ANSI C, ISO C, and Standard C are successive standards for the C programming language published by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 14 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Historically, the names referred specifically to the original and best-supported version of the standard. Software developers writing in C are encouraged to conform to the standards, as doing so helps portability between compilers.

The International Organization for Standardization is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.

ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, Information technology—8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets—Part 1: Latin alphabet No. 1, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. ISO/IEC 8859-1 encodes what it refers to as "Latin alphabet no. 1", consisting of 191 characters from the Latin script. This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa. It is the basis for some popular 8-bit character sets and the first two blocks of characters in Unicode.
ISO/IEC 8859 is a joint ISO and IEC series of standards for 8-bit character encodings. The series of standards consists of numbered parts, such as ISO/IEC 8859-1, ISO/IEC 8859-2, etc. There are 15 parts, excluding the abandoned ISO/IEC 8859-12. The ISO working group maintaining this series of standards has been disbanded.

The International Electrotechnical Commission is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology". IEC standards cover a vast range of technologies from power generation, transmission and distribution to home appliances and office equipment, semiconductors, fibre optics, batteries, solar energy, nanotechnology, and marine energy, as well as many others. The IEC also manages four global conformity assessment systems that certify whether equipment, system or components conform to its international standards.
ISO/IEC 8859-3:1999, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 3: Latin alphabet No. 3, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1988. It is informally referred to as Latin-3 or South European. It was designed to cover Turkish, Maltese and Esperanto, though the introduction of ISO/IEC 8859-9 superseded it for Turkish. The encoding was popular for users of Esperanto, but fell out of use as application support for Unicode became more common.
ISO/IEC 14443Identification cards – Contactless integrated circuit cards – Proximity cards is an international standard that defines proximity cards used for identification, and the transmission protocols for communicating with it.
ISO/IEC 646 is a set of ISO/IEC standards, described as Information technology — ISO 7-bit coded character set for information interchange, and developed in cooperation with ASCII at least since 1964. Since its first edition in 1967 it has specified a 7-bit character code from which several national standards are derived.

CENELEC is responsible for European standardization in the area of electrical engineering. Together with ETSI (telecommunications) and CEN, it forms the European system for technical standardization. Standards harmonised by these agencies are regularly adopted in many countries outside Europe which follow European technical standards. Although CENELEC works closely with the European Union, it is not an EU institution. Nevertheless, its standards are "EN" EU standards, thanks to EU Regulation 1025/2012.
A data control language (DCL) is a syntax similar to a computer programming language used to control access to data stored in a database (authorization). In particular, it is a component of Structured Query Language (SQL). Data Control Language is one of the logical group in SQL Commands. SQL is the standard language for relational database management systems. SQL statements are used to perform tasks such as insert data to a database, delete or update data in a database, or retrieve data from a database.

The IP code or ingress protection code indicates how well a device is protected against water and dust. It is defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) under the international standard IEC 60529 which classifies and provides a guideline to the degree of protection provided by mechanical casings and electrical enclosures against intrusion, dust, accidental contact, and water. It is published in the European Union by the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) as EN 60529.
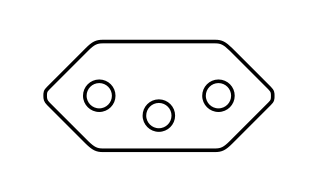
IEC 60906-1 is an international standard designed "to provide a standard for a safe, compact and practical 16 A 250 V AC system of plugs and socket-outlets that could be accepted by many countries as their national standard, even if not in the near future." The standard was originally published by the International Electrotechnical Commission in 1986; the current edition is ed2.0 published in 2009. Although it is almost identical to the Swiss SEV 1011 T12 plug for 10 A 250 V a.c. standardised in 1937, its dimensions are slightly different and its polarization is flipped. As of July 2014, only South Africa has introduced a standard based closely on IEC 60906-1. Brazil used it as the basis for its NBR 14136 standard, but this is not fully compatible with IEC 60906-1. In 2017 the European Union (EU) published recommendations advising against the harmonisation of domestic plug and socket systems in the EU.
IEC standard 61511 is a technical standard which sets out practices in the engineering of systems that ensure the safety of an industrial process through the use of instrumentation. Such systems are referred to as Safety Instrumented Systems. The title of the standard is "Functional safety - Safety instrumented systems for the process industry sector".
ISO/IEC 14651:2016, Information technology -- International string ordering and comparison -- Method for comparing character strings and description of the common template tailorable ordering, is an International Organization for Standardization (ISO)/International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard specifying an algorithm that can be used when comparing two strings. This comparison can be used when collating a set of strings. The standard also specifies a data file, the Common Tailorable Template (CTT), which outlines the comparison order. This order is meant to be tailored for different languages, making the CTT a template rather than a default. In many cases, however, the empty tailoring—where no weightings are changed—is appropriate, as different languages have incompatible ordering requirements. One such tailoring is European ordering rules (EOR), which in turn is supposed to be tailored for different European languages.

IEC 62196Plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets – Conductive charging of electric vehicles is a series of international standards that define requirements and tests for plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets for conductive charging of electric vehicles and is maintained by the technical subcommittee SC 23H “Plugs, Socket-outlets and Couplers for industrial and similar applications, and for Electric Vehicles” of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).

The Al-Hadi School of Accelerative Learning (AHS) is an Islamic primary and secondary school in Southwest Houston, Texas. The school is founded by Nasser Biria and is located on the premises of the Islamic Education Center of Greater Houston (IEC) of Houston, which also houses one of the largest mosques in Houston. According to Faheem Kazimi, the chairperson of the IEC, it is a Houston-area school that runs on tuition fees that comes from the students ranging to $5000. The school is near Westheimer Road.
IEC 62325 is a set of standards related to deregulated energy market communications, based on the Common Information Model. IEC 62325 is a part of the International Electrotechnical Commission's (IEC) Technical Committee 57 (TC57) reference architecture for electric power systems, and is the responsibility of Working Group 16 (WG16).
IEC Technical Specification 62700: DC Power supply for notebook computer is an IEC specification of a common standard for external laptop computer AC adapters. Laptops and AC adapters following this standard will have interchangeable power supplies, which will enable easy reuse of used power supplies and make buying a new compatible power supply for a laptop simpler.
ISO 5426 is a character set developed by ISO, similar to ISO/IEC 6937. It was first published in 1983.








