
Herbicides, also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds. Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides kill plants indiscriminately. The combined effects of herbicides, nitrogen fertilizer, and improved cultivars has increased yields of major crops by three to six times from 1900 to 2000.

Pesticide resistance describes the decreased susceptibility of a pest population to a pesticide that was previously effective at controlling the pest. Pest species evolve pesticide resistance via natural selection: the most resistant specimens survive and pass on their acquired heritable changes traits to their offspring. If a pest has resistance then that will reduce the pesticide's efficacy – efficacy and resistance are inversely related.

Glyphosate is a broad-spectrum systemic herbicide and crop desiccant. It is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphonate, which acts by inhibiting the plant enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSP). Glyphosate-based herbicides are used to kill weeds, especially annual broadleaf weeds and grasses that compete with crops. Its herbicidal effectiveness was discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970. Monsanto brought it to market for agricultural use in 1974 under the trade name Roundup. Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000.

Alachlor is an herbicide from the chloroacetanilide family. It is an odorless, white solid. The greatest use of alachlor is for control of annual grasses and broadleaf weeds in crops. Use of alachlor is illegal in the European Union and no products containing alachlor are currently registered in the United States.
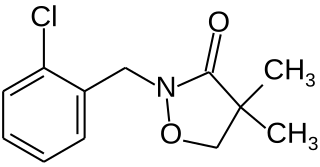
Clomazone is an agricultural herbicide, and has been the active ingredient of products named "Command" and "Commence". The molecule consists of a 2-chlorobenzyl group bound to a N-O heterocycle called isoxazolidinone. It is a white solid.

Pendimethalin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class used premergently and postemergently to control annual grasses and certain broadleaf weeds. It inhibits cell division and cell elongation. Pendimethalin is a K1-group according to the Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (HRAC) classification and is approved in Europe, North America, South America, Africa, Asia and Oceania for different crops including cereals, corn, soybeans, rice, potato, legumes, fruits, vegetables, and nuts, plus lawns and ornamental plants.
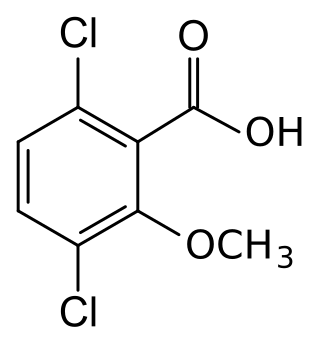
Dicamba is a selective systemic herbicide first registered in 1967. Brand names for formulations of this herbicide include Dianat, Banvel, Diablo, Oracle and Vanquish. This chemical compound is a chlorinated derivative of o-anisic acid. It has been described as a "widely used, low-cost, environmentally friendly herbicide that does not persist in soils and shows little or no toxicity to wildlife and humans."
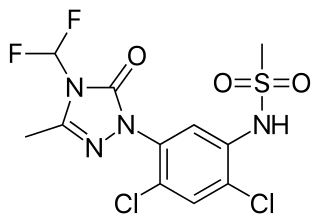
Sulfentrazone is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as a broad-spectrum herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase. It was first marketed in the US in 1997 by FMC Corporation with the brand name Authority.

Pesticide drift, also known as spray drift refers to the unintentional diffusion of pesticides toward nontarget species. It is one of the most negative effects of pesticide application. Drift can damage human health, environment, and crops. Together with runoff and leaching, drift is a mechanism for agricultural pollution. Some drift results from contamination of sprayer tanks.

