
In academic publishing, a preprint is a version of a scholarly or scientific paper that precedes formal peer review and publication in a peer-reviewed scholarly or scientific journal. The preprint may be available, often as a non-typeset version available free, before or after a paper is published in a journal.

Academic publishing is the subfield of publishing which distributes academic research and scholarship. Most academic work is published in academic journal articles, books or theses. The part of academic written output that is not formally published but merely printed up or posted on the Internet is often called "grey literature". Most scientific and scholarly journals, and many academic and scholarly books, though not all, are based on some form of peer review or editorial refereeing to qualify texts for publication. Peer review quality and selectivity standards vary greatly from journal to journal, publisher to publisher, and field to field.

An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and discussion of research. They nearly universally require peer review for research articles or other scrutiny from contemporaries competent and established in their respective fields.

Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which research outputs are distributed online, free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined, or libre open access, barriers to copying or reuse are also reduced or removed by applying an open license for copyright.

Elsevier is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as The Lancet, Cell, the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, Trends, the Current Opinion series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics, and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group, known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier, a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2022 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,800 journals; as of 2018 its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads.
RELX plc is a British multinational information and analytics company headquartered in London, England. Its businesses provide scientific, technical and medical information and analytics; legal information and analytics; decision-making tools; and organise exhibitions. It operates in 40 countries and serves customers in over 180 nations. It was previously known as Reed Elsevier, and came into being in 1993 as a result of the merger of Reed International, a British trade book and magazine publisher, and Elsevier, a Netherlands-based scientific publisher.

The Social Science Research Network (SSRN) is a repository for preprints devoted to the rapid dissemination of scholarly research in the social sciences, humanities, life sciences, and health sciences, among others. Elsevier bought SSRN from Social Science Electronic Publishing Inc. in May 2016. It is not an electronic journal, but rather an eLibrary and search engine.
An institutional repository (IR) is an archive for collecting, preserving, and disseminating digital copies of the intellectual output of an institution, particularly a research institution. Academics also utilize their IRs for archiving published works to increase their visibility and collaboration with other academics. However, most of these outputs produced by universities are not effectively accessed and shared by researchers and other stakeholders. As a result academics should be involved in the implementation and development of an IR project so that they can learn the benefits and purpose of building an IR.

Self-archiving is the act of depositing a free copy of an electronic document online in order to provide open access to it. The term usually refers to the self-archiving of peer-reviewed research journal and conference articles, as well as theses and book chapters, deposited in the author's own institutional repository or open archive for the purpose of maximizing its accessibility, usage and citation impact. The term green open access has become common in recent years, distinguishing this approach from gold open access, where the journal itself makes the articles publicly available without charge to the reader.
Digital Commons is a commercial, hosted institutional repository platform owned by RELX Group. This hosted service, licensed by bepress, is used by over 500 academic institutions, healthcare centers, public libraries, and research centers to showcase their scholarly output and special collections.
Scholarly communication involves the creation, publication, dissemination and discovery of academic research, primarily in peer-reviewed journals and books. It is “the system through which research and other scholarly writings are created, evaluated for quality, disseminated to the scholarly community, and preserved for future use." This primarily involves the publication of peer-reviewed academic journals, books and conference papers.
DPubS, developed by Cornell University Library and Penn State University Libraries, is a free open access publication management software. DPubS arose out of Project Euclid, an electronic publishing platform for journals in mathematics and statistics. DPubS is free software released under Educational Community License.
An open-access mandate is a policy adopted by a research institution, research funder, or government which requires or recommends researchers—usually university faculty or research staff and/or research grant recipients—to make their published, peer-reviewed journal articles and conference papers open access (1) by self-archiving their final, peer-reviewed drafts in a freely accessible institutional repository or disciplinary repository or (2) by publishing them in an open-access journal or both.
Academic journal publishing reform is the advocacy for changes in the way academic journals are created and distributed in the age of the Internet and the advent of electronic publishing. Since the rise of the Internet, people have organized campaigns to change the relationships among and between academic authors, their traditional distributors and their readership. Most of the discussion has centered on taking advantage of benefits offered by the Internet's capacity for widespread distribution of reading material.
Library publishing, also known as campus-based publishing, is the practice of an academic library providing publishing services.
The following is a timeline of the international movement for open access to scholarly communication.

Open access to scholarly communication in Germany has evolved rapidly since the early 2000s. Publishers Beilstein-Institut, Copernicus Publications, De Gruyter, Knowledge Unlatched, Leibniz Institute for Psychology Information, ScienceOpen, Springer Nature, and Universitätsverlag Göttingen belong to the international Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association.

In France, open access to scholarly communication is relatively robust and has strong public support. Revues.org, a digital platform for social science and humanities publications, launched in 1999. Hyper Articles en Ligne (HAL) began in 2001. The French National Center for Scientific Research participated in 2003 in the creation of the influential Berlin Declaration on Open Access to Knowledge in the Sciences and Humanities. Publishers EDP Sciences and OpenEdition belong to the international Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association.
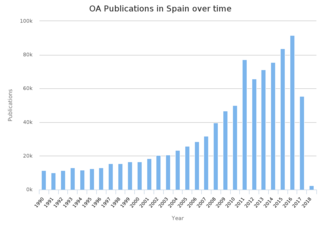
In Spain, the national 2011 "Ley de la Ciencia, la Tecnología y la Innovación" requires open access publishing for research that has been produced with public funding. The first peer-reviewed open access Spanish journal, Relieve, began in 1995. Publishers CSIC Press and Hipatia Press belong to the international Open Access Scholarly Publishers Association.
The economics of open science describe the economic aspects of making a wide range of scientific outputs to all levels of society.








