Hermitage, The Hermitage or L'Hermitage may refer to:
The Greater Richmond, Virginia area has many neighborhoods and districts.
Arthur Ashe Boulevard is a historic street in the near the West End of Richmond, Virginia, providing access to Byrd Park. It serves as the border between the Carytown/Museum District to the west and the Fan district to the east. Attempts were made to rename the street after Arthur Ashe, a tennis star and social activist who was born and grew up in Richmond, but previous attempts failed until February 2019 when Richmond City Council voted in favor of changing the name to Arthur Ashe Boulevard. Near the south end is Richmond's Boulevard Bridge across the James River. Arthur Ashe Boulevard intersects with main arteries Cary Street, Main Street, Monument Avenue, Broad Street, Leigh Street, and Interstate 64/95, and terminates at Hermitage Road. The Diamond is located on Arthur Ashe Boulevard. The intersection of Arthur Ashe Boulevard and Monument Avenue featured a statue of Stonewall Jackson.
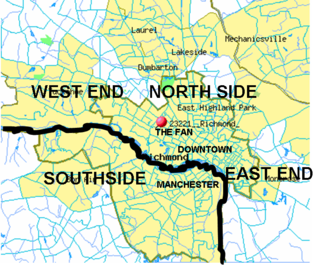
The Northside is an area composed of northern Richmond, Virginia and some parts of Henrico County, Virginia.

The C.F. Sauer Company is a cooking products business that makes extracts and other food products. It was founded in 1887 by Conrad Frederick Sauer in Richmond, Virginia, where it maintains its headquarters.

Hermitage Road Historic District (HRHD) is a Northside neighborhood in the independent city of Richmond, Virginia. The district is a Richmond Old and Historic District, as well as being listed on the Virginia Landmarks Register and the National Register of Historic Places.

Shockoe Bottom historically known as Shockoe Valley, is an area in Richmond, Virginia, just east of downtown, along the James River. Located between Shockoe Hill and Church Hill, Shockoe Bottom contains much of the land included in Colonel William Mayo's 1737 plan of Richmond, making it one of the city's oldest neighborhoods.

Shockoe Slip is a district in the downtown area of Richmond, Virginia. The name "slip" referred to a narrow passageway leading from Main Street to where goods were loaded and unloaded from the former James River and Kanawha Canal. The rough boundaries of Shockoe Slip include 14th Street, Main Street, Canal Street and 12th Street.

Downtown Norfolk serves as the traditional center of commerce, government, and culture in the Hampton Roads region. Norfolk, Virginia's downtown waterfront shipping and port activities historically played host to numerous and often noxious port and shipping-related uses. With the advent of containerized shipping in the mid-19th century, the shipping uses located on Norfolk's downtown waterfront became obsolete as larger and more modern port facilities opened elsewhere in the region. The vacant piers and cargo warehouses eventually became a blight on downtown and Norfolk's fortunes as a whole. But in the second half of the century, Norfolk had a vibrant retail community in its suburbs; companies like Smith & Welton, High's, Colonial Stores, Goldman's Shoes, Lerner Shops, Hofheimer's, Giant Open Air, Dollar Tree and K & K Toys were regional leaders in their respective fields. Norfolk was also the birthplace of Econo-Travel, now Econo Lodge, one of the nation's first discount motel chains.

Jobbers Canyon Historic District was a large industrial and warehouse area comprising 24 buildings located in downtown Omaha, Nebraska, US. It was roughly bound by Farnam Street on the north, South Eighth Street on the east, Jackson Street on the south, and South Tenth Street on the west. In 1989, all 24 buildings in Jobbers Canyon were demolished, representing the largest National Register historic district loss to date.

The Lower Basin Historic District is a national historic district located in Lynchburg, Virginia. The district defines a commercial and industrial warehouse area located between the downtown commercial area to the south and the James River waterfront to the north. The district contains a variety of mostly late 19th- and early 20th-century, multi-story, brick warehouses and factories, two-to-three-story brick commercial buildings, and a number of structures associated with the James River and Kanawha Canal and the Norfolk and Western and Chesapeake and Ohio Railways. The district is named for a wide basin of the canal that once extended between Ninth Street and Horseford Road, and contains 60 contributing buildings, two contributing structures, and one contributing object-a monument commemorating the site of 18th-century Lynch's Ferry.

