Related Research Articles

Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters.

Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic.

An acetylcholine receptor is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter.
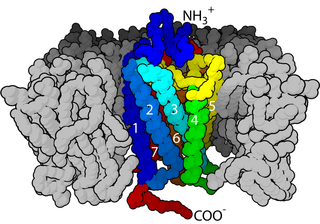
A neurotransmitter receptor is a membrane receptor protein that is activated by a neurotransmitter. Chemicals on the outside of the cell, such as a neurotransmitter, can bump into the cell's membrane, in which there are receptors. If a neurotransmitter bumps into its corresponding receptor, they will bind and can trigger other events to occur inside the cell. Therefore, a membrane receptor is part of the molecular machinery that allows cells to communicate with one another. A neurotransmitter receptor is a class of receptors that specifically binds with neurotransmitters as opposed to other molecules.

In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and produce physiological responses such as change in the electrical activity of a cell. For example, GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter inhibits electrical activity of neurons by binding to GABAA receptors. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway.
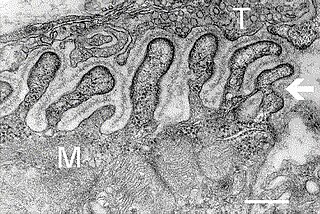
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.

Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system.

Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system.

Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter.

Jean-Pierre Changeux is a French neuroscientist known for his research in several fields of biology, from the structure and function of proteins, to the early development of the nervous system up to cognitive functions. Although being famous in biological sciences for the MWC model, the identification and purification of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and the theory of epigenesis by synapse selection are also notable scientific achievements. Changeux is known by the non-scientific public for his ideas regarding the connection between mind and physical brain. As put forth in his book, Conversations on Mind, Matter and Mathematics, Changeux strongly supports the view that the nervous system functions in a projective rather than reactive style and that interaction with the environment, rather than being instructive, results in the selection amongst a diversity of preexisting internal representations.
The Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel superfamily is composed of nicotinic acetylcholine, GABAA, GABAA-ρ, glycine, 5-HT3, and zinc-activated (ZAC) receptors. These receptors are composed of five protein subunits which form a pentameric arrangement around a central pore. There are usually 2 alpha subunits and 3 other beta, gamma, or delta subunits (some consist of 5 alpha subunits). The name of the family refers to a characteristic loop formed by 13 highly conserved amino acids between two cysteine (Cys) residues, which form a disulfide bond near the N-terminal extracellular domain.
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems.
A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine.

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7, also known as nAChRα7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA7 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of certain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAchR).

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-4, also known as nAChRα4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA4 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of certain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR). Alpha4-containing nAChRs appear to play a crucial role in the addictive response to nicotine..

Cell surface receptors are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral membrane proteins that allow communication between the cell and the extracellular space. The extracellular molecules may be hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, or nutrients; they react with the receptor to induce changes in the metabolism and activity of a cell. In the process of signal transduction, ligand binding affects a cascading chemical change through the cell membrane.
Dennis A. Dougherty is the George Grant Hoag Professor of Chemistry at California Institute of Technology. His research applies physical organic chemistry to systems of biological importance. Dougherty utilizes a variety of approaches to further our understanding of the human brain, including the in vivo nonsense suppression methodology for incorporating unnatural amino acids into a variety of ion channels for structure-function studies.
The alpha-3 beta-4 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α3β4 receptor and the ganglion-type nicotinic receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of α3 and β4 subunits. It is located in the autonomic ganglia and adrenal medulla, where activation yields post- and/or presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Na+ and K+ permeability.
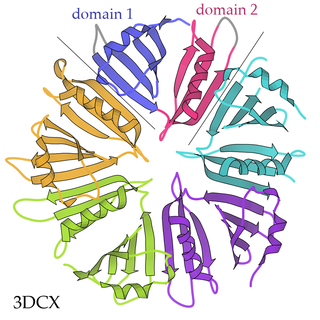
A pentameric protein is a quaternary protein structure that consists of five protein subunits.
Ionotropic GABA receptors (iGABARs) are ligand-gated ion channel of the GABA receptors class which are activated by gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and include:
References
- ↑ Tasneem A, Iyer L, Jakobsson E, Aravind L (2004). "Identification of the prokaryotic ligand-gated ion channels and their implications for the mechanisms and origins of animal Cys-loop ion channels". Genome Biology. 6 (1): R4. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-6-1-r4 . ISSN 1465-6906. PMC 549065 . PMID 15642096.
- ↑ Bocquet N, Nury H, Baaden M, Le Poupon C, Changeux JP, Delarue M, Corringer PJ (2009). "X-ray structure of a pentameric ligand-gated ion channel in an apparently open conformation". Nature. 457 (7225): 111–114. Bibcode:2009Natur.457..111B. doi:10.1038/nature07462. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 18987633. S2CID 4395028.
- ↑ Hilf RJ, Dutzler R (2009). "Structure of a potentially open state of a proton-activated pentameric ligand-gated ion channel". Nature. 457 (7225): 115–U122. Bibcode:2009Natur.457..115H. doi:10.1038/nature07461. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 18987630. S2CID 4365841.