
Explorer 35,, was a spin-stabilized spacecraft built by NASA as part of the Explorer program. It was designed for the study of the interplanetary plasma, magnetic field, energetic particles, and solar X-rays, from lunar orbit.

Explorer 6, or S-2, was a NASA satellite, launched on 7 August 1959, at 14:24:20 GMT. It was a small, spherical satellite designed to study trapped radiation of various energies, galactic cosmic rays, geomagnetism, radio propagation in the upper atmosphere, and the flux of micrometeorites. It also tested a scanning device designed for photographing the Earth's cloud cover. On 14 August 1959, Explorer 6 took the first photos of Earth from a satellite.

Explorer 11 was a NASA satellite that carried the first space-borne gamma-ray telescope. This marked the beginning of space gamma-ray astronomy. Launched on 27 April 1961 by a Juno II, the satellite returned data until 17 November 1961, when power supply problems ended the science mission. During the spacecraft's seven-month lifespan it detected twenty-two events from gamma-rays and approximately 22,000 events from cosmic radiation.

The Global Geospace Science (GGS) Wind satellite is a NASA science spacecraft designed to study radio waves and plasma that occur in the solar wind and in the Earth's magnetosphere. It was launched on 1 November 1994, at 09:31:00 UTC, from launch pad LC-17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Merritt Island, Florida, aboard a McDonnell Douglas Delta II 7925-10 rocket. Wind was designed and manufactured by Martin Marietta Astro Space Division in East Windsor Township, New Jersey. The satellite is a spin-stabilized cylindrical satellite with a diameter of 2.4 m and a height of 1.8 m.

The Solar Anomalous and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer was a NASA solar and magnetospheric observatory and was the first spacecraft in the Small Explorer program. It was launched into low Earth orbit on 3 July 1992, from Vandenberg Air Force Base aboard a Scout G-1 launch vehicle. SAMPEX was an international collaboration between NASA and the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics of Germany. The Solar Anomalous and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer (SAMPEX) is the first of a series of spacecraft that was launched under the Small Explorer (SMEX) program for low-cost spacecraft.

Explorer 18, also called IMP-A, IMP-1, Interplanetary Monitoring Platform-1 and S-74, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorer program. Explorer 18 was launched on 27 November 1963 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Florida, with a Thor-Delta C launch vehicle. Explorer 18 was the first satellite of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform (IMP). Explorer 21 (IMP-B) launched in October 1964 and Explorer 28 (IMP-C) launched in May 1965 also used the same general spacecraft design.

Explorer 14, also called EPE-B or Energetic Particles Explorer-B, was a NASA spacecraft instrumented to measure cosmic-ray particles, trapped particles, solar wind protons, and magnetospheric and interplanetary magnetic fields. It was the second of the S-3 series of spacecraft, which also included Explorer 12, 14, 15, and 26. It was launched on 2 October 1962, aboard a Thor-Delta launch vehicle.

The ISEE-1 was an Explorer-class mother spacecraft, International Sun-Earth Explorer-1, was part of the mother/daughter/heliocentric mission. ISEE-1 was a 340.2 kg (750 lb) space probe used to study magnetic fields near the Earth. ISEE-1 was a spin-stabilized spacecraft and based on the design of the prior IMP series of spacecraft. ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 were launched on 22 October 1977, and they re-entered on 26 September 1987.

The ISEE-2 was an Explorer-class daughter spacecraft, International Sun-Earth Explorer-2, was part of the mother/daughter/heliocentric mission. ISEE-2 was a 165.78 kg (365.5 lb) space probe used to study magnetic fields near the Earth. ISEE-2 was a spin-stabilized spacecraft and based on the design of the prior IMP series of spacecraft. ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 were launched on 22 October 1977, and they re-entered on 26 September 1987.

Explorer 12, also called EPE-A or Energetic Particles Explorer-A and as S3), was a NASA satellite built to measure the solar wind, cosmic rays, and the Earth's magnetic field. It was the first of the S-3 series of spacecraft, which also included Explorer 12, 14, 15, and 26. It was launched on 16 August 1961, aboard a Thor-Delta launch vehicle. It ceased transmitting on 6 December 1961 due to power failure.

