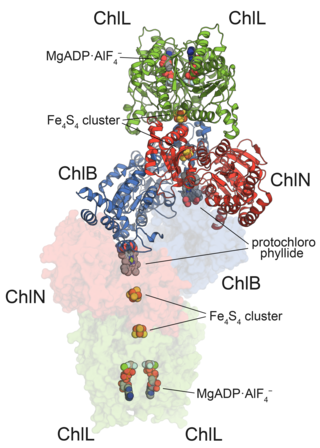
In enzymology, protochlorophyllide reductases (POR) are enzymes that catalyze the conversion from protochlorophyllide to chlorophyllide a. They are oxidoreductases participating in the biosynthetic pathway to chlorophylls.
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde oxime monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.68) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 8-dimethylallylnaringenin 2'-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.103) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-methylcoclaurine 3'-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.71) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.91) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme ornithine cyclodeaminase catalyzes the chemical reaction
Tyrosine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.41, tyrosine N-hydroxylase, CYP79A1) is an enzyme with systematic name L-tyrosine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ent-kaurene oxidase (EC 1.14.14.86, Formerly EC 1.14.13.78) is an enzyme with systematic name ent-kaur-16-ene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Magnesium-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (oxidative) cyclase, is an enzyme with systematic name magnesium-protoporphyrin-IX 13-monomethyl ester, ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (hydroxylating). In plants this enzyme catalyses the following overall chemical reaction
Epi-isozizaene 5-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.106, CYP170A1) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-epi-isozizaene,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (5-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
3-Epi-6-deoxocathasterone 23-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.112, cytochrome P450 90C1, CYP90D1, CYP90C1) is an enzyme with systematic name 3-epi-6-deoxocathasterone,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (C-23-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Isoleucine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.117, CYP79D3, CYP79D4) is an enzyme with systematic name L-isoleucine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Valine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.118, CYP79D1, CYP79D2) is an enzyme with systematic name L-valine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phenylalanine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.40, phenylalanine N-hydroxylase, CYP79A2) is an enzyme with systematic name L-phenylalanine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Tryptophan N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.125, tryptophan N-hydroxylase, CYP79B1, CYP79B2, CYP79B3) is an enzyme with systematic name L-tryptophan,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pentalenene oxygenase (EC 1.14.15.32, Formerly EC 1.14.13.133, PtlI) is an enzyme with systematic name pentalenene,NADPH:oxygen 13-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Indole-3-pyruvate monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.168, YUC2 (gene), spi1 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name indole-3-pyruvate,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (1-hydroxylating, decarboxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Sphinganine C4-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.169, sphingolipid C4-hydroxylase, SUR2 (gene), SBH1 (gene), SBH2 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name sphinganine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (C4-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Neopentalenolactone D synthase (EC 1.14.13.171, ptlE (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-deoxy-11-oxopentalenate,NADH:oxygen oxidoreductase (neopentalenolactone-D forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Chlorophyllide a and Chlorophyllide b are the biosynthetic precursors of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b respectively. Their propionic acid groups are converted to phytyl esters by the enzyme chlorophyll synthase in the final step of the pathway. Thus the main interest in these chemical compounds has been in the study of chlorophyll biosynthesis in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyllide a is also an intermediate in the biosynthesis of bacteriochlorophylls.





