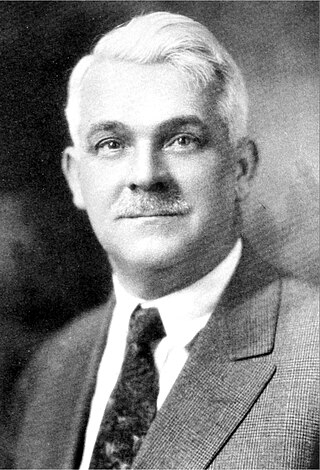
Thomas White Lamb was a Scottish-born, American architect. He was one of the foremost designers of theaters and cinemas of the 20th century.

State Theatre New Jersey is a nonprofit theater, located in New Brunswick, New Jersey. It has seating for 1,850 people. Designed by architect Thomas W. Lamb in 1921, it is one of the oldest theaters in the State of New Jersey.

Benjamin Franklin Keith was an American vaudeville theater owner, who played an important role in the evolution of variety theater into vaudeville.

Edward Franklin Albee II was an American vaudeville impresario.
The Keith-Albee-Orpheum Corporation was the owner of a chain of vaudeville and motion picture theatres. It was formed by the merger of the holdings of Benjamin Franklin Keith and Edward Franklin Albee II and Martin Beck's Orpheum Circuit.

The Keith-Albee Theatre is a performing arts center, located across the street from the Frederick Building in downtown Huntington, West Virginia, United States.

The Connor Palace, also known as the Palace Theatre and historically as the RKO Palace, is a theater located at 1615 Euclid Avenue in Downtown Cleveland, Ohio, part of Playhouse Square.

The Keith Building is a skyscraper in downtown Cleveland, Ohio's Playhouse Square theater district. The Keith is 272 feet tall and 21 stories, and houses the Palace Theater, a former flagship theater of the Keith vaudeville circuit. As of 2017, the renovated building is in use as an office tower.

The Palace Theatre is a 2,695-seat restored movie palace located at 34 W. Broad Street in Columbus, Ohio. It was designed and built in 1926 by the American architect Thomas W. Lamb as part of the American Insurance Union Citadel. Today the theater functions as a multi-use performing arts venue. It is owned and operated by The Columbus Association for the Performing Arts. The Palace Theater's "house" is considered separate from LeVeque Tower, while the marquee and lobby are part of the LeVeque complex.

The Pretzinger name belongs to a family of architects and engineers in Dayton, Ohio. Albert Pretzinger started the family's architectural legacy.

The Boston Opera House, also known as the Citizens Bank Opera House, is a performing arts and esports venue located at 539 Washington St. in Boston, Massachusetts. It was originally built as the B.F. Keith Memorial Theatre, a movie palace in the Keith-Albee chain. The chain became part of RKO when it was established just before the theater opened on October 29, 1928, and it was also known as the RKO Keith's Theater. After operating for more than 50 years as a movie theater, it was rededicated in 1980 as a home for the Opera Company of Boston, which performed there until the opera company closed down in 1990 due to financial problems. The theater was reopened in 2004 after a major restoration, and it currently serves as the home of the Boston Ballet and also hosts touring Broadway shows.

The RKO Keith's Theater was an RKO Pictures movie theater at 135-35 Northern Boulevard in the Flushing neighborhood of Queens in New York City. It was designed by architect Thomas W. Lamb and built in 1928. While the RKO Keith's had a plain three-story facade, its interior was elaborately designed in a Spanish Baroque Revival style. The theater had a square ticket lobby and an oval grand foyer, which led to the double-level auditorium. The auditorium was designed as an atmospheric theater with a blue ceiling and gilded-plaster decorations; it contained 2,974 seats across two levels. There were also four lounges and a mezzanine promenade.
Vlastimil Koubek was an American architect who designed more than 100 buildings, most of them in the Washington metropolitan area, and whose total value topped $2 billion. Most of his work is Modernist in style, although he developed a few structures in other vernaculars. He created the site plan for the redevelopment of Rosslyn, Virginia, and his Ames Center anchored the area's economic recovery. He designed the World Building in Silver Spring, Maryland, which sparked redevelopment of that town's downtown; and the L'Enfant Plaza Hotel in Washington, D.C. In 1985, Washingtonian magazine called him one of 20 people "who in the past 20 years had the greatest impact on the way we live and who forever altered the look of Washington." In 1988, The Washington Post newspaper said his Willard Hotel renovation was one of 28 projects in the area that made a signal contribution to the "feel" and look of Washington, D.C.

Rhodes Tavern is the site of a historic tavern in the early history of Washington, D.C. It was located at 15th Street and F Street, Northwest, Washington, D.C.
The RKO Boston Theatre was a movie theatre in Boston, Massachusetts, located at 616 Washington Street, near Essex Street in the Boston Theater District. It opened as the Keith-Albee Boston Theatre on October 5, 1925.
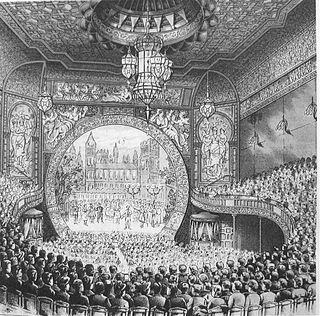
The Bijou Theatre (1882–1943) in Boston, Massachusetts, occupied the second floor of 545 Washington Street near today's Theatre District. Architect George Wetherell designed the space, described by a contemporary reviewer as "dainty." Proprietors included Edward Hastings, George Tyler, and B.F. Keith. Around the 1900s, it featured a "staircase of heavy glass under which flowed an illuminated waterfall." The Bijou "closed 31 December 1943 and was razed in 1951." The building's facade still exists. It is currently a pending Boston Landmark by the Boston Landmarks Commission.

The Financial Historic District, previously known as the Fifteenth Street Financial Historic District, is a historic district in Washington, D.C. The boundaries of the historic district include 38 buildings, 2 of which are non-contributing properties. Before 2016, the historic district included 20 buildings. The construction of the Treasury Building just east of the White House played a significant role in the financial district's development. Major banks and other financial institutions wanted to be close to the Treasury Building; therefore, many of the historic district's buildings were constructed along 15th Street NW, from Pennsylvania Avenue to I Street.

The B. F. Keith Circuit was a chain of vaudeville theaters in the United States and Canada owned by Benjamin Franklin Keith for the acts that he booked. Known for a time as the United Booking Office, and under various other names, the circuit was managed by Edward Franklin Albee, who gained control of it in 1918, following the death of Keith's son A. Paul Keith.

The Pantages Theatre or Jones Building in Tacoma, Washington was designed by the architect B. Marcus Priteca. The unusual structure opened in January 1918. However, the theatre was commissioned in 1916 by the theatre manager Alexander Pantages. It was designed to be an office building and a vaudeville theatre. The theater's Second Renaissance Revival style is juxtaposed with the Commercial style. The exterior above the ground floor is largely unaltered. The building still houses entertainment and commercial activities A brief overview of the owner and renovation history, in 1916–1918, B. Marcus Priteca with Edwin W. Houghton; 1955 remodel, Carlson, Eley, and Grevstad; 1982–1983 renovation, Richard F. McCann; 2006 entrance/lobby renovation, Korth Sunseri Hagey and Grulich Architecture and Planning; 2014 stage expansion and structural renovations, BCRA. 901 Broadway.

The Coliseum Theatre was a cultural and performing arts center located at 4260 Broadway between West 181st and 182nd Streets in the Washington Heights neighborhood of Manhattan in New York City. It was full-block building, bounded on the east by Bennett Avenue.