Related Research Articles

Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated.
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen (glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise.

Sialic acids are a class of alpha-keto acid sugars with a nine-carbon backbone. The term "sialic acid" was first introduced by Swedish biochemist Gunnar Blix in 1952. The most common member of this group is N-acetylneuraminic acid found in animals and some prokaryotes.
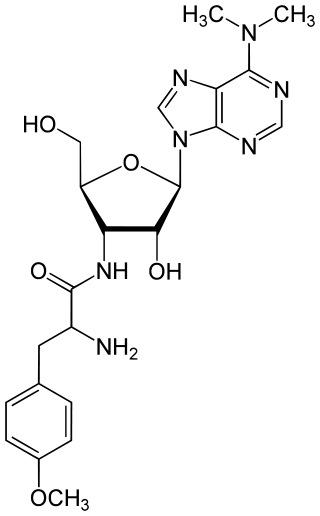
Puromycin is an antibiotic protein synthesis inhibitor which causes premature chain termination during translation.

Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT level, and their ratio are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels.

Membrane alanyl aminopeptidase also known as alanyl aminopeptidase (AAP) or aminopeptidase N (AP-N) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANPEP gene.
Exo-α-sialidase is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
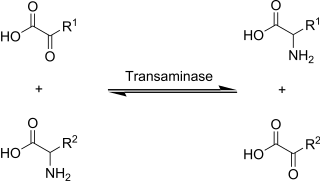
Transaminases or aminotransferases are enzymes that catalyze a transamination reaction between an amino acid and an α-keto acid. They are important in the synthesis of amino acids, which form proteins.
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen by catalyzing the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine:
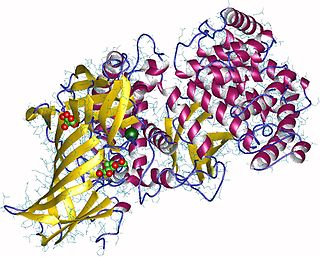
Aminopeptidases are enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of amino acids from the amino terminus (N-terminus) of proteins or peptides (exopeptidases). They are widely distributed throughout the animal and plant kingdoms and are found in many subcellular organelles, in cytosol, and as membrane components. Aminopeptidases are used in essential cellular functions. Many, but not all, of these peptidases are zinc metalloenzymes.
Protein metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism.
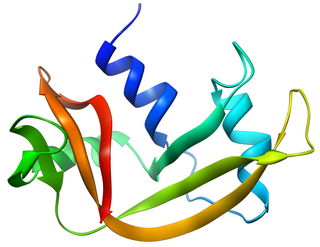
Pancreatic ribonuclease family is a superfamily of pyrimidine-specific endonucleases found in high quantity in the pancreas of certain mammals and of some reptiles.

Methionine aminopeptidase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the METAP2 gene.
In enzymology, an alanine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Puromycin-sensitive amino peptidase also known as cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase or alanine aminopeptidase (AAP) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NPEPPS gene. It is used as a biomarker to detect damage to the kidneys, and that may be used to help diagnose certain kidney disorders. It is found at high levels in the urine when there are kidney problems.

Viral neuraminidase is a type of neuraminidase found on the surface of influenza viruses that enables the virus to be released from the host cell. Neuraminidases are enzymes that cleave sialic acid groups from glycoproteins. Neuraminidase inhibitors are antiviral agents that inhibit influenza viral neuraminidase activity and are of major importance in the control of influenza.
Feline coronavirus (FCoV) is a positive-stranded RNA virus that infects cats worldwide. It is a coronavirus of the species Alphacoronavirus 1 which includes canine coronavirus (CCoV) and porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus (TGEV). It has two different forms: feline enteric coronavirus (FECV) that infects the intestines and feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV) that causes the disease feline infectious peritonitis (FIP).
Aminopeptidase Ey is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses differs from other aminopeptidases in broad specificity for amino acids in the P1 position and the ability to hydrolyse peptides of four or five residues that contain Pro in the P1' position
Zinc D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase (EC 3.4.17.14, Zn2+ G peptidase, D-alanyl-D-alanine hydrolase, D-alanyl-D-alanine-cleaving carboxypeptidase, DD-carboxypeptidase, G enzyme, DD-carboxypeptidase-transpeptidase) is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Amastatin, also known as 3-amino-2-hydroxy-5-methylhexanoyl-L-valyl-L-valyl-L-aspartic acid, is a naturally occurring, competitive and reversible aminopeptidase inhibitor that was isolated from Streptomyces sp. ME 98-M3. It specifically inhibits leucyl aminopeptidase, alanyl aminopeptidase, bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase, leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase (oxytocinase/vasopressinase), and, to a lesser extent, glutamyl aminopeptidase, as well as other aminopeptidases. It does not inhibit arginyl aminopeptidase. Amastatin has been found to potentiate the central nervous system effects of oxytocin and vasopressin in vivo. It also inhibits the degradation of met-enkephalin, dynorphin A, and other endogenous peptides.
References
- ↑ Starnes WL, Behal FJ (July 1974). "A human liver aminopeptidase. The amino acid and carbohydrate content, and some physical properties of a sialic acid containing glycoprotein". Biochemistry. 13 (16): 3221–7. doi:10.1021/bi00713a004. PMID 4841062.
- ↑ Kao YJ, Starnes WL, Behal FJ (July 1978). "Human kidney alanine aminopeptidase: physical and kinetic properties of a sialic acid containing glycoprotein". Biochemistry. 17 (15): 2990–4. doi:10.1021/bi00608a008. PMID 698181.
- ↑ Sidorowicz W, Hsia WC, Maslej-Zownir O, Behal FJ (November 1980). "Multiple molecular forms of human alanine aminopeptidase: immunochemical properties". Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry. 107 (3): 245–56. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(80)90452-0. PMID 6108169.