A constitutional coup occurs when a person or group seizes political power in a way consistent with their country's constitution, as opposed to a traditional violent coup d'état, often by exploiting loopholes or ambiguities in said constitution. Supporters of constitutional coups exploit their political power to semi-legally seize more. Constitutional coups can be carried out in many ways, including removing term or age limits, changing electoral rules to hinder opposing candidates, and postponing elections indefinitely.

John Charles Eastman is an American lawyer and academic. He is known for his efforts to overturn the 2020 United States presidential election and block the certification of Joe Biden's victory, for which he has been criminally indicted, ordered inactive by the State Bar of California, and recommended for disbarment. Eastman has lost eligibility to practice law in California state courts, pending his appeal of the state bar judge's ruling that recommended him for disbarment. Eastman is also named as a co-conspirator in the federal indictment brought against Trump over his attempts to subvert the 2020 election results and prevent certification of Biden's election.
The president-elect of the United States is the candidate who has presumptively won the United States presidential election and is awaiting inauguration to become the president. There is no explicit indication in the U.S. Constitution as to when that person actually becomes president-elect, although the Twentieth Amendment uses the term "president-elect", thereby giving the term constitutional basis. It is assumed the Congressional certification of votes cast by the Electoral College of the United States – occurring after the third day of January following the swearing-in of the new Congress, per provisions of the Twelfth Amendment – unambiguously confirms the successful candidate as the official "president-elect" under the U.S. Constitution. As an unofficial term, president-elect has been used by the media since at least the latter half of the 19th century and was in use by politicians since at least the 1790s. Politicians and the media have applied the term to the projected winner, even on election night, and very few who turned out to lose have been referred to as such.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 3, 2020. The Democratic ticket of former vice president Joe Biden and the junior U.S. senator from California Kamala Harris defeated the incumbent Republican president Donald Trump, and vice president Mike Pence. The election took place against the backdrop of the global COVID-19 pandemic and related recession. The election saw the highest voter turnout by percentage since 1900. Biden received more than 81 million votes, the most votes ever cast for a presidential candidate in U.S. history.

Anthony Kern is an American politician and a Republican former member of the Arizona Senate, representing District 27 since 2023. He previously represented District 20 in the State House of Representatives from January 5, 2015, to January 11, 2021.
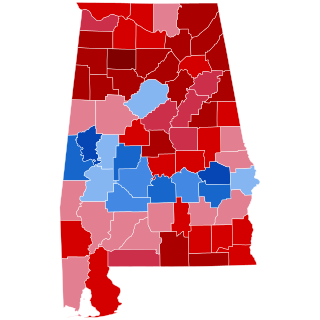
The 2020 United States presidential election in Alabama took place on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states and the District of Columbia participated. Alabama voters chose nine electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting incumbent Republican President Donald Trump and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Mike Pence, against Democratic challenger and former Vice President Joe Biden and his running mate, United States Senator Kamala Harris of California. Also on the ballot was the Libertarian nominee, psychology lecturer Jo Jorgensen and her running mate, entrepreneur and podcaster Spike Cohen. Write-in candidates were permitted without registration, and their results were not individually counted.

The Electoral Count Act of 1887 (ECA) is a United States federal law that added to procedures set out in the Constitution of the United States for the counting of electoral votes following a presidential election. In its unamended form, it last governed at the time of the 2021 United States Electoral College vote count. The Act has since been substantially amended by the Electoral Count Reform and Presidential Transition Improvement Act of 2022.
Members of the United States Republican Party have reacted differently to Republican president Donald Trump's claims about the 2020 United States presidential election, with many publicly supporting them, many remaining silent, and a few publicly denouncing them. Trump claimed to have won the election, and made many claims of election fraud. By December 11, 2020, 126 out of 196 Republican members of the House backed a lawsuit filed in the United States Supreme Court supported by nineteen Republican state attorneys general seeking to subvert the election and overturn the election results. The Trump campaign hired the Berkeley Research Group to investigate whether there had been voter fraud. The researchers found nothing, and the consultancy reported this to Trump and his chief of staff Mark Meadows on a conference call in the final days of the year, before the attack on the Capitol.

