC is able to transport 60,000 protein molecules across the nuclear envelope every minute.

Nesprin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYNE2 gene. The human SYNE2 gene consists of 116 exons and encodes nesprin-2, a member of the nuclear envelope (NE) spectrin-repeat (nesprin) family. Nesprins are modular proteins with a central extended spectrin-repeat (SR) rod domain and a C-terminal Klarsicht/ANC-1/Syne homology (KASH) transmembrane domain, which acts as a NE-targeting motif. Nesprin-2 (Nesp2) binds to cytoplasmic F-actin, tethering the nucleus to the cytoskeleton and maintaining the structural integrity of the nucleus.

Protein unc-84 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UNC84A gene.
Nesprins are a family of proteins that are found primarily in the outer nuclear membrane, as well as other subcellular compartments. They contain a C-terminal KASH transmembrane domain and are part of the LINC complex which is a protein network that associates the nuclear envelope to the cytoskeleton, outside the nucleus, and the nuclear lamina, inside the nucleus. Nesprin-1 and -2 bind to the actin filaments. Nesprin-3 binds to plectin, which is bound to the intermediate filaments, while nesprin-4 interacts with kinesin-1.
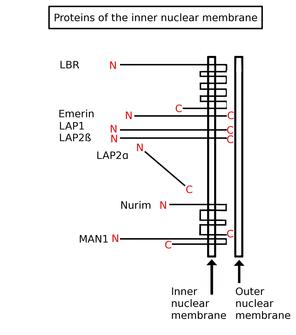
Inner nuclear membrane proteins are membrane proteins that are embedded in or associated with the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope. There are about 60 INM proteins, most of which are poorly characterized with respect to structure and function. Among the few well-characterized INM proteins are lamin B receptor (LBR), lamina-associated polypeptide 1 (LAP1), lamina-associated polypeptide-2 (LAP2), emerin and MAN1.

Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initial discovery in flies, where a mutation in the dishevelled gene was observed to cause improper orientation of body and wing hairs. There are vertebrate homologs in zebrafish, Xenopus (Xdsh), mice and humans. Dsh relays complex Wnt signals in tissues and cells, in normal and abnormal contexts. It is thought to interact with the SPATS1 protein when regulating the Wnt Signalling pathway.
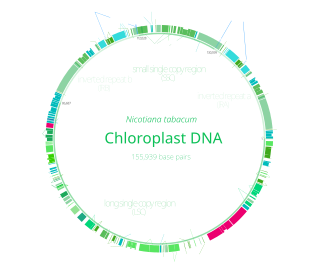
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and Marchantia polymorpha (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced.

Autophagy-related protein 101 also known as ATG101 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C12orf44 gene.

MORN1 containing repeat 1, also known as Morn1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MORN1 gene.
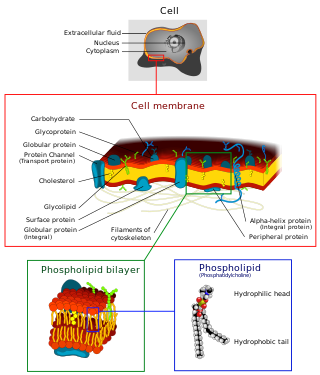
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity, and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall and the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, as well as the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.
The LINC complex is a protein complex associated with both inner and outer membranes of the nucleus. It is composed of SUN-domain proteins and KASH-domain proteins. The SUN-domain proteins are associated with both nuclear lamins and chromatin and cross the inner nuclear membrane. They interact with the KASH domain proteins in the perinuclear (lumen) space between the two membranes. The KASH domain proteins cross the outer nuclear membrane and interact with actin filaments, microtubule filaments, intermediate filaments, centrosomes and cytoplasmic organelles. The number of SUN-domain and KASH-domain proteins increased in evolution.
A target peptide is a short peptide chain that directs the transport of a protein to a specific region in the cell, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), chloroplast, apoplast, peroxisome and plasma membrane. Some target peptides are cleaved from the protein by signal peptidases after the proteins are transported.

MIF4GD, or MIF4G domain-containing protein, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MIF4GD gene. It is also known as SLIP1, SLBP -interacting protein 1, AD023, and MIFD. MIF4GD is expressed ubiquitously in humans, and has been found to be involved in activating proteins for histone mRNA translation, alternative splicing and translation of mRNAs, and is a factor in the regulation of cell proliferation.
References
- ↑ Uzer G, Thompson WR, Sen B, Xie Z, Yen SS, Miller S, Bas G, Styner M, Rubin CT, Judex S, Burridge K, Rubin J (June 2015). "Cell Mechanosensitivity to Extremely Low-Magnitude Signals Is Enabled by a LINCed Nucleus". Stem Cells. 33 (6): 2063–76. doi:10.1002/stem.2004. PMC 4458857 . PMID 25787126.
- ↑ Tzur YB, Wilson KL, Gruenbaum Y (October 2006). "SUN-domain proteins: 'Velcro' that links the nucleoskeleton to the cytoskeleton". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 7 (10): 782–8. doi:10.1038/nrm2003. PMID 16926857. S2CID 19519227.
- ↑ Hodzic DM, Yeater DB, Bengtsson L, Otto H, Stahl PD (June 2004). "Sun2 is a novel mammalian inner nuclear membrane protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (24): 25805–12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313157200 . PMID 15082709.
- ↑ Raff JW (September 1999). "The missing (L) UNC?". Current Biology. 9 (18): R708-10. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80446-1 . PMID 10508607. S2CID 14827859.