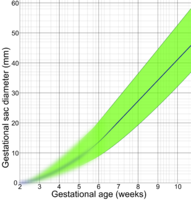
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals. It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregnancy can have one or more gestations at the same time, for example in a multiple birth.
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's birth weight percentile. The causes of IUGR are broad and may involve maternal, fetal, or placental complications.
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive.

Selective reduction is the practice of reducing the number of fetuses in a multiple pregnancy, such as quadruplets, to a twin or singleton pregnancy. The procedure is also called multifetal pregnancy reduction. The procedure is most commonly done to reduce the number of fetuses in a multiple pregnancy to a safe number, when the multiple pregnancy is the result of use of assisted reproductive technology; outcomes for both the mother and the babies are generally worse the higher the number of fetuses. The procedure is also used in multiple pregnancies when one of the fetuses has a serious and incurable disease, or in the case where one of the fetuses is outside the uterus, in which case it is called selective termination.

Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.
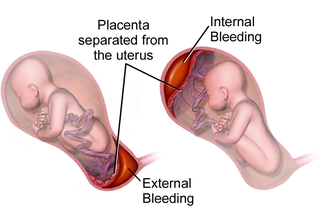
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth.
Fetal viability is the ability of a human fetus to survive outside the uterus. Medical viability is generally considered to be between 23 and 24 weeks gestational age. Viability depends upon factors such as birth weight, gestational age, and the availability of advanced medical care. In low-income countries, half of newborns born at or below 32 weeks gestational age died due a lack of medical access; in high-income countries, the vast majority of newborns born above 24 weeks gestational age survive.

Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestates) inside a woman's womb. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a spontaneous miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An embryo is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation, after which the term fetus is used until birth. Signs and symptoms of early pregnancy may include missed periods, tender breasts, morning sickness, hunger, and frequent urination. Pregnancy may be confirmed with a pregnancy test. Methods of birth control—or, more accurately, contraception—are used to avoid pregnancy.
Prenatal development includes the development of the embryo and of the foetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth.

Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis.

Human fertilization is the union of a human egg and sperm, occurring in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. The result of this union leads to the production of a zygote cell, or fertilized egg, initiating prenatal development. Scientists discovered the dynamics of human fertilization in the nineteenth century.
Postterm pregnancy is when a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the typical 40-week duration of pregnancy. Postmature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including fetal malnutrition, meconium aspiration syndrome, and stillbirths. After the 42nd week of gestation, the placenta, which supplies the baby with nutrients and oxygen from the mother, starts aging and will eventually fail. Postterm pregnancy is a reason to induce labor.
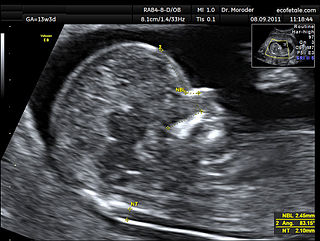
A nuchal scan or nuchal translucency (NT) scan/procedure is a sonographic prenatal screening scan (ultrasound) to detect chromosomal abnormalities in a fetus, though altered extracellular matrix composition and limited lymphatic drainage can also be detected.
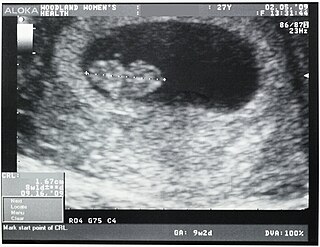
Crown-rump length (CRL) is the measurement of the length of human embryos and fetuses from the top of the head (crown) to the bottom of the buttocks (rump). It is typically determined from ultrasound imagery and can be used to estimate gestational age.

Velamentous cord insertion is a complication of pregnancy where the umbilical cord is inserted in the fetal membranes. It is a major cause of antepartum hemorrhage that leads to loss of fetal blood and associated with high perinatal mortality. In normal pregnancies, the umbilical cord inserts into the middle of the placental mass and is completely encased by the amniotic sac. The vessels are hence normally protected by Wharton's jelly, which prevents rupture during pregnancy and labor. In velamentous cord insertion, the vessels of the umbilical cord are improperly inserted in the chorioamniotic membrane, and hence the vessels traverse between the amnion and the chorion towards the placenta. Without Wharton's jelly protecting the vessels, the exposed vessels are susceptible to compression and rupture.
A fetus or foetus is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal development begins from the ninth week after fertilization and continues until birth. Prenatal development is a continuum, with no clear defining feature distinguishing an embryo from a fetus. However, a fetus is characterized by the presence of all the major body organs, though they will not yet be fully developed and functional and some not yet situated in their final anatomical location.
The estimated date of delivery (EDD), also known as expected date of confinement, and estimated due date or simply due date, is a term describing the estimated delivery date for a pregnant woman. Normal pregnancies last between 38 and 42 weeks. Children are delivered on their expected due date about 4% of the time.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to obstetrics:
Post-maturity syndrome develops in about 20% of human pregnancies continuing past the expected dates. Ten years ago it was generally held that the postmature fetus ran some risk of dying in the uterus before the onset of labour because of degeneration and calcification of the placenta. Features of post-maturity syndrome include oligohydramnios, meconium aspiration, macrosomia and fetal problems such as dry peeling skin, overgrown nails, abundant scalp hair, visible creases on palms and soles, minimal fat deposition and skin colour become green or yellow due to meconeum staining. Post-maturity refers to any baby born after 42 weeks gestation or 294 days past the first day of the mother's last menstrual period. Less than 6 percent of all babies are born at 42 weeks or later. In most cases, continued fetal growth between 39 and 43 wk gestation results in a macrosomic infant. However, sometimes the placenta involutes, and multiple infarcts and villous degeneration cause placental insufficiency syndrome. In this syndrome, the fetus receives inadequate nutrients and oxygen from the mother, resulting in a thin, small-for-gestational-age, undernourished infant with depleted glycogen stores. Post term, the amniotic fluid volume eventually decreases, leading to oligohydramnios. Although pregnancy is said to last nine months, health care providers track pregnancy by weeks and days. The estimated delivery date, also called the estimated due date or EDD, is calculated as 40 weeks or 280 days from the first day of the last menstrual period. Only 4 percent women will deliver on their due date. The terms Post-maturity or "Post-term" are both words used to describe babies born after 42 weeks. The terms "post-maturity" and "post-term" are interchangeable. As there are many definitions for prolonged pregnancy the incidence varies from 2 to 10%.When incidence is taken as delivery beyond 42 weeks it is 10%, if it is taken according to the delivered baby's weight and length it is 2%.The baby may have birth weight of 4kg and length of 54 cm but these findings are variable, even the baby may have underweight. Post-maturity is more likely to happen when a mother has had a post-term pregnancy before. After one post-term pregnancy, the risk of a second post-term birth increases by 2 to 3 times. Other, minor risk factors include an older or obese mother, a white mother, male baby, or a family history of post-maturity. Maternal risks include obstructed labor, perennial damage, instrumental vaginal delivery, a Cesarean section, infection, and post postpartum hemorrhage. Accurate pregnancy due dates can help identify babies at risk for post-maturity. Ultrasound examinations early in pregnancy help establish more accurate dating by measurements taken of the fetus. Pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes, hypertension, or other high-risk conditions should be managed according to guidelines for those conditions.

Prenatal nutrition addresses nutrient recommendations before and during pregnancy. Nutrition and weight management before and during pregnancy has a profound effect on the development of infants. This is a rather critical time for healthy development since infants rely heavily on maternal stores and nutrient for optimal growth and health outcome later in life.