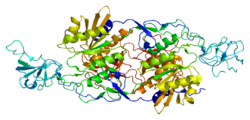
The glycine receptor is the receptor of the amino acid neurotransmitter glycine. GlyR is an ionotropic receptor that produces its effects through chloride current. It is one of the most widely distributed inhibitory receptors in the central nervous system and has important roles in a variety of physiological processes, especially in mediating inhibitory neurotransmission in the spinal cord and brainstem.

Hyperekplexia is a very rare neurologic disorder classically characterised by pronounced startle responses to tactile or acoustic stimuli and hypertonia. The hypertonia may be predominantly truncal, attenuated during sleep and less prominent after a year of age.

Gephyrin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPHN gene.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRG2 gene.

Glycine receptor subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLRA1 gene.

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-4, also known as nAChRα4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA4 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of certain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR). Alpha4-containing nAChRs appear to play a crucial role in the addictive response to nicotine..

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNB2 gene.

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-3, also known as nAChRα3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of certain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAchR). Research with mecamylamine in animals has implicated alpha-3-containing nAChRs in the abusive and addictive properties of ethanol.

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNB4 gene.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRB1 gene.

Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNB1 gene.

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-5, also known as nAChRα5, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA5 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of certain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAchR).

Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNB3 gene. This gene has been identified as a candidate for predisposition to tobacco dependence.

Sodium- and chloride-dependent glycine transporter 2, also known as glycine transporter 2 (GlyT2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A5 gene.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA4 gene.

Glycine receptor subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLRA2 gene.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit delta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRD gene. In the mammalian brain, the delta (δ) subunit forms specific GABAA receptor subtypes by co-assembly leading to δ subunit containing GABAA receptors.

Cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 6, also known as nAChRα6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CHRNA6 gene. The CHRNA6 gene codes for the α6 nicotinic receptor subunit that is found in certain types of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors found primarily in the brain. Neural nicotinic acetylcholine receptors containing α6 subunits are expressed on dopamine-releasing neurons in the midbrain, and dopamine release following activation of these neurons is thought to be involved in the addictive properties of nicotine. Due to their selective localisation on dopaminergic neurons, α6-containing nACh receptors have also been suggested as a possible therapeutic target for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. In addition to nicotine, research in animals has implicated alpha-6-containing nAChRs in the abusive and addictive properties of ethanol, with mecamylamine demonstrating a potent ability to block these properties.

The Glycine receptor subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLRA3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the glycine receptor.

The glycine receptor, alpha 4, also known as GLRA4, is a human pseudogene. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the glycine receptor.