
Gamma-glutamyltransferase is a transferase that catalyzes the transfer of gamma-glutamyl functional groups from molecules such as glutathione to an acceptor that may be an amino acid, a peptide or water. GGT plays a key role in the gamma-glutamyl cycle, a pathway for the synthesis and degradation of glutathione as well as drug and xenobiotic detoxification. Other lines of evidence indicate that GGT can also exert a pro-oxidant role, with regulatory effects at various levels in cellular signal transduction and cellular pathophysiology. This transferase is found in many tissues, the most notable one being the liver, and has significance in medicine as a diagnostic marker.

Transglutaminases are enzymes that in nature primarily catalyze the formation of an isopeptide bond between γ-carboxamide groups ( -(C=O)NH2 ) of glutamine residue side chains and the ε-amino groups ( -NH2 ) of lysine residue side chains with subsequent release of ammonia ( NH3 ). Lysine and glutamine residues must be bound to a peptide or a protein so that this cross-linking (between separate molecules) or intramolecular (within the same molecule) reaction can happen. Bonds formed by transglutaminase exhibit high resistance to proteolytic degradation (proteolysis). The reaction is
Cysteine metabolism refers to the biological pathways that consume or create cysteine. The pathways of different amino acids and other metabolites interweave and overlap to creating complex systems.
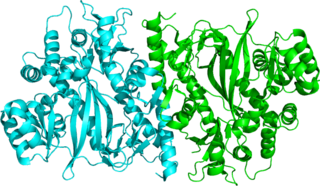
Glutathione synthetase (GSS) is the second enzyme in the glutathione (GSH) biosynthesis pathway. It catalyses the condensation of gamma-glutamylcysteine and glycine, to form glutathione. Glutathione synthetase is also a potent antioxidant. It is found in many species including bacteria, yeast, mammals, and plants.
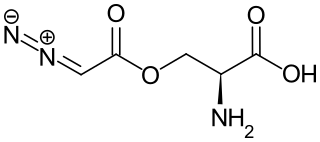
Azaserine is a naturally occurring serine derivative diazo compound with antineoplastic and antibiotic properties deriving from its action as a purinergic antagonist and structural similarity to glutamine. Azaserine acts by competitively inhibiting glutamine amidotransferase, a key enzyme responsible for glutamine metabolism.
Glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL) EC 6.3.2.2), previously known as γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS), is the first enzyme of the cellular glutathione (GSH) biosynthetic pathway that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
In enzymology, a glutamate-putrescine ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathionylspermidine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.94) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutathionylspermidine amidase (EC 3.5.1.78) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Glutathione S-transferase, C-terminal domain is a structural domain of glutathione S-transferase (GST).

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 (GGT1), also known as CD224, is a human gene.

Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 4 regulatory subunit 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP4R1 gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGT7 gene.

Gamma-glutamyltransferase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGT5 gene.
4-(γ-Glutamylamino)butanoic acid is molecule that consists of L-glutamate conjugated to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). It is the substrate of the enzyme γ-glutamyl-γ-aminobutyrate hydrolase, which is involved in the biosynthesis of polyamines.

Neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 (NCEH) also known as arylacetamide deacetylase-like 1 (AADACL1) or KIAA1363 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NCEH1 gene.
Endo-α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase (EC 3.2.1.97, endo-α-acetylgalactosaminidase, endo-α-N-acetyl-D-galactosaminidase, mucinaminylserine mucinaminidase, D-galactosyl-3-(N-acetyl-α-D-galactosaminyl)-L-serine mucinaminohydrolase, endo-α-GalNAc-ase, D-galactosyl-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine D-galactosyl-N-acetyl-galactosaminohydrolase) is an enzyme with systematic name glycopeptide-D-galactosyl-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine D-galactosyl-N-acetyl-galactosaminohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Ghk.
Leukotriene-C4 hydrolase (EC 3.4.19.14, gamma-glutamyl leukotrienase) is an enzyme. Gamma-glutamyltransferase 5 (GGT5) is a human gene which encodes an enzyme protein that belongs to this class of enzymes. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction










