
Washington Crossing State Park is a 3,575-acre (14 km2) New Jersey state park that is part of Washington's Crossing, a U.S. National Historic Landmark area. It is located in the Washington Crossing and Titusville sections of Hopewell Township in Mercer County, north of Trenton along the Delaware River. The park is operated and maintained by the New Jersey Division of Parks and Forestry. It is supported by the Washington Crossing Park Association, a friends group that works to preserve, enhance, and advocate for the park.

The Hatchie River is a 238-mile-long (383 km) river in northern Mississippi and southwestern Tennessee. It is of considerable geographic, cultural, and historic significance. In large measure this is because it is the only major river of West Tennessee that has never been impounded, channelized, or otherwise modified by human activity to any major degree, although several of its tributaries have. Its environs are indicative of what much of West Tennessee must have resembled prior to the time of European settlement in early 19th century.

Titusville is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) located within Hopewell Township in Mercer County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The area includes a post office with its own ZIP Code (08560), several restaurants, gas stations, a firehouse, and a small cluster of homes. The Washington Crossing State Park, dedicated to George Washington's crossing of the Delaware River in 1776, is adjacent to the community.

The Battle of Hatchie's Bridge, also known as Battle of Davis Bridge or Matamora, was fought on October 5, 1862, in Hardeman County and McNairy County, Tennessee, as the final engagement of the Iuka–Corinth Campaign of the American Civil War. Confederate Major General Earl Van Dorn's army successfully evaded capture by the Union Army, following his defeat at the Battle of Corinth.
The National Register of Historic Places in the United States is a register including buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects. The Register automatically includes all National Historic Landmarks as well as all historic areas administered by the U.S. National Park Service. Since its introduction in 1966, more than 90,000 separate listings have been added to the register.

The Siege and Battle of Corinth Sites are a National Historic Landmark District encompassing surviving elements of three significant American Civil War engagements in and near Corinth, Mississippi. Included are landscape and battlefield features of the Siege of Corinth, the Second Battle of Corinth, and the lesser Battle of Hatchie's Bridge on October 5, 1862. The district includes features located in both Alcorn County, Mississippi and Hardeman County, Tennessee, with some of the former preserved as part of Shiloh National Military Park. It was designated a landmark in 1991.

This is a list of properties and historic districts in Washington that are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. There are at least three listings in each of Washington's 39 counties.
This is a list of properties and historic districts in Tennessee that are listed on the National Register of Historic Places. There are over 2,000 in total. Of these, 29 are National Historic Landmarks. Each of Tennessee's 95 counties has at least one listing.

Knights Ferry is an unincorporated historic community in Stanislaus County, California, United States. Nestled in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada, it is about 30 miles (48 km) east of Modesto on the Stanislaus River. The Williams Ranch near the town was one of many filming locations for the television series Bonanza and Little House on the Prairie.

State Road 2 is a former east–west state highway in the Arkansas Timberlands and Lower Arkansas Delta. The route was approximately 195 miles (314 km), and ran from US Route 67 (US 67) in Texarkana east to cross the Mississippi River near Lake Village, continuing as Mississippi Highway 10. On July 1, 1931, the route was entirely replaced by US Highway 82 (US 82) by the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHTO). The route was maintained by the Arkansas Highway Department (AHD), now known as the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT).

State Route 261 (SR 261) is a 62.71-mile-long (100.92 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Washington. Serving Columbia, Franklin, and Adams counties, the highway begins at U.S. Route 12 (US 12) east of Starbuck and becomes concurrent with SR 260 from Kahlotus to SR 26 in Washtucna before ending at Interstate 90 (I-90) and US 395 in Ritzville. The highway has been legislated since 1937 from Ritzville to Washtucna as Secondary State Highway 11E (SSH 11E) and in 1957 from Washtucna to the Starbuck area as a branch of SSH 11B. The two secondary highways became SR 261 during the 1964 highway renumbering, and a gap between Washtucna and Starbuck was not paved until the construction of the Snake River Bridge was completed in 1968.

Yuma Crossing is a site in Arizona and California that is significant for its association with transportation and communication across the Colorado River. It connected New Spain and Las Californias in the Spanish Colonial period in and also during the Western expansion of the United States. Features of the Arizona side include the Yuma Quartermaster Depot and Yuma Territorial Prison. Features on the California Side include Fort Yuma, which protected the area from 1850 to 1885.
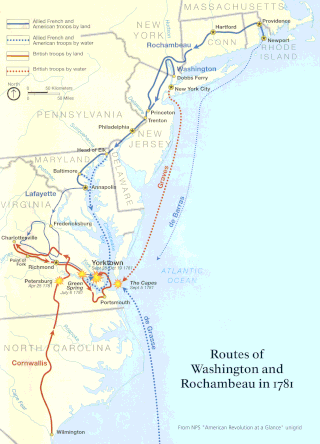
The Washington–Rochambeau Revolutionary Route is a 680-mile (1,090 km) series of roads used in 1781 by the Continental Army under the command of George Washington and the Expédition Particulière under the command of Jean-Baptiste de Rochambeau during their 14-week march from Newport, Rhode Island to Yorktown, Virginia. 4,000 French and 3,000 American soldiers began the march.

The High Hills of Santee, sometimes known as the High Hills of the Santee, is a long, narrow hilly region in the western part of Sumter County, South Carolina. It has been called "one of the state's most famous areas". The High Hills of Santee region lies north of the Santee River and east of the Wateree River, one of the two rivers that join to form the Santee. It extends north almost to the Kershaw county line and northeasterly to include the former summer resort town of Bradford Springs. Since 1902 the town has been included in Lee County.

The Casselman Bridge is an historic transportation structure on the Casselman River, located immediately east of Grantsville in Garrett County, Maryland. The bridge was built in 1813-1814 as part of the National Road. Historic markers posted at each end read:
Erected 1813 by David Shriver, Jr.,
Sup't of the "Cumberland Road". This 80 foot span
was the largest stone arch in America
at the time. It was continuously
used from 1813 to 1933.

The B & O Railroad Potomac River Crossing is a 15-acre (6.1 ha) historic site where a set of railroad bridges, originally built by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad, span the Potomac River between Sandy Hook, Maryland and Harpers Ferry, West Virginia. The site was added to the National Register of Historic Places on February 14, 1978, for its significance in commerce, engineering, industry, invention, and transportation.

The Rocks Village Historic District is a historic district in eastern Haverhill, Massachusetts. It encompasses a dense community of 25 mainly residential structures at the western end of the Rocks Village Bridge, an early crossing point of the Merrimack River, of which 15 date to the 18th century. The village is significant for its association with the poet John Greenleaf Whittier, who was born nearby, and for the artwork of Rufus Porter, found in one of the houses. The area was designated a local historic district in 1975, and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.

Blue Hills Parkway is a historic parkway that runs in a straight line from a crossing of the Neponset River, at the south border of Boston to the north edge of the Blue Hills Reservation in Milton, Massachusetts. It was built in 1893 to a design by the noted landscape architect, Charles Eliot, who is perhaps best known for the esplanades along the Charles River. The parkway is a connecting road between the Blue Hills Reservation and the Neponset River Reservation, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2003.

Spring Mill is an unincorporated community in Whitemarsh Township, Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, United States.

The Bradley Covered Bridge is a historic covered bridge, carrying Center Street over Miller Run, a tributary of the Passumpsic River, in Lyndon, Vermont. Built in 1878, it is the last of Vermont's many 19th-century covered bridges to carry a numbered state highway. The bridge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977.




















