
The 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season was one of the least active South Pacific tropical cyclone seasons on record, with only four tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific basin to the east of 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 2007, until April 30, 2008, although the first cyclone, Tropical Depression 01F, developed on October 17. The most intense tropical cyclone of the season was Severe Tropical Cyclone Daman, which reached a minimum pressure of 925 hPa (27.32 inHg) as it affected Fiji. After the season had ended, the names Daman, Funa, and Gene were retired from the tropical cyclone naming lists.
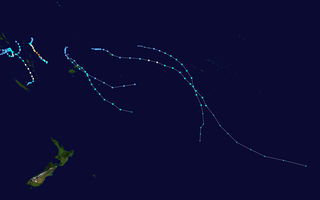
The 2006–07 South Pacific cyclone season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. It began on November 1, 2006 and ended on April 30, 2007. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the southern Pacific Ocean east of 160°E. Additionally, the regional tropical cyclone operational plan defines a tropical cyclone year separately from a tropical cyclone season, and the "tropical cyclone year" runs from July 1, 2006 to June 30, 2007.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Daman was the strongest cyclone of the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season. Cyclone Daman was the fourth tropical depression and the first severe tropical cyclone to form east of longitude 180° during the 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season. Due to the severity of the storm, the name Daman was retired and replaced with Denia.

The 2007–08 South Pacific cyclone season was a below-average season with only four tropical cyclones, forming within the South Pacific to the east of 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 2007, to April 30, 2008, although the first cyclone, Tropical Depression 01F, formed on October 17.

The 2008–09 South Pacific cyclone season was a below average tropical cyclone season, which featured six named tropical cyclones compared to an average of about nine. Ahead of the season officially starting on November 1, 2008, the Island Climate Update tropical cyclone outlook predicted that the season, would feature an average risk of tropical cyclones impacting the South Pacific between 160°E and 120°W. The first tropical disturbance of the season developed to the northeast of the Samoan Islands on December 1, however, it remained weak and was last noted during the next day.

The 2008–09 South Pacific cyclone season was a below-average season with only six tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific between 160°E and 120°W. The season officially ran from November 1, 2008 to April 30, 2009 with the first disturbance of the season forming on December 1 and the last disturbance moving out of the region on April 11.

The 2009–10 South Pacific cyclone season began on December 3, 2009 with the formation of Tropical Disturbance 01F, 32 days after the cyclone season had officially begun on November 1, 2009. The season ended on April 30, 2010. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the southern Pacific Ocean east of 160°E. Additionally, the regional tropical cyclone operational plan defines a tropical cyclone year separately from a tropical cyclone season; the "tropical cyclone year" began on July 1, 2009 and ended on June 30, 2010. Tropical cyclones between 160°E and 120°W and north of 25°S are monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service. Those that move south of 25°S are monitored by the Tropical Cyclone Warning Centre in Wellington, New Zealand. The first tropical disturbance of the season formed on December 3, about 1015 km (700 mi) to the north of Suva, Fiji and later intensified into Tropical Cyclone Mick. The last system, 15F, dissipated on April 5 of the following year.

The 2003–04 South Pacific cyclone season was a below-average season with only three tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific to the east of 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 2003, to April 30, 2004, with the first disturbance of the season forming on December 4 and the last disturbance dissipating on April 23. This is the period of the year when most tropical cyclones form within the South Pacific Ocean.

This timeline documents all of the events of the 2009–10 South Pacific cyclone season which is the period that tropical cyclones formed in the southern Pacific Ocean. Within the Southern Pacific Ocean, most tropical cyclones form within the cyclone season which began on November 1 and will end on April 30, though occasionally cyclones form outside these times. The scope of this article is limited to tropical cyclones that form in the Indian Ocean 160°E and 120°W to the south of the equator. Should a tropical cyclone form to the west of 160°E then it will be monitored within the Australian region by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, should a tropical cyclone form to the east of 120°W, it is unclear how it will be handled as no tropical cyclone has ever been observed in the South Pacific Ocean east of 120°W.