The Buckingham Historic District is a national historic district located at Arlington County, Virginia. It contains 151 contributing buildings in a residential neighborhood in North Arlington. They were built in six phases between 1937 and 1953, and primarily consist of two- and three-story, brick garden apartment buildings in the Colonial Revival-style. There is a single three-story brick building that was built in the International style. The buildings are arranged around U-shaped courtyards. The district also includes a community center, four single family dwellings, three commercial buildings and two commercial blocks.

The Carver Industrial Historic District is a national historic district located at Carver, Richmond, Virginia. The district encompasses 13 contributing buildings located west of downtown Richmond. The industrial area developed between 1890 and 1930, along the tracks of the Richmond, Fredericksburg and Potomac Railroad. The buildings are in a variety of popular 19th-century and early 20th century architectural styles including Queen Anne and Romanesque.

The Laburnum Park Historic District is a national historic district located at Richmond, Virginia. The district encompasses 226 contributing buildings and 2 contributing structures located north of downtown Richmond. The primarily residential area developed starting in the early-20th century as one of the city's early "streetcar suburbs" and as home to several important local institutions. The buildings are in a variety of popular early-20th century architectural styles including Queen Anne and Colonial Revival. It was developed as neighborhood of middle-to-upper-class, single-family dwellings. Notable buildings include the Laburnum House (1908), Richmond Memorial Hospital (1954-1957), Richmond Memorial Hospital Nursing School (1960-1961), "The Hermitage" (1911), Laburnum Court (1919), Veritas School.

The Brookland Park Historic District is a national historic district located at Richmond, Virginia. The district encompasses 1,157 contributing buildings located north of downtown Richmond and Barton Heights.

The Scott's Addition Historic District is a national historic district located in Richmond, Virginia.

Salem Avenue–Roanoke Automotive Commercial Historic District is a national historic district located of Roanoke, Virginia. It encompasses 59 contributing buildings in the southwestern part of the City of Roanoke. The district includes a variety of buildings having automotive, warehouse, light industrial and residential uses. Most of the buildings are small-scale, one or two-story brick or concrete block buildings, with the majority built between about 1920 and 1954. Notable buildings include the former Enfield Buick Dealership, Lindsay-Robinson & Co. Building (1918), Fulton Motor Company Auto Sales & Service (1928), Lacy Edgerton Motor Company, Roanoke Motor Car Company, and Fire Department No. 3 (1909).

Shockoe Valley is an area in Richmond, Virginia, just east of downtown, along the James River, and is the entertainment center of the city. Located between Shockoe Hill and Church Hill, Shockoe Valley contains much of the land included in Colonel William Mayo's 1737 plan of Richmond, making it one of the city's oldest neighborhoods. Shockoe Valley encompasses the smaller neighborhoods of Shockoe Slip, Shockoe Bottom and Tobacco Row along Cary Street.

The Williamston–Woodland Historic District encompasses a light industrial area of Norfolk, Virginia. It is roughly bounded by Omohundro Avenue on the west, 18th Street on the south, Church Street on the east, and the Norfolk and Southern Railroad tracks to the north. The area was developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and features a mix of architectural styles, from modest commercial styles to Moderne and Art Deco structures. Most of the buildings are either warehouses or light industrial plants, ranging in height from one to three stories. The land for much of this area was owned by Theodorick Williams prior to its development.

The American Tobacco Company, South Richmond Complex Historic District encompasses a complex of tobacco storage, processing, and research facilities at 400-800 Jefferson Davis Highway in Richmond, Virginia. Included in the 16-acre (6.5 ha) site are four large warehouses, processing buildings including a stemmery and a re-drying plant, and ancillary buildings and structures, including the American Tobacco Company's 1939 research laboratory. The complex exhibits a historical range of trends in the processing and storage of tobacco.




















