
The giant freshwater stingray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is found in large rivers and estuaries in Southeast Asia and Borneo, though historically it may have been more widely distributed in South and Southeast Asia. The largest freshwater fish and the largest stingray in the world, this species grows up to 2.2 m (7.2 ft) across and can reach up to 300 kg (660 lb) in weight. It has a relatively thin, oval pectoral fin disc that is widest anteriorly, and a sharply pointed snout with a protruding tip. Its tail is thin and whip-like, and lacks fin folds. This species is uniformly grayish brown above and white below; the underside of the pectoral and pelvic fins bear distinctive wide, dark bands on their posterior margins.

The white-edge freshwater whipray is an extremely rare species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, native to four river systems in Southeast Asia. Measuring up to 60 cm (24 in) across, this ray has an oval pectoral fin disc and a very long, whip-like tail without fin folds. It can be identified by the presence of a sharply delineated white band running around the margin of its otherwise brown disc, as well as by its white tail and a band of dermal denticles along the middle of its back. This species feeds on benthic invertebrates and is aplacental viviparous. Its two long tail spines are potentially dangerous to humans. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed the white-edge freshwater whipray as Endangered, as it is under heavy pressure from fishing and habitat loss, degradation, and fragmentation.

Urogymnus is a genus of stingrays in the family Dasyatidae from marine, brackish and freshwater habitats in the Indo-Pacific and tropical East Atlantic regions. The genus was previously considered to be monotypic, containing only the porcupine ray. Molecular phylogenetic research published in 2016 reassigned several species from Himantura to Urogymnus.

The whitespotted whipray or sharpnose stingray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is found in coastal regions including estuaries, in the Indo-Pacific, and has also been recorded in the Ganges River. It reaches a maximum disc width of 2 m (6.6 ft). As presently defined, it is probably a species complex.

The whiptail stingrays are a family, the Dasyatidae, of rays in the order Myliobatiformes. They are found worldwide in tropical to temperate marine waters, and a number of species have also penetrated into fresh water in Africa, Asia, and Australia. Members of this family have flattened pectoral fin discs that range from oval to diamond-like in shape. Their common name comes from their whip-like tails, which are much longer than the disc and lack dorsal and caudal fins. All whiptail stingrays, except the porcupine ray, have one or more venomous stings near the base of the tail, which is used in defense. In order to sting their victims, they jerk their tails as the stinger falls off and stays in the wound that they have created. The stinger of a whiptail stingray is pointy, sharp with jagged edges. They range in size from 0.18 to 2.0 m or more across in the case of the smalleye stingray and giant freshwater stingray.

The reticulate whipray or honeycomb stingray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It inhabits coastal waters in the western Indian Ocean including the Red Sea, Natal and the Arabian Sea; also a Lessepsian transmigrant in the eastern Mediterranean. A large species reaching 2 m (6.6 ft) in width, the reticulate whipray has a diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and an extremely long tail without fin folds. Both its common and scientific names refer to its ornate dorsal color pattern of many small, close-set dark spots or reticulations on a lighter background. However, the reticulate whipray is only one of several large spotted stingrays in the Indo-Pacific which, coupled with the variability of its coloration with age and locality, has resulted in a great deal of taxonomic confusion.

The pink whipray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, with a wide but ill-defined distribution in the tropical Indo-Pacific from southern Africa to Polynesia. It is a bottom dweller that generally inhabits shallow water under 70 m (230 ft) deep, in sandy areas associated with coral reefs. Individuals exhibit a high degree of fidelity to particular locations. The pink whipray has a diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc wider than long, with a broad-angled snout and a very long, whip-like tail without fin folds. It has only a few small thorns on its back and is uniform brownish to grayish pink in color, becoming much darker past the tail sting. This large ray can reach 1.8 m (5.9 ft) across and over 5 m (16 ft) long.

