Interstate 70 (I-70) is a major east–west Interstate Highway in the United States that runs from I-15 near Cove Fort, Utah, to a park and ride lot just east of I-695 in Baltimore, Maryland, and is the fifth-longest Interstate in the country. I-70 approximately traces the path of U.S. Route 40 east of the Rocky Mountains. West of the Rockies, the route of I-70 was derived from multiple sources. The Interstate runs through or near many major cities, including Denver, Topeka, Kansas City, St. Louis, Indianapolis, Columbus, Pittsburgh, and Baltimore. The sections of the Interstate in Missouri and Kansas have laid claim to be the first Interstate in the United States. The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) has claimed the section of I-70 through Glenwood Canyon, Colorado, completed in 1992, to be the last piece of the Interstate Highway System, as originally planned, to open to traffic. The construction of I-70 in Colorado and Utah is considered an engineering marvel, as the route passes through the Eisenhower Tunnel, Glenwood Canyon, and the San Rafael Swell. The Eisenhower Tunnel is the highest point along the Interstate Highway System, with an elevation of 11,158 feet (3,401 m).
Interstate 64 (I-64) is an east–west Interstate Highway in the Eastern United States. Its western terminus is at I-70, U.S. Route 40 (US 40), and US 61 in Wentzville, Missouri. Its eastern terminus is at an interchange with I-264 and I-664 at Bower's Hill in Chesapeake, Virginia. I-64 connects the major metropolitan areas of St. Louis, Missouri; Louisville and Lexington in Kentucky; Charleston, West Virginia; and Richmond and Hampton Roads in Virginia. At 953.74 miles (1,534.90 km), I-64 is the second longest Interstate Highway not ending with a 5 or 0, after I-94.
Interstate 77 (I-77) is a north–south Interstate Highway in the eastern United States. It traverses diverse terrain, from the mountainous state of West Virginia to the rolling farmlands of North Carolina and Ohio. It largely supplants the old US Route 21 (US 21) between Cleveland, Ohio, and Columbia, South Carolina, as an important north–south corridor through the middle Appalachians. The southern terminus of I-77 is in Cayce, South Carolina in Lexington County at the junction with I-26. The northern terminus is in Cleveland at the junction with I-90. Other major cities that I-77 connects to include Charlotte, North Carolina; Charleston, West Virginia; and Akron, Ohio. The East River Mountain Tunnel, connecting Virginia and West Virginia, is one of only two instances in the United States where a mountain road tunnel crosses a state line. The other is the Cumberland Gap Tunnel, connecting Tennessee and Kentucky. I-77 is a snowbird route to the Southern United States for those traveling from the Great Lakes region.

Bon Air is a census-designated place (CDP) in Chesterfield County, Virginia, United States. The population was 16,366 at the 2010 census. The community is considered a suburb of the independent city of Richmond in the Richmond-Petersburg region and is a part of the Southside neighborhoods. Originally developed as a resort, a central portion of Bon Air has been designated as a National Historic District with many structures of Victorian design from the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its name means "good air," reflecting its role as a resort getaway that wealthy Richmonders enjoyed for its fresh air as opposed to the dirty air of Richmond's industrial downtown of the late 19th century.
Florida's Turnpike, designated as unsigned State Road 91, is a toll road in the U.S. state of Florida, maintained by Florida's Turnpike Enterprise (FTE). Spanning approximately 309 miles (497 km) along a northwest–southeast axis, the turnpike is in two sections. The SR 91 mainline runs roughly 265 miles (426 km), from its southern terminus at an interchange with Interstate 95 (I-95) in Miami Gardens to an interchange with I-75 in Wildwood at its northern terminus. The Homestead Extension of Florida's Turnpike continues from the southern end of the mainline for another 48 miles (77 km) to US Highway 1 in Florida City. The slogan for the road is "The Less Stressway". The mainline opened in stages between 1957 and 1964, while the extension was completed in 1974. The turnpike runs through Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and West Palm Beach, where it parallels I-95, and through Orlando, where it crosses I-4.
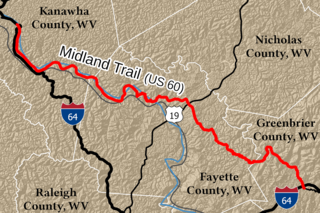
The Midland Trail is a National Scenic Byway which carries U.S. Route 60 (US 60) through a portion of the southern part of the U.S. state of West Virginia between Charleston and Sam Black Church. It was part of the longer transcontinental Midland Trail.

West Virginia Route 97 is an east–west state highway in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The western terminus of the route is at U.S. Route 52 and West Virginia Route 80 in Hanover. The eastern terminus is at exit 42 of the West Virginia Turnpike in Mabscott. West Virginia Route 16, which runs concurrent with WV 97 between Sophia and Mabscott, continues north into Beckley on Robert C. Byrd Drive, the right-of-way of both WV 16 and WV 97.

