
Cumulonimbus is a dense, towering vertical cloud, forming from water vapor carried by powerful upward air currents. If observed during a storm, these clouds may be referred to as thunderheads. Cumulonimbus can form alone, in clusters, or along cold front squall lines. These clouds are capable of producing lightning and other dangerous severe weather, such as tornadoes and hailstones. Cumulonimbus progress from overdeveloped cumulus congestus clouds and may further develop as part of a supercell. Cumulonimbus is abbreviated Cb.

The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. Lapse rate arises from the word lapse, in the sense of a gradual fall.

In meteorology, convective available potential energy, is the integrated amount of work that the upward (positive) buoyancy force would perform on a given mass of air if it rose vertically through the entire atmosphere. Positive CAPE will cause the air parcel to rise, while negative CAPE will cause the air parcel to sink. Nonzero CAPE is an indicator of atmospheric instability in any given atmospheric sounding, a necessary condition for the development of cumulus and cumulonimbus clouds with attendant severe weather hazards.

This is a list of meteorology topics. The terms relate to meteorology, the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere that focuses on weather processes and forecasting.
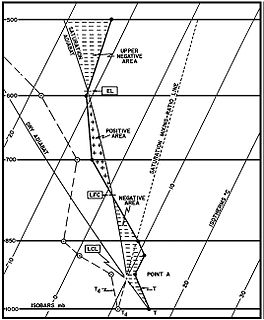
Convective inhibition is a numerical measure in meteorology that indicates the amount of energy that will prevent an air parcel from rising from the surface to the level of free convection.

In meteorology, convective instability or stability of an air mass refers to its ability to resist vertical motion. A stable atmosphere makes vertical movement difficult, and small vertical disturbances dampen out and disappear. In an unstable atmosphere, vertical air movements tend to become larger, resulting in turbulent airflow and convective activity. Instability can lead to significant turbulence, extensive vertical clouds, and severe weather such as thunderstorms.

The level of free convection (LFC) is the altitude in the atmosphere where the temperature of the environment decreases faster than the moist adiabatic lapse rate of a saturated air parcel at the same level.
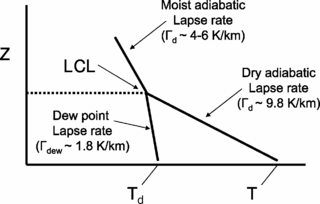
The lifted condensation level or lifting condensation level (LCL) is formally defined as the height at which the relative humidity (RH) of an air parcel will reach 100% with respect to liquid water when it is cooled by dry adiabatic lifting. The RH of air increases when it is cooled, since the amount of water vapor in the air remains constant, while the saturation vapor pressure decreases almost exponentially with decreasing temperature. If the air parcel is lifting further beyond the LCL, water vapor in the air parcel will begin condensing, forming cloud droplets. The LCL is a good approximation of the height of the cloud base which will be observed on days when air is lifted mechanically from the surface to the cloud base.
Atmospheric thermodynamics is the study of heat-to-work transformations that take place in the earth's atmosphere and manifest as weather or climate. Atmospheric thermodynamics use the laws of classical thermodynamics, to describe and explain such phenomena as the properties of moist air, the formation of clouds, atmospheric convection, boundary layer meteorology, and vertical instabilities in the atmosphere. Atmospheric thermodynamic diagrams are used as tools in the forecasting of storm development. Atmospheric thermodynamics forms a basis for cloud microphysics and convection parameterizations used in numerical weather models and is used in many climate considerations, including convective-equilibrium climate models.

An overshooting top is a dome-like protrusion shooting out of the top of the anvil of a thunderstorm and into the lower stratosphere. When an overshooting top is present for 10 minutes or longer, it is a strong indication that the storm is severe.

In meteorology, the equilibrium level (EL), or level of neutral buoyancy (LNB), or limit of convection (LOC), is the height at which a rising parcel of air is at the same temperature as its environment.
The convective condensation level (CCL) represents the height where an air parcel becomes saturated when heated from below and lifted adiabatically due to buoyancy.

The lifted index (LI) is the temperature difference between the environment Te(p) and an air parcel lifted adiabatically Tp(p) at a given pressure height in the troposphere of the atmosphere, usually 500 hPa (mb). The temperature is measured in Celsius. When the value is positive, the atmosphere is stable and when the value is negative, the atmosphere is unstable.

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.
The maximum parcel level (MPL) is the highest level in the atmosphere that a moist convectively rising air parcel will reach after ascending from the level of free convection (LFC) through the free convective layer (FCL) and reaching the equilibrium level (EL), near the tropopause. As the parcel rises through the FCL it expands adiabatically causing its temperature to drop, often below the temperature of its surroundings, and eventually lose buoyancy. Because of this, the EL is approximately the region where the distinct flat tops, often observed around the upper portions of cumulonimbus clouds. If the air parcel ascended quickly enough then it retains momentum after it has cooled and continues rising past the EL, ceasing at the MPL.

Atmospheric instability is a condition where the Earth's atmosphere is generally considered to be unstable and as a result the weather is subjected to a high degree of variability through distance and time. Atmospheric stability is a measure of the atmosphere's tendency to discourage or deter vertical motion, and vertical motion is directly correlated to different types of weather systems and their severity. In unstable conditions, a lifted thing, such as a parcel of air will be warmer than the surrounding air at altitude. Because it is warmer, it is less dense and is prone to further ascent.
The following is a glossary of tornado terms. It includes scientific as well as selected informal terminology.
A castellanus is a cloud that displays at least in its upper part cumuliform protuberances having the shape of turrets that give a crenellated aspect. Some of these turrets are higher than they are wide; they have a common base and seem to be arranged in a line. The castellanus characteristic is particularly obvious when the clouds are observed from the side.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.

A shower is a mode of precipitation characterized by an abrupt start and end and by rapid variations in intensity. Often strong and short-lived, it comes from convective clouds, like cumulus congestus. A shower will produce rain if the temperature is above the freezing point in the cloud, or snow/ice pellets/snow pellets if the temperature is below it at some point. In a meteorological observation, such as the METAR, they are noted SH giving respectively SHRA, SHSN, SHPL and SHGS.












