
Cyclic nucleotide–gated ion channels or CNG channels are ion channels that function in response to the binding of cyclic nucleotides. CNG channels are nonselective cation channels that are found in the membranes of various tissue and cell types, and are significant in sensory transduction as well as cellular development. Their function can be the result of a combination of the binding of cyclic nucleotides and either a depolarization or a hyperpolarization event. Initially discovered in the cells that make up the retina of the eye, CNG channels have been found in many different cell types across both the animal and the plant kingdoms. CNG channels have a very complex structure with various subunits and domains that play a critical role in their function. CNG channels are significant in the function of various sensory pathways including vision and olfaction, as well as in other key cellular functions such as hormone release and chemotaxis. CNG channels have also been found to exist in prokaryotes, including many spirochaeta, though their precise role in bacterial physiology remains unknown.

Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, and/or Cl− to pass through the membrane in response to the binding of a chemical messenger (i.e. a ligand), such as a neurotransmitter.

Excitatory amino-acid transporter 4 (EAAT4) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A6 gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 also known as Kv1.1 is a shaker related voltage-gated potassium channel that in humans is encoded by the KCNA1 gene. Isaacs syndrome is a result of an autoimmune reaction against the Kv1.1 ion channel.

Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRPM3 gene.

P2X purinoceptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RX1 gene.

Neuropeptides B/W receptor 2, also known as NPBW2, is a human protein encoded by the NPBWR2 gene.

Prokineticin receptor 2 (PKR2), is a dimeric G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the PROKR2 gene in humans.

Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCN2 gene.
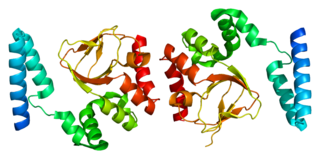
Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCN4 gene.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA3 gene.

Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCN1 gene.

P2X purinoceptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RX2 gene.
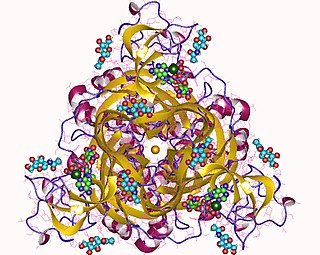
P2X purinoceptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the P2RX3 gene.

CHRNA7-FAM7A fusion protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRFAM7A gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shal-related subfamily, member 1 (KCND1), also known as Kv4.1, is a human gene.

Potassium/sodium hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channel 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HCN3 gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 10 also known as Kv1.8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNA10 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a voltage-gated potassium channel subunit.

Potassium channel subfamily T, member 2, also known as KCNT2 is a human gene that encodes the KNa protein. KCNT2, also known as the Slick channel is an outwardly rectifying potassium channel activated by internal raises in sodium or chloride ions.

CatSper2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CATSPER2 gene. CatSper2 is a member of the cation channels of sperm family of protein. The four proteins in this family together form a Ca2+-permeant ion channel specific essential for the correct function of sperm cells.
