Explorer 26 was a NASA satellite launched on 21 December 1964, as part of NASA's Explorer program. Its primary mission was to study the Earth's magnetic field.

Explorer 28, also called IMP-C, IMP-3 and Interplanetary Monitoring Platform-3, was a NASA satellite launched on 29 May 1965 to study space physics, and was the third spacecraft launched in the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform program. It was powered by chemical batteries and solar panels. There were 7 experiments on board, all devoted to particle studies. Performance was normal until late April 1967, when intermittent problems began. It stayed in contact until 12 May 1967, when contact was lost. The orbit decayed until it re-entered the atmosphere on 4 July 1968. The spacecraft design was similar to its predecessors Explorer 18 (IMP-A), launched in November 1963, and Explorer 21 (IMP-B), launched in October 1964, though this satellite was a few kilograms lighter. The successor Explorer 33 (IMP-D) began the use of a new design.
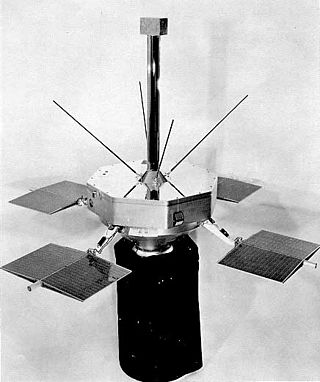
Explorer 15, also called EPE-C or Energetic Particles Explorer-C, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorer program. Explorer 15 was launched on 27 October 1962, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, United States, with a Thor-Delta A.

Explorer 21, also called IMP-B, IMP-2 and Interplanetary Monitoring Platform-2, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 21 was launched on 4 October 1964, at 03:45:00 GMT from Cape Canaveral (CCAFS), Florida, with a Thor-Delta C launch vehicle. Explorer 21 was the second satellite of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform, and used the same general design as its predecessor, Explorer 18 (IMP-A), launched the previous year, in November 1963. The following Explorer 28 (IMP-C), launched in May 1965, also used a similar design.

Explorer 34, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 34 as launched on 24 May 1967 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, with Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 34 was the fifth satellite launched as part of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform program, but was known as "IMP-4" because the preceding launch was more specifically part of the "Anchored IMP" sub-program. The spacecraft was put into space between the launches of Explorer 33 in 1966 and Explorer 35 in July 1967, but the next satellite to use Explorer 34's general design was Explorer 41, which flew in 1969.

Explorer 41, also called IMP-G and IMP-5, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorers program. Explorer 41 launched on 21 June 1969 from Vandenberg AFB, California, with a Thor-Delta E1 launch vehicle. Explorer 41 was the seventh satellite launched as part of the overall Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, though it received the post-launch designation "IMP-5" because two previous flights had used the "AIMP" designation instead. It was preceded by the second of those flights, Explorer 35, launched in July 1967. Its predecessor in the strict IMP series of launches was Explorer 34, launched in May 1967, which shared a similar design to Explorer 41. The next launch of an IMP satellite was Explorer 43 in 1971.

Explorer 43, also called IMP-I and IMP-6, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorers program. Explorer 43 was launched on 13 March 1971 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) with a Thor-Delta M6 launch vehicle. Explorer 43 was the sixth satellite of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform.

Explorer 45 was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 45 was the only one to be released from the program Small Scientific Satellite.

Explorer 50, also known as IMP-J or IMP-8, was a NASA satellite launched to study the magnetosphere. It was the eighth and last in a series of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform.

AMPTE-Charge Composition Explorer, also called as AMPTE-CCE or Explorer 65, was a NASA satellite designed and tasked to study the magnetosphere of Earth, being launched as part of the Explorer program. The AMPTE mission was designed to study the access of solar wind ions to the magnetosphere, the convective-diffusive transport and energization of magnetospheric particles, and the interactions of plasmas in space.




















