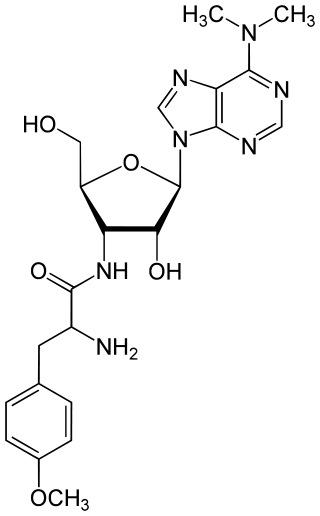
Puromycin is an antibiotic protein synthesis inhibitor which causes premature chain termination during translation.

Cathepsin C (CTSC) also known as dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPP-I) is a lysosomal exo-cysteine protease belonging to the peptidase C1 protein family, a subgroup of the cysteine cathepsins. In humans, it is encoded by the CTSC gene.
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4), also known as adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2 or CD26 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the DPP4 gene. DPP4 is related to FAP, DPP8, and DPP9. The enzyme was discovered in 1966 by Hopsu-Havu and Glenner, and as a result of various studies on chemism, was called dipeptidyl peptidase IV [DP IV].

Xaa-Pro dipeptidase, also known as prolidase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PEPD gene.

Dipeptidyl-peptidase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DPP3 gene.

Dipeptidyl-peptidase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DPP7 gene.

Dipeptidyl peptidase 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DPP8 gene.

Dipeptidyl peptidase 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DPP9 gene.
Cathepsin X is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dipeptidyl-peptidase III is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Bacterial leucyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Xaa-Trp aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Xaa-Pro dipeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dipeptidyl-peptidase II is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Xaa-Pro dipeptidyl-peptidase (EC 3.4.14.11, X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase, PepX, X-prolyl dipeptidyl peptidase is an enzyme. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
Xaa-Xaa-Pro tripeptidyl-peptidase is an enzyme. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pyroglutamyl-peptidase II is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
C-terminal processing peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Signal peptidase II is an enzyme.









