
Charleston is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of West Virginia. Located at the confluence of the Elk and Kanawha rivers, the city had a population of 51,400 at the 2010 census and an estimated population of 47,215 in 2018. The Charleston metropolitan area as a whole had an estimated 211,037 residents in 2018. Charleston is the center of government, commerce, and industry for Kanawha County, of which it is the county seat.

The Virginian Railway was a Class I railroad located in Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The VGN was created to transport high quality "smokeless" bituminous coal from southern West Virginia to port at Hampton Roads.

The Norfolk and Western Railway was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America". During the Civil War, the N&W was the largest railroad in the Confederacy and played an important role in moving supplies for the war effort.

The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad (1852–1983) which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation.
The Battle of Matewan was a shootout in the town of Matewan in Mingo County and the Pocahontas Coalfield mining district, in southern West Virginia. It occurred on May 19, 1920 between local coal miners and the Baldwin–Felts Detective Agency.

Cass Scenic Railroad State Park is a state park located in Cass, Pocahontas County, West Virginia.

Fairfax Stone Historical Monument State Park is a West Virginia state park commemorating the Fairfax Stone, a surveyor's marker and boundary stone at the source of the North Branch of the Potomac River. The original stone was placed on October 23, 1746 to settle a boundary dispute between Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron and the English Privy Council concerning the Northern Neck of Virginia. It determined the proprietorship and boundaries of a large tract of mostly unsurveyed land in the English colonies of Maryland and Virginia.
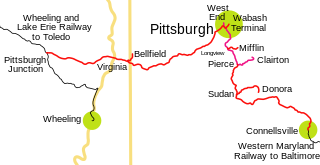
The Pittsburgh and West Virginia Railway was a railroad in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania and Wheeling, West Virginia, areas. Originally built as the Wabash Pittsburgh Terminal Railway, a Pittsburgh extension of George J. Gould's Wabash Railroad, the venture entered receivership in 1908 and the line was cut loose. An extension completed in 1931 connected it to the Western Maryland Railway at Connellsville, Pennsylvania, forming part of the Alphabet Route, a coalition of independent lines between the Northeastern United States and the Midwest. It was leased by the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1964 in conjunction with the N&W acquiring several other sections of the former Alphabet Route, but was leased to the new spinoff Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway in 1990, just months before the N&W was merged into the Norfolk Southern Railway.
The Richmond and Alleghany Railroad was built along the James River along the route of the James River and Kanawha Canal from Richmond on the Fall Line at the head of navigation to a point west of Lynchburg near Buchanan, Virginia, and combined with the Buchanan and Clifton Forge Railway Company to reach Clifton Forge, Virginia.

Pipestem Resort State Park is a 4,050-acre (1,640 ha) state park located in southern West Virginia, on the border between Mercer and Summers counties. The park was built with grants provided by the Area Redevelopment Administration of the U.S. Department of Commerce under the administration of President John F. Kennedy. It is located in the gorge of the Bluestone River.

The steamship Virginia V is the last operational example of a Puget Sound Mosquito Fleet steamer. She was once part of a large fleet of small passenger and freight carrying ships that linked the islands and ports of Puget Sound in Washington State in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. She is a Seattle landmark and a National Historic Landmark.
Nelson Evans Whitaker was an American businessman and politician, principally in the state of West Virginia.

The Sinks of Gandy — also called the Sinks of Gandy Creek, or simply "The Sinks" — are a modestly celebrated cave and underground stream at Osceola in eastern Randolph County, West Virginia, United States. The Sinks are on private property adjacent to Monongahela National Forest.

Hu Maxwell was a local historian, novelist, editor, poet, and author of several histories of West Virginia counties.
Virginia Congressional District 19 is an obsolete congressional district in Virginia. It was created in 1793 after the 1790 U.S. Census and was eliminated in 1843 after the 1840 U.S. Census. Its last Congressman was George W. Summers.

Vandalia was the name in the late 1700s of a proposed British colony in North America. The colony would have been located south of the Ohio River, primarily in what are now West Virginia and northeastern Kentucky.
Frontier West Virginia, Inc. is one of the original Bell Operating Companies and provides local telephone service in the U.S. state of West Virginia.
The Coal and Coke Railway was a railway operated by the Coal and Coke Railway Company in central West Virginia between 1905 and 1916. The line was made up of branches acquired from other companies and new construction. It ran from Elkins, West Virginia at its northeastern terminus, to Charleston, West Virginia at its southwestern terminus. Gassaway, West Virginia was roughly the halfway point in the railway's approximate length of 196 miles.

Howard Llewellyn Swisher was an American businessperson, real estate developer, orchardist, editor, writer, and historian. As a prominent businessman, he established several companies responsible for the development of businesses and real estate in Morgantown, West Virginia.















