
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations. 5-HT is short for 5-hydroxy-tryptamine or serotonin. This is the main excitatory receptor subtype among the GPCRs for serotonin, although 5-HT2A may also have an inhibitory effect on certain areas such as the visual cortex and the orbitofrontal cortex. This receptor was first noted for its importance as a target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. Later it came back to prominence because it was also found to be mediating, at least partly, the action of many antipsychotic drugs, especially the atypical ones.
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems.
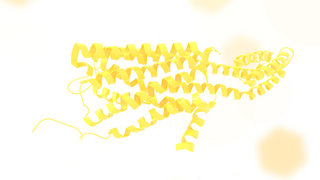
The 5-HT2C receptor is a subtype of 5-HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gq/G11 and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR2C denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor, that in humans is located at the X chromosome. As males have one copy of the gene and in females one of the two copies of the gene is repressed, polymorphisms at this receptor can affect the two sexes to differing extent.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR3A gene.

5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR4 gene.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptor, or 5-HT receptor, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarisation and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1B also known as the 5-HT1B receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR1B gene. The 5-HT1B receptor is a 5-HT receptor subtype.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D, also known as HTR1D, is a 5-HT receptor, but also denotes the human gene encoding it. 5-HT1D acts on the central nervous system, and affects locomotion and anxiety. It also induces vasoconstriction in the brain.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) 1E receptor (5-HT1E) is a highly expressed human G-protein coupled receptor that belongs to the 5-HT1 receptor family. The human gene is denoted as HTR1E.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1F, also known as HTR1F is a 5-HT1 receptor protein and also denotes the human gene encoding it.
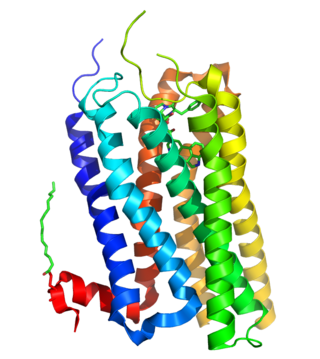
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (5-HT2B) also known as serotonin receptor 2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR2B gene. 5-HT2B is a member of the 5-HT2 receptor family that binds the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT).

5-Hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 5A, also known as HTR5A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR5A gene. Agonists and antagonists for 5-HT receptors, as well as serotonin uptake inhibitors, present promnesic (memory-promoting) and/or anti-amnesic effects under different conditions, and 5-HT receptors are also associated with neural changes.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.
In genetics, rs6313 also called T102C or C102T is a gene variation—a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)—in the human HTR2A gene that codes for the 5-HT2A receptor. The SNP is a synonymous substitution located in exon 1 of the gene where it is involved in coding the 34th amino acid as serine.
rs6295, also called C(-1019)G, is a gene variation—a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)—in the HTR1A gene. It is one of the most investigated SNPs of its gene. The C-allele is the most prevalent with 0.675 against the G-allele with 0.325 among Caucasian.
In genetics, rs6314, also called His452Tyr or H452Y, is a gene variation, a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), in the HTR2A gene that codes for the 5-HT2A receptor. The SNP is located in exon 3 of the gene and the change between C and T results in a change between histidine (His) and tyrosine (Tyr) at the 452nd amino acid, i.e., it is a missense substitution.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR3C gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the 5-HT3 receptor.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR3D gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the 5-HT3 receptor.

5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 3E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR3E gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the 5-HT3 receptor.














