
Gloucester County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 38,711. Its county seat is Gloucester Courthouse. The county was founded in 1651 in the Virginia Colony and is named for Henry Stuart, Duke of Gloucester.

Caroline County is a United States county located in the eastern part of the Commonwealth of Virginia. The northern boundary of the county borders on the Rappahannock River, notably at the historic town of Port Royal. The Caroline county seat is Bowling Green.

Tappahannock is the oldest town in Essex County, Virginia, United States. The population was 2,375 at the 2010 census, up from 2,068 at the 2000 census. Located on the Rappahannock River, Tappahannock is the county seat of Essex County. Its name comes from an Algonquian language word lappihanne, meaning "Town on the rise and fall of water" or "where the tide ebbs and flows." The Rappahannock is a tidal estuary from above this point and downriver to its mouth on Chesapeake Bay.

Mechanicsville is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Hanover County, Virginia, United States. The population was 39,482 during the 2020 census, up from 36,348 in the 2010 census.

The George Washington Birthplace National Monument is a national monument in Westmoreland County, Virginia, at the confluence of Popes Creek and the Potomac River. It commemorates the birthplace location of George Washington, a Founding Father and the first President of the United States, who was born here on February 22, 1732. Washington lived at the residence until age three and later returned to live there as a teenager.
The Greater Richmond, Virginia area has many neighborhoods and districts.

Westover Plantation is a historic colonial tidewater plantation located on the north bank of the James River in Charles City County, Virginia. Established in c. 1730–1750, it is the homestead of the Byrd family of Virginia. State Route 5, a scenic byway, runs east–west to the north of the plantation, connecting the independent cities of Richmond and Williamsburg.

Piscataway is an unincorporated community in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. It is one of the oldest European-colonized communities in the state. The Piscataway Creek provided sea transportation for export of tobacco. It is located near the prior Piscataway tribe village of Kittamaqundi.

York River State Park is located near the unincorporated town of Croaker in James City County, Virginia on the south bank of the York River about 10 miles downstream from West Point.

The Mattaponi tribe is one of only two Virginia Indian tribes in the Commonwealth of Virginia that owns reservation land, which it has held since the colonial era. The larger Mattaponi Indian Tribe lives in King William County on the reservation, which stretches along the borders of the Mattaponi River, near West Point, Virginia.
Tsenacommacah is the name given by the Powhatan people to their native homeland, the area encompassing all of Tidewater Virginia and parts of the Eastern Shore. More precisely, its boundaries spanned 100 miles (160 km) by 100 miles (160 km) from near the south side of the mouth of the James River all the way north to the south end of the Potomac River and from the Eastern Shore west to about the Fall Line of the rivers.

Hanover is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Hanover County, Virginia, United States. It is the county seat and is located at the junction of U.S. Route 301 and State Route 54 south of the Pamunkey River. While historically known as Hanover Courthouse, the U.S. Geological Survey, Census Bureau, Postal Service and residents refer to it as "Hanover". The population as of the 2010 census was 252.

Scotchtown is a plantation located in Hanover County, Virginia, that from 1771 to 1778 was owned and used as a residence by U.S. Founding Father Patrick Henry, his wife Sarah and their children. He was a revolutionary and elected in 1778 as the first Governor of Virginia. The house is located in Beaverdam, Virginia, 10 miles (16 km) northwest of Ashland, Virginia on VA 685. The house, at 93 feet (28 m) by 35 feet (11 m), is one of the largest 18th-century homes to survive in the Americas. In its present configuration, it has eight substantial rooms on the first floor surrounding a central passage, with a full attic above and English basement with windows below. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965.
Pamunkey Regional Library serves the counties of Goochland, Hanover, King and Queen, and King William, and the towns of Ashland and West Point in central Virginia.

Broad Creek in Prince George's County was the first footprint of European settlement in the immediate counties around what would become the nation's capital, Washington, D.C. The area is part of greater Fort Washington.
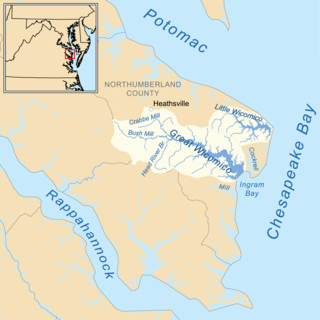
The Wicocomico were an Algonquian-speaking tribe who lived in Northumberland County, Virginia, at the head and slightly north of the Little Wicomico River.

Windsor Shades is located on the Pamunkey River in Sweet Hall, Virginia, United States. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Archeological native artifacts found on the property surrounding the house suggest it was the site of Kupkipcok, a Pamunkey village noted on John Smith's 1609 map.

The Tobacco Inspection Act of 1730 was a 1730 law of the Virginia General Assembly designed to improve the quality of tobacco exported from Colonial Virginia. Proposed by Virginia Lieutenant Governor Sir William Gooch, the law was far-reaching in impact in part because it gave warehouses the power to destroy substandard crops and issue bills of exchange that served as currency. The law centralized the inspection of tobacco at 40 locations described in the law.

Fort Mattapony/Ryefield is a historic archaeological site located near Walkerton, King and Queen County, Virginia. The Fort Mattapony/Ryefield archeological sites, which has been dated archeologically to the fourth quarter of the 17th century, are located in a one-acre area on prominent grassy hilltop overlooking the Mattaponi River, Walkerton and Locust Grove. Collectively designated 44KQ7 in Virginia's official inventory of archeological sites, the site consists of two closely associated components, the Fort Mattapony storehouse and a domestic structure called Ryefield. After abandonment of the fort at the close of the 17th century and the domestic structure by the mid-18th century, a later colonial plantation, Locust Grove, developed in the surrounding area, which continues to be occupied by descendants.
Cumberland was an unincorporated town in New Kent County in the U.S. state of Virginia that almost became the capital of Virginia colony in 1748.





