The Jenkins' whipray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, with a wide distribution in the Indo-Pacific region from South Africa to the Malay Archipelago to northern Australia. This large species grows to 1.5 m (4.9 ft) across and has a broad, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and a whip-like tail without fin folds. It has a band of heart-shaped dermal denticles running from between the eyes to the tail on its upper surface, along with a characteristic row of large spear-like thorns along the midline. It is uniform yellowish brown above, becoming grayish on the tail past the stinging spine, and white below; there is apparently a spotted color variant that had previously been described as a different species, the dragon stingray.
The tubemouth whipray is a little-known species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, named for its distinctive, highly protrusible jaws. It is found in shallow, brackish water near mangrove forests and large river mouths along the coasts of southwestern Borneo and southern Sumatra. Measuring up to 1 m (3.3 ft) across, this species has a diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc with an elongated, pointed snout and broadly rounded outer corners. The upper surface of the disc is a plain grayish or brownish in color, and covered by small, flattened dermal denticles. The tubemouth whipray is relatively common at present, but is heavily pressured by habitat degradation and coastal fisheries. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has listed it as Vulnerable.
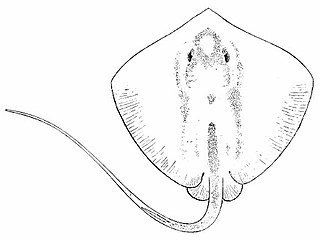
Himantura alcockii, the pale-spot whip ray, is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is found in coastal regions including estuaries, in the Indian Ocean. As presently defined, it is probably a species complex.
The Hortle's whipray is a little-known species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, occurring in shallow estuaries and mud flats off southern New Guinea. This species, growing to 71 cm (28 in) across, has a heart-shaped pectoral fin disc with a long, pointed snout and minute eyes. It has a wide dorsal band of dermal denticles extending from in front of the eyes to the tail, as well as scattered sharp denticles on the snout. The underside of the disc is a distinctive bright yellow in color, sometimes with darker markings around the nostrils, mouth, and gill slits. The Hortle's whipray is threatened by extensive seine fisheries and habitat degradation, leading the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) to assess it as Near Threatened.

The black-spotted whipray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, found in the coastal waters off southern New Guinea and northern Australia. Long thought to be a variant of the related brown whipray, this species has an angular, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and a whip-like tail without fin folds. It is characterized by its dorsal color pattern, which consists of a variably extensive covering of small, close-set dark, and sometimes also white spots, on a grayish-brown background. In addition, the tail has alternating light and dark saddles past the stinging spine. This species reaches a maximum recorded width of 80 cm (31 in).

The brown whipray is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, common in inshore, muddy habitats along the northern coast of Australia. It has often been confused in literature for the honeycomb stingray and the black-spotted whipray, which until recently was thought to be the same species. This species has an angular, diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc and a long, very thin tail without fin folds. It is plain brown above, sometimes with white dots or flecks near the edge of the disc, and white below; the tail is dark all over, with alternating dark and light bands near the tip. The maximum recorded disc width is 74 cm (29 in).

The leopard whipray is a little-known species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae, found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans from the Andaman Sea to the Coral Triangle. It is found close to shore at depths shallower than 70 m (230 ft), over soft substrates. Attaining a width of 1.8 m (5.9 ft), this species has a diamond-shaped pectoral fin disc with a pointed snout and an extremely long, whip-like tail without fin folds. Adult rays have a leopard-like dorsal pattern of dark brown rings on a yellowish brown background, as well as a row of enlarged, heart-shaped dermal denticles along the midline of the disc. Newborns and small juveniles have large, solid dark spots and few denticles. The leopard whipray is caught by fisheries in many parts of its range, primarily for meat.

Brevitrygon is a genus of stingrays in the family Dasyatidae from the Indo-Pacific. Its species were formerly contained within the genus Himantura.

Fluvitrygon is a genus of stingrays in the family Dasyatidae from freshwater in southeast Asia. Its species were formerly contained within the genus Himantura.

Maculabatis is a genus of stingrays in the family Dasyatidae from the Indo-Pacific. Its species were formerly contained within the genus Himantura.

Pateobatis is a genus of stingrays in the family Dasyatidae from the Indo-Pacific. Its species were formerly contained within the genus Himantura.
The Arabian banded whipray, is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is native to the Persian Gulf. It reaches a length of 41.2 cm (16.2 in).
Maculabatis ambigua, Baraka's whipray, is a species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. It is found in the Western Indian Ocean: from the Red Sea south to Tanzania and the island of Zanzibar. This species reaches a length of 90 cm (35 in).