2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula Cl2C6H3OCH2CO2H. It is usually referred to by its ISO common name 2,4-D. It is a systemic herbicide that kills most broadleaf weeds by causing uncontrolled growth, but most grasses such as cereals, lawn turf, and grassland are relatively unaffected.
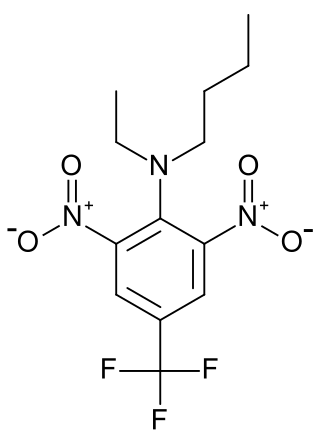
Benfluralin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class. The mechanism of action of benfluralin involves pre-emergent inhibition of mitosis, root and shoot development, same as trifluralin, from which benfluralin was developed in 1963.
4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) inhibitors are a class of herbicides that prevent growth in plants by blocking 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase, an enzyme in plants that breaks down the amino acid tyrosine into molecules that are then used by plants to create other molecules that plants need. This process of breakdown, or catabolism, and making new molecules from the results, or biosynthesis, is something all living things do. HPPD inhibitors were first brought to market in 1980, although their mechanism of action was not understood until the late 1990s. They were originally used primarily in Japan in rice production, but since the late 1990s have been used in Europe and North America for corn, soybeans, and cereals, and since the 2000s have become more important as weeds have become resistant to glyphosate and other herbicides. Genetically modified crops are under development that include resistance to HPPD inhibitors. There is a pharmaceutical drug on the market, nitisinone, that was originally under development as an herbicide as a member of this class and is used to treat an orphan disease, type I tyrosinemia.
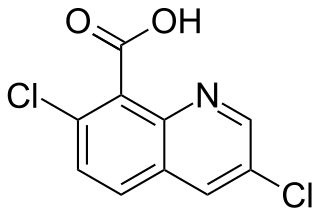
Quinclorac is an organic compound with the formula C9NH4Cl2CO2H. A colorless solid, it is soluble in hydrocarbons and alcohols. The compound is the carboxylic acid of 3,7-dichloroquinoline.

Fomesafen is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPO) which is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis. Soybeans naturally have a high tolerance to fomesafen, via metabolic disposal by glutathione S-transferase. As a result, soy is the most common crop treated with fomesafen, followed by other beans and a few other crop types. It is not safe for maize/corn or other Poaceae.

Aclonifen is a diphenyl ether herbicide which has been used in agriculture since the 1980s. Its mode of action has been uncertain, with evidence suggesting it might interfere with carotenoid biosynthesis or inhibit the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPO). Both mechanisms could result in the observed whole-plant effect of bleaching and the compound includes chemical features that are known to result in PPO effects, as seen with acifluorfen, for example. In 2020, further research revealed that aclonifen has a different and novel mode of action, targeting solanesyl diphosphate synthase which would also cause bleaching.

Nitralin is a selective pre-emergent dinitroaniline herbicide that is closely related to trifluralin, and released two years later in 1966. Today it is largely obsolete. It was used in the USA, France and Australia to control annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds, and was applied on vines, crops and turf.

Profluralin is a dinitroaniline herbicide used preëmergently to control annual grasses and broadleaf weeds, in cotton, soybeans, peanuts, sunflower, cabbage, cauliflower, tomato and others. Profluralin has largely fallen out of use. It rose out of the related, still in common use, trifluralin.

Butralin is a herbicide, used to control suckers on tobacco in the United States,, Australia, Mozambique and, for food crops also, China. It is a preëmergent dinitroaniline, first registered in the US in 1976. It was used in the EU, until a ban for exotoxicity in 2009.

Isopropalin is a herbicide. Introduced in 1969, it is a preëmergent selective dinitroaniline to control annual grasses and broadleaf weeds. Brought by DowElanco in 1972 to the US and Australia, it is now considered obsolete. In 1974, American farmers used 250,000 pounds (110,000 kg) of isopropalin.

Dinitramine is a preëmergent dinitroaniline herbicide incorporated into soil to control weeds for months after. It is no longer approved in the U.S.A., and is not in the European Union, though in Iran it has been used to control annual grasses and broadleaf weeds in cotton and soybeans, as it was in the U.S. as of 1975, where it was also used on sunflower.



