Severe Tropical Cyclone Pat was a small but strong tropical cyclone that passed directly over Aitutaki, Cook Islands, in southern Pacific Ocean on February 10, 2010. Part of a series of storms to impact the group of islands early that year, Pat was first identified as a tropical depression on February 6 well to the northeast of the Samoan Islands. The storm steadily organized as it moved generally southeast, becoming a tropical cyclone on February 8. Turning to the south, intensification began in earnest and the system acquired hurricane-force winds within 48 hours of being named. The 445 km (275 mi) wide system displayed annular characteristics and a 19 km (12 mi) wide eye. Pat reached its peak strength early on February 10 as a severe tropical cyclone with winds of 140 km/h (85 mph) and a barometric pressure of 960 mbar. Hours later it struck Aitutaki, producing gusts in excess of 185 km/h (115 mph) on the island. Hostile wind shear then prompted rapid weakening of the cyclone. The system degraded below gale-intensity on February 11, just 24 hours after it peaked, and was last noted early on February 12.

The 2014–15 South Pacific cyclone season was a slightly-below average tropical cyclone season, with five tropical cyclones occurring within the basin between 160°E and 120°W. The season officially ran from November 1, 2014, to April 30, 2015. During the season, tropical cyclones were officially monitored by the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) in Nadi, Fiji and the Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers in Brisbane, Australia and Wellington, New Zealand. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) also monitored the basin and issued unofficial warnings for American interests. RSMC Nadi attaches a number and an F suffix to tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. RSMC Nadi, TCWC Wellington and TCWC Brisbane all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate windspeeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimated sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).

The 2015–16 South Pacific cyclone season was one of the most disastrous South Pacific tropical cyclone seasons on record, with a total of 50 deaths and $1.405 billion in damage. Throughout the season, 8 systems attained tropical cyclone status, whilst 5 became severe tropical cyclones. The most notable cyclone of the season by far was Winston, which attained a minimum pressure of 884 hPa, and maximum ten-minute sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h), making it the most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Southern Hemisphere. Winston went on to devastate Fiji, causing $1.4 billion in damage and 44 deaths across the country.

The 2016–17 South Pacific cyclone season was the least active South Pacific cyclone season since the 2011–12 season, with only four tropical cyclones occurring within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E. Two of the four systems developed into severe tropical cyclones on the Australian tropical cyclone intensity scale. The season officially ran from November 1, 2016 until April 30, 2017. However, May featured two post-season systems: Donna and Ella, of which the former was the strongest post-season South Pacific tropical cyclone ever recorded in that month. Overall, 22 tropical disturbances were monitored by a combination of the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS), Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BoM) and New Zealand's MetService.
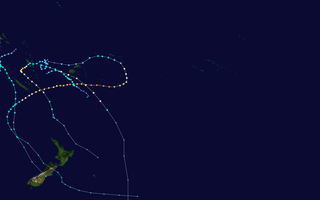
The 2017–18 South Pacific cyclone season was a slightly below-average season that produced 6 tropical cyclones, 3 of which became severe tropical cyclones. The season officially began on November 1, 2017, and ended on April 30, 2018; however, a tropical cyclone could form at any time between July 1, 2017, and June 30, 2018, and would count towards the season total. During the season, tropical cyclones were officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service, MetService and the Australian Bureau of Meteorology, while the United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) also monitored the basin and issued warnings for American interests. The FMS attaches a number and an F suffix to significant tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin, while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The BoM, FMS and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate wind speeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimates sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).

