Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Curium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This transuranic actinide element was named after eminent scientists Marie and Pierre Curie, both known for their research on radioactivity. Curium was first intentionally made by the team of Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James, and Albert Ghiorso in 1944, using the cyclotron at Berkeley. They bombarded the newly discovered element plutonium with alpha particles. This was then sent to the Metallurgical Laboratory at University of Chicago where a tiny sample of curium was eventually separated and identified. The discovery was kept secret until after the end of World War II. The news was released to the public in November 1947. Most curium is produced by bombarding uranium or plutonium with neutrons in nuclear reactors – one tonne of spent nuclear fuel contains ~20 grams of curium.

Einsteinium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Es and atomic number 99. Einsteinium is a member of the actinide series and it is the seventh transuranium element. It was named in honor of Albert Einstein.

Plutonium(III) chloride is a chemical compound with the formula PuCl3. This ionic plutonium salt can be prepared by reacting the metal with hydrochloric acid.

Few compounds of californium have been made and studied. The only californium ion that is stable in aqueous solutions is the californium(III) cation. The other two oxidation states are IV (strong oxidizing agents) and II (strong reducing agents). The element forms a water-soluble chloride, nitrate, perchlorate, and sulfate and is precipitated as a fluoride, oxalate or hydroxide. If problems of availability of the element could be overcome, then CfBr2 and CfI2 would likely be stable.

Californium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, a salt with a chemical formula CfBr3. Like in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3), californium(III) chloride, and californium(III) iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.
Berkelium(IV) oxide, also known as berkelium dioxide, is a chemical compound with the formula BkO2. This compound slowly decays to californium(IV) oxide. It can be converted to berkelium(III) oxide by hydrogen reduction at 600 °C.
Curium compounds are compounds containing the element curium (Cm). Curium usually forms compounds in the +3 oxidation state, although compounds with curium in the +4, +5 and +6 oxidation states are also known.
Curium(III) bromide is the bromide salt of curium. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure.

Berkelium(III) nitrate is the berkelium salt of nitric acid with the formula Bk(NO3)3. It commonly forms the tetrahydrate, Bk(NO3)3·4H2O, which is a light green solid. If heated to 450 °C, it decomposes to berkelium(IV) oxide and 22 milligrams of the solution of this compound is reported to cost one million dollars.
Praseodymium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal praseodymium (Pr). In these compounds, praseodymium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as PrCl3, Pr(NO3)3 and Pr(CH3COO)3. However, compounds with praseodymium in the +2 and +4 oxidation states, and unlike other lanthanides, the +5 oxidation state, are also known.
Einsteinium compounds are compounds that contain the element einsteinium (Es). These compounds largely have einsteinium in the +3 oxidation state, or in some cases in the +2 and +4 oxidation states. Although einsteinium is relatively stable, with half-lives ranging from 20 days upwards, these compounds have not been studied in great detail.

Berkelium(III) chloride also known as berkelium trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula BkCl3. It is a water-soluble green salt with a melting point of 603 °C. This compound forms the hexahydrate, BkCl3·6H2O.
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium. These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states.
Americium compounds are compounds containing the element americium (Am). These compounds can form in the +2, +3, and +4, although the +3 oxidation state is the most common. The +5, +6 and +7 oxidation states have also been reported.
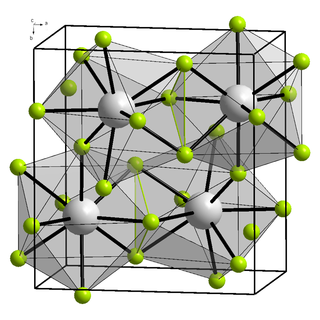
Californium(III) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of californium and fluorine with the formula CfF
3
Californium(III) oxide is a binary inorganic compound of californium and oxygen with the formula Cf
2O
3. It is one of the first obtained solid compounds of californium, synthesized in 1958.

Berkelium(III) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and fluorine with the chemical formula BkF
3.
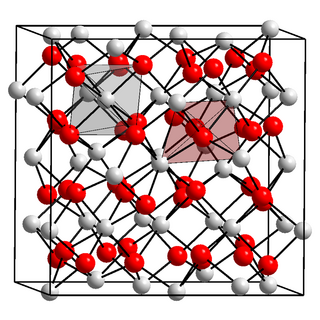
Berkelium(III) oxide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and oxygen with the chemical formula Bk
2O
3.

Berkelium bromide is a bromide of berkelium, with the chemical formula BkBr3.















