Related Research Articles

Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe, meaning that it can grow without oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The bacterium is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.

Clostridium perfringens is a Gram-positive, bacillus (rod-shaped), anaerobic, spore-forming pathogenic bacterium of the genus Clostridium. C. perfringens is ever-present in nature and can be found as a normal component of decaying vegetation, marine sediment, the intestinal tract of humans and other vertebrates, insects, and soil. It has the shortest reported generation time of any organism at 6.3 minutes in thioglycolate medium.
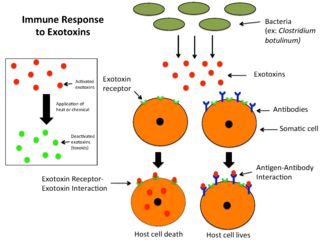
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during lysis of the cell. Gram negative pathogens may secrete outer membrane vesicles containing lipopolysaccharide endotoxin and some virulence proteins in the bounding membrane along with some other toxins as intra-vesicular contents, thus adding a previously unforeseen dimension to the well-known eukaryote process of membrane vesicle trafficking, which is quite active at the host–pathogen interface.

Superantigens (SAgs) are a class of antigens that result in excessive activation of the immune system. Specifically they cause non-specific activation of T-cells resulting in polyclonal T cell activation and massive cytokine release. Superantigens act by binding to the MHC proteins on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and to the TCRs on their adjacent helper T-cells, bringing the signaling molecules together, and thus leading to the activation of the T-cells, regardless of the peptide displayed on the MHC molecule. SAgs are produced by some pathogenic viruses and bacteria most likely as a defense mechanism against the immune system. Compared to a normal antigen-induced T-cell response where 0.0001–0.001% of the body's T-cells are activated, these SAgs are capable of activating up to 20% of the body's T-cells. Furthermore, Anti-CD3 and Anti-CD28 antibodies (CD28-SuperMAB) have also shown to be highly potent superantigens.

An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines. They can be chromosomally or plasmid encoded. They are heat labile, of low molecular weight and water-soluble. Enterotoxins are frequently cytotoxic and kill cells by altering the apical membrane permeability of the mucosal (epithelial) cells of the intestinal wall. They are mostly pore-forming toxins, secreted by bacteria, that assemble to form pores in cell membranes. This causes the cells to die.
Gluten exorphins are a group of opioid peptides formed during the digestion of the gluten protein. These peptides work as external regulators for gastrointestinal movement and hormonal release. The breakdown of gliadin, a polymer of wheat proteins, creates amino acids that stop the gluten epitopes from entering the immune system to activate inflammatory reactions. During this process, gluten does not fully break down, thus increasing the presence of gluten exorphins. Because of this, researchers think this is what might lead to various diseases.

Guanylate cyclase 2C, also known as guanylyl cyclase C (GC-C), intestinal guanylate cyclase, guanylate cyclase-C receptor, or the heat-stable enterotoxin receptor (hSTAR) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GUCY2C gene.

Bacteroides is a genus of Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacteria. Bacteroides species are non endospore–forming bacilli, and may be either motile or nonmotile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40–48% GC. Unusual in bacterial organisms, Bacteroides membranes contain sphingolipids. They also contain meso-diaminopimelic acid in their peptidoglycan layer.

Bacteroides fragilis is an anaerobic, Gram-negative, pleomorphic to rod-shaped bacterium. It is part of the normal microbiota of the human colon and is generally commensal, but can cause infection if displaced into the bloodstream or surrounding tissue following surgery, disease, or trauma.
Virulence factors are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that enable microbial pathogens to achieve the following:
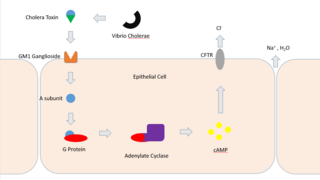
Cholera toxin is an AB5 multimeric protein complex secreted by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. CTX is responsible for the massive, watery diarrhea characteristic of cholera infection. It is a member of the heat-labile enterotoxin family.
Clostridioides difficile toxin B (TcdB) is a cytotoxin produced by the bacteria Clostridioides difficile. It is one of two major kinds of toxins produced by C. difficile, the other being a related enterotoxin. Both are very potent and lethal.

Clostridioides difficile toxin A (TcdA) is a toxin produced by the bacteria Clostridioides difficile, formerly known as Clostridium difficile. It is similar to Clostridioides difficile Toxin B. The toxins are the main virulence factors produced by the gram positive, anaerobic, Clostridioides difficile bacteria. The toxins function by damaging the intestinal mucosa and cause the symptoms of C. difficile infection, including pseudomembranous colitis.
Microbial toxins are toxins produced by micro-organisms, including bacteria, fungi, protozoa, dinoflagellates, and viruses. Many microbial toxins promote infection and disease by directly damaging host tissues and by disabling the immune system. Endotoxins most commonly refer to the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or lipooligosaccharide (LOS) that are in the outer plasma membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. The botulinum toxin, which is primarily produced by Clostridium botulinum and less frequently by other Clostridium species, is the most toxic substance known in the world. However, microbial toxins also have important uses in medical science and research. Currently, new methods of detecting bacterial toxins are being developed to better isolate and understand these toxins. Potential applications of toxin research include combating microbial virulence, the development of novel anticancer drugs and other medicines, and the use of toxins as tools in neurobiology and cellular biology.
Hathewaya histolytica is a species of bacteria found in feces and the soil. It is a motile, gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobe. H. histolytica is pathogenic in many species, including guinea pigs, mice, and rabbits, and humans. H. histolytica has been shown to cause gas gangrene, often in association with other bacteria species.