The 2019–20 South Pacific cyclone season was a slightly above-average season in which tropical cyclones formed within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E. The season officially ran from November 1, 2019, to April 30, 2020, however a tropical cyclone could form at any time between July 1, 2019, and June 30, 2020, and would count towards the season total. The season began on November 22 with the formation of Tropical Cyclone Rita, which would later become a severe tropical cyclone. The season has been near-average in terms of activity, with 8 tropical cyclones and 4 severe tropical cyclones forming during the season. The season featured Cyclone Harold, the first Category 5 severe tropical cyclone in the basin since Cyclone Gita, and one of the strongest since Cyclone Winston. During the season, tropical cyclones are officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS), Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) and New Zealand's MetService. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) also monitors the basin and issue unofficial warnings for American interests. The FMS attaches a number and an F suffix to tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The FMS, BoM and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate wind speeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimated sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).
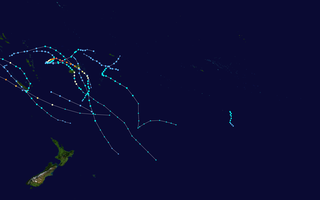
The 2020–21 South Pacific cyclone season was an average season where most tropical cyclones formed within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E. The season officially started on November 1, 2020, and officially ended on April 30, 2021, however a tropical cyclone could form at any time between July 1, 2020, and June 30, 2021, and would count towards the season total. During the season, tropical cyclones will be officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS), Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BoM), New Zealand's MetService. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) will also monitor the basin and issue unofficial warnings for American interests. RSMC Nadi attaches a number and an F suffix to tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. RSMC Nadi, TCWC Wellington and TCWC Brisbane all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate windspeeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimated sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).

Severe Tropical Cyclone Freda was an intense tropical cyclone that developed during the 2012–13 South Pacific cyclone season and affected New Caledonia and the Solomon Islands as a weak tropical cyclone. The system that was to become Cyclone Freda was first classified on 26 December 2012, as a tropical disturbance. It gradually developed and was classified as a tropical cyclone and named Freda as it passed through the Solomon Islands on 28 December.

The 2021–22 South Pacific cyclone season was a near average tropical cyclone season within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E. The season officially started from November 1, 2021, and officially ended on April 30, 2022, however a tropical cyclone could form at any time between July 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022, and would count towards the season total. During the season, tropical cyclones will be officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service, Australian Bureau of Meteorology and New Zealand's MetService. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) will also monitor the basin and issue unofficial warnings for American interests. The FMS attaches a number and an F suffix to tropical disturbances that form in or move into the basin while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The BoM, FMS and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate windspeeds over a period of ten minutes, while the JTWC estimated sustained winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).

Severe Tropical Cyclone Cody was a strong tropical cyclone in the South Pacific which caused widespread damage in Fiji. The second tropical cyclone and first severe tropical cyclone of the 2021–22 South Pacific cyclone season, Cody was first noted by the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS) on 5 January as Tropical Disturbance 03F. The tropical depression killed one person, and over 4,500 people were evacuated. On 10 January, the system was upgraded to a Category 1 tropical cyclone by the FMS, receiving the name Cody. While the FMS recorded a peak intensity of 130 km/h (80 mph), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) only recorded a peak intensity of 95 km/h (60 mph). Cody was the first tropical cyclone in 2022.

The 2023–24 South Pacific cyclone season was a below-average season within the South Pacific Ocean to the east of 160°E. The season officially started on November 1, 2023, and ended on April 30, 2024, however a tropical cyclone could form between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024, and still be included in the season, as shown by Cyclone Lola which formed in October. During the season, tropical cyclones will be officially monitored by the Fiji Meteorological Service, Australian Bureau of Meteorology and New Zealand's MetService. The United States Armed Forces through the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) will also monitor the basin and issue unofficial warnings for American interests. The FMS attaches a number and an F suffix to systems that are active in the basin while the JTWC designates significant tropical cyclones with a number and a P suffix. The BoM, FMS and MetService all use the Australian Tropical Cyclone Intensity Scale and estimate winds with a 10-minute period, while the JTWC estimates winds over a 1-minute period, which are subsequently compared to the Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS).



