In the United States, a certificate of ascertainment is an official document that identifies a state's appointed electors for U.S. President and Vice President, and the final vote count for each candidate that received popular votes.

After Democratic nominee Joe Biden won the 2020 United States presidential election, Republican nominee and then-incumbent president Donald Trump pursued an unprecedented effort to overturn the election, with support from his campaign, proxies, political allies, and many of his supporters. These efforts culminated in the January 6 Capitol attack by Trump supporters in an attempted self-coup d'état. Trump and his allies used the "big lie" propaganda technique to promote claims that had been proven false and conspiracy theories asserting the election was stolen by means of rigged voting machines, electoral fraud and an international conspiracy. Trump pressed Department of Justice leaders to challenge the results and publicly state the election was corrupt. However, the attorney general, director of National Intelligence, and director of the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency – as well as some Trump campaign staff – dismissed these claims. State and federal judges, election officials, and state governors also determined the claims were baseless.
The following is a timeline of major events before, during, and after the 2020 United States presidential election, the 59th quadrennial United States presidential election, from November 2020 to January 2021. For prior events, see Timeline of the 2020 United States presidential election (2017–2019) and Timeline of the 2020 United States presidential election.

The count of the Electoral College ballots during a joint session of the 117th United States Congress, pursuant to the Electoral Count Act, on January 6–7, 2021, was held as the final step to confirm then President-elect Joe Biden's victory in the 2020 presidential election over incumbent President Donald Trump.

Donald Trump's first farewell address was the final official speech of Donald Trump as the 45th President of the United States, delivered as a recorded, online video message on January 19, 2021. The farewell address was delivered the day before Joe Biden, who defeated him in the 2020 United States presidential election, was sworn in as his successor. Trump was the first president to not attend his successor's inauguration since Andrew Johnson in 1869.

The Eastman memos, also known as the "coup memo", are documents by John Eastman, an American law professor retained by then-President Donald Trump, advancing the fringe legal theory that a U.S. Vice President has unilateral authority to reject certified state electors. This would have the effect of nullifying an election in order to produce an outcome personally desired by the Vice President, such as a result in the Vice President's own party's favor, including retaining himself as Vice President, or if the Vice President is himself the presidential candidate, then to unilaterally make himself president.

The count of the Electoral College ballots during a joint session of the 115th United States Congress, pursuant to the Electoral Count Act, on January 6, 2017, was held as the final step to confirm then President-elect Donald Trump's victory in the 2016 presidential election over former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton.
Gregory Jacob is an American lawyer who was legal counsel to U.S. Vice President Mike Pence during the administration of Donald Trump. He is currently a partner in the Washington office of the law firm, O'Melveny & Myers, specializing in ERISA matters.
Kenneth John Chesebro is an American attorney known as the architect of the Trump fake electors plot that conspired to overturn the 2020 U.S. presidential election.
The Trump fake electors plot was an attempt by U.S. president Donald Trump and associates to have him remain in power after losing the 2020 United States presidential election. After the results of the election determined Trump had lost, he, his associates, and Republican Party officials in seven states devised a scheme to submit fraudulent certificates of ascertainment to falsely claim Trump had won the Electoral College vote in crucial states. The plot was one of Trump and his associates' attempts to overturn the 2020 United States presidential election.

State of Wisconsin v. Kenneth Chesebro, et al. is a state criminal prosecution concerning the Trump fake electors plot in Wisconsin. The three defendants, Kenneth J. Chesebro,Michael A. Roman, and James R. Troupis, were lawyers and political aides to Donald Trump's 2020 presidential campaign involved in planning and producing fraudulent electoral vote paperwork as part of a plot to replace or nullify the official electoral votes of the state of Wisconsin in the 2020 presidential election. The three defendants are each charged with a single count of conspiracy to utter forged official documents as legitimate.

The count of the Electoral College ballots during a joint session of the 119th United States Congress, pursuant to the Electoral Count Act and Electoral Count Reform and Presidential Transition Improvement Act of 2022, on January 6, 2025, was held as the final step that confirmed President-elect Donald Trump's victory in the 2024 presidential election over incumbent Vice President Kamala Harris.