Transportation in the Commonwealth of Virginia is by land, sea and air. Virginia's extensive network of highways and railroads were developed and built over a period almost 400 years, beginning almost immediately after the founding of Jamestown in 1607, and often incorporating old established trails of the Native Americans.
State Road 826 is a bypass route around the greater Miami area, traveling approximately 30 miles (48 km) in a northeasterly arc from U.S. Route 1 in Pinecrest to its terminus at State Road A1A in Sunny Isles Beach. Between its southern terminus and the Golden Glades Interchange, State Road 826 is known as the Palmetto Expressway, a heavily traveled freeway with portions of the road carrying in excess of 250,000 vehicles a day. Unlike many of the other non-interstate freeways in Miami-Dade County, the Palmetto Expressway is untolled. East of the interchange, State Road 826 is a surface road connecting North Miami and North Miami Beach to Sunny Isles Beach over the Intracoastal Waterway.

Providence Forge is an unincorporated community in New Kent County, Virginia, United States. It was one of the earliest settlements in the county and the site of a colonial iron forge that was destroyed by British General Banastre Tarleton during the American Revolutionary War.
U.S. Route 50 is a transcontinental highway which stretches from Ocean City, Maryland to West Sacramento, California. In the U.S. state of Virginia, US 50 extends 86 miles (138 km) from the border with Washington, D.C. at a Potomac River crossing at Rosslyn in Arlington County to the West Virginia state line near Gore in Frederick County.
Interstate 77 (I-77) in the US state of West Virginia is a major north–south Interstate Highway. It extends for 187.21 miles (301.29 km) between Bluefield at the Virginia state line and Williamstown at the Ohio state line.
Interstate 64 (I-64) is an Interstate Highway in the US state of West Virginia. It travels through the state for 184 miles (296 km) passing by the major towns and cities of Huntington, Charleston, Beckley, and Lewisburg.
U.S. Route 60 (US 60) in the Commonwealth of Virginia runs 303 miles (488 km) west to east through the central part of the state, generally close to and paralleling the Interstate 64 corridor, except for the crossing of the Blue Ridge Mountains, and in the South Hampton Roads area.
Interstate 81 (I-81) is an 855.02-mile-long (1,376.02 km) Interstate Highway. In the US state of Virginia, I-81 runs for 324.92 miles (522.91 km), making the portion in Virginia longer than any other state's portion. It is also the longest Interstate Highway within the borders of Virginia. It stretches from the Tennessee state line near Bristol to the West Virginia state line near Winchester. It enters Virginia from Bristol, Tennessee, and leaves Virginia into Berkeley County, West Virginia.

Winterplace Ski Resort is a ski resort located in Ghent, West Virginia on Raleigh County's Flat Top Mountain. The southernmost ski resort in West Virginia, Winterplace is a popular attraction due to its proximity to Interstate 77. It operates in conjunction with The Resort at Glade Springs, a four season golf resort and spa.
In Oklahoma, U.S. Highway 62 (US 62) runs diagonally across the state, from the Texas state line in far southwestern Oklahoma to the Arkansas state line near Fayetteville. US-62 spends a total of 402.48 miles (647.73 km) in the Sooner State. The highway passes through fifteen of Oklahoma's counties. Along the way the route serves two of Oklahoma's largest cities, Lawton and Oklahoma City, as well as many regionally important cities, like Altus, Chickasha, Muskogee, and Tahlequah. Despite this, US-62 has no lettered spur routes like many other U.S. routes in Oklahoma do.
Sharon is an unincorporated community and coal town in southeastern Kanawha County, West Virginia, United States, located along the West Virginia Turnpike.

The Center for National Response is located inside a former 2,802 feet (854 m) two-lane vehicular tunnel opened November 8, 1954 as part of the West Virginia Turnpike. Originally known as Memorial Tunnel, the tunnel formerly carried West Virginia Turnpike through/under Paint Creek Mountain in Standard, West Virginia in Kanawha County. Its construction required the movement of 91,000 cubic yards (70,000 m3) of earth, and was the first tunnel in the nation to have closed-circuit television monitoring. at a final cost of $5 million. The facility is administered by the West Virginia National Guard.
Linda K. Epling Stadium is a baseball field in Beckley, West Virginia. It opened in 2010. The field was built by the Epling family after it sold out its interests in the coal business. The stadium seats 2,500. It is used by the West Virginia Miners of the Prospect League and the WVU Tech Golden Bears. The facility has also been the home to select games of the Marshall University baseball team from 2010–18, and was the home for select West Virginia University games in 2012 and 2013.








