
Scottish Power Limited, trading as ScottishPower, is a vertically integrated energy company based in Glasgow, Scotland. It is a subsidiary of Spanish utility firm Iberdrola.

The National Grid is the high-voltage electric power transmission network supporting the UK's electricity market, connecting power stations and major substations, and ensuring that electricity generated anywhere on the grid can be used to satisfy demand elsewhere. The network serves the majority of Great Britain and some of the surrounding islands. It does not cover Northern Ireland, which is part of the Irish single electricity market.
The Renewables Obligation (RO) is a market support mechanism designed to encourage generation of electricity from eligible renewable sources in the United Kingdom. There are three related schemes for the three legal jurisdictions of the UK. In April 2002 the Renewables Obligation was introduced in England and Wales, and in Scotland as the Renewables Obligation (Scotland). The RO was later introduced in Northern Ireland in April 2005. In all cases, the RO replaced the Non-Fossil Fuel Obligation which operated from 1990.
Price-cap regulation is a form of incentive regulation capping the prices that firms in a natural monopoly position may charge their customers. Designed in the 1980s by UK Treasury economist Stephen Littlechild, it has been applied to all privatised British network utilities. It is contrasted with both rate-of-return regulation, with utilities being permitted a set rate of return on capital, and with revenue-cap regulation, with total revenue being the regulated variable.
Centrica plc is a British multinational energy and services company with its headquarters in Windsor, Berkshire. Its principal activity is the supply of electricity and gas to consumers in the United Kingdom and Ireland.

The Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (Ofgem), supporting the Gas and Electricity Markets Authority, is the government regulator for the electricity and downstream natural gas markets in Great Britain. It was formed by the merger of the Office of Electricity Regulation (OFFER) and Office of Gas Supply (Ofgas).

Good Energy Group PLC is a British energy company based in Chippenham, Wiltshire that provides services in the electrification of transport and decentralised renewable energy generation such as domestic solar panels. The company is also an energy retailer, and built a portfolio of wind and solar generation which was sold in 2022. Founded by Juliet Davenport, its CEO is Nigel Pocklington.
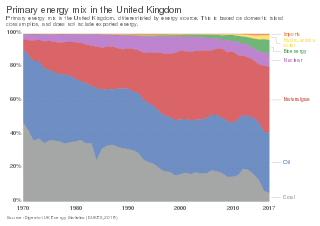
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.
E.ON UK is a British energy company and one of the largest suppliers of energy in the UK, following its acquisition of Npower. It is a subsidiary of E.ON of Germany and one of the Big Six energy suppliers. It was founded in 1989 as Powergen, and was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. It has been a subsidiary of E.ON since 1 July 2002.

Npower Limited was a British supplier of gas and electricity to businesses. It has been a subsidiary of E.ON UK since January 2019. The company was formerly known as Innogy plc and was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

SSE plc is a multinational energy company headquartered in Perth, Scotland. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange, and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. SSE operates in the United Kingdom and Ireland.

The availability and uptake of green electricity in the United Kingdom has increased in the 21st century. There are a number of suppliers offering green electricity in the United Kingdom. In theory these types of tariffs help to lower carbon dioxide emissions by increasing consumer demand for green electricity and encouraging more renewable energy plant to be built. Since Ofgem's 2014 regulations there are now set criteria defining what can be classified as a green source product. As well as holding sufficient guarantee of origin certificates to cover the electricity sold to consumers, suppliers are also required to show additionality by contributing to wider environmental and low carbon funds.

EnServe Group Limited is a support services company headquartered in Macclesfield, United Kingdom which provides infrastructure services to the utility sector. Formerly listed on the London Stock Exchange and a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index, it was wholly owned by the private equity company Cinven between 2010 and 2016, when it was bought by Rubicon.

OVO Energy is a major energy supplier based in Bristol, England.

ECA is the main trade association for companies involved in electrotechnical and other technical engineering projects in England, Northern Ireland and Wales. In 2022 it had some 2600 registered members - companies who collectively generated annual revenues of over £6billion. ECA also has associate categories open to industry manufacturers, distributors, educators, clients and specifiers who wish to engage and collaborate with members.
The Japan Electric Association (日本電気協会) (JEA) is a membership organisation for the electricity sector in Japan and, although it has roots dating back to 1892, was founded in October 1921. It currently has around 4,800 corporate and individual members.

The Electricity Act 1989 provided for the privatisation of the electricity supply industry in Great Britain, by replacing the Central Electricity Generating Board in England and Wales and by restructuring the South of Scotland Electricity Board and the North of Scotland Hydro-Electric Board. The Act also established a licensing regime and a regulator for the industry called the Office of Electricity Regulation (OFFER), which has since become the Office of Gas and Electricity Markets (OFGEM).
The Big Six were the United Kingdom's largest retail suppliers of gas and electricity, who dominated the market following liberalisation in the late 1990s. By 2002, six companies – British Gas, EDF Energy, E.ON, RWE npower, Scottish Power and SSE – had emerged from the 15 former incumbent monopoly suppliers.

The Gas Act 1986 created the framework for privatisation of the gas supply industry in Great Britain. The legislation replaced the British Gas Corporation with British Gas plc. The Act also established a licensing regime, a Gas Consumers’ Council, and a regulator for the industry called the Office of Gas Supply (OFGAS).

Central Training Institute, popularly known as CTI Jabalpur, is located in Nayagaon, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. It is an apex engineering and civil service training institute of the Madhya Pradesh Poorv Kshetra Vidyut Vitaran Company Ltd (MPPKVVCL), wholly owned by the Government of Madhya Pradesh. The institute provides technical and managerial training to assistant engineers, junior engineers, accounts officers, HR managers, office assistants, line men, and testing assistants.