In the field of molecular biology, enterotoxin type B, also known as Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB), is an enterotoxin produced by the gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is a common cause of food poisoning, with severe diarrhea, nausea and intestinal cramping often starting within a few hours of ingestion. Being quite stable, the toxin may remain active even after the contaminating bacteria are killed. It can withstand boiling at 100 °C for a few minutes. Gastroenteritis occurs because SEB is a superantigen, causing the immune system to release a large amount of cytokines that lead to significant inflammation.

Aureolysin is an extracellular metalloprotease expressed by Staphylococcus aureus. This protease is a major contributor to the bacterium's virulence, or ability to cause disease, by cleaving host factors of the innate immune system as well as regulating S. aureus secreted toxins and cell wall proteins. To catalyze its enzymatic activities, aureolysin requires zinc and calcium which it obtains from the extracellular environment within the host.

Clostridioides difficile is a bacterium known for causing serious diarrheal infections, and may also cause colon cancer. It is known also as C. difficile, or C. diff, and is a Gram-positive species of spore-forming bacteria. Clostridioides spp. are anaerobic, motile bacteria, ubiquitous in nature and especially prevalent in soil. Its vegetative cells are rod-shaped, pleomorphic, and occur in pairs or short chains. Under the microscope, they appear as long, irregular cells with a bulge at their terminal ends. Under Gram staining, C. difficile cells are Gram-positive and show optimum growth on blood agar at human body temperatures in the absence of oxygen. C. difficile is catalase- and superoxide dismutase-negative, and produces up to three types of toxins: enterotoxin A, cytotoxin B and Clostridioides difficile transferase. Under stress conditions, the bacteria produce spores that are able to tolerate extreme conditions that the active bacteria cannot tolerate.

Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacterium and a prominent member of the human gut microbiota, particularly within the large intestine. B. thetaiotaomicron belongs to the Bacteroides genus – a group that is known for its role in the complex microbial community of the gut microbiota. Its proteome, consisting of 4,779 members, includes a system for obtaining and breaking down dietary polysaccharides that would otherwise be difficult to digest for the human body.

Phocaeicola vulgatus,, is a mutualistic anaerobic Gram negative rod bacteria commonly found in the human gut microbiome and isolated from feces. P. vulgatus has medical relevance and has been notable in scientific research due to its production of fatty acids, potential use as a probiotic, and associations with protecting against and worsening some inflammatory diseases. Due to the difficulties in culturing anaerobic bacteria, P. vulgatus is still highly uncharacterised so efforts are being made to make use of multi-omic approaches to investigate the human gut microbiome more thoroughly in hopes to fully understand the role of this species in the development of and protection against diseases, as well as its potential uses in medicine and research. Generally, P. vulgatus is considered as a beneficial bacteria that contributes to digestion and a balanced microbiome, but it has been known to cause opportunistic infections and induce or worsen inflammatory responses. Due to its abundance in the microbiome, some researchers are investigating these species in hopes that it will be a suitable model organism for gut microbiome research, like Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron.
References
- ↑ Moncrief JS, Obiso R, Barroso LA, Kling JJ, Wright RL, Van Tassell RL, Lyerly DM, Wilkins TD (January 1995). "The enterotoxin of Bacteroides fragilis is a metalloprotease". Infection and Immunity. 63 (1): 175–81. PMC 172975 . PMID 7806355.
- ↑ Obiso RJ, Lyerly DM, Van Tassell RL, Wilkins TD (October 1995). "Proteolytic activity of the Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin causes fluid secretion and intestinal damage in vivo". Infection and Immunity. 63 (10): 3820–6. PMC 173537 . PMID 7558286.
- ↑ Donelli G, Fabbri A, Fiorentini C (January 1996). "Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin induces cytoskeletal changes and surface blebbing in HT-29 cells". Infection and Immunity. 64 (1): 113–9. PMC 173735 . PMID 8557328.
- ↑ Koshy SS, Montrose MH, Sears CL (December 1996). "Human intestinal epithelial cells swell and demonstrate actin rearrangement in response to the metalloprotease toxin of Bacteroides fragilis". Infection and Immunity. 64 (12): 5022–8. PMC 174483 . PMID 8945541.
- ↑ Kling JJ, Wright RL, Moncrief JS, Wilkins TD (January 1997). "Cloning and characterization of the gene for the metalloprotease enterotoxin of Bacteroides fragilis". FEMS Microbiology Letters. 146 (2): 279–84. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1097(96)00488-0 . PMID 9011050.