
The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes.

Andesite is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende.

Mount Bailey is a relatively young tephra cone and shield volcano in the Cascade Range, located on the opposite side of Diamond Lake from Mount Thielsen in southern Oregon, United States. Bailey consists of a 2,000-foot (610 m)-high main cone on top of an old basaltic andesite shield volcano. With a volume of 8 to 9 km3, Mount Bailey is slightly smaller than neighboring Diamond Peak. Mount Bailey is a popular destination for recreational activities. Well known in the Pacific Northwest region as a haven for skiing in the winter months, the mountain's transportation, instead of a conventional chairlift, is provided by snowcats—treaded, tractor-like vehicles that can ascend Bailey's steep, snow-covered slopes and carry skiers to the higher reaches of the mountain. In the summer months, a 5-mile (8 km) hiking trail gives foot access to Bailey's summit. Mount Bailey is one of Oregon's Matterhorns.

Mount Washington is a deeply eroded volcano in the Cascade Range of Oregon. It lies within Deschutes and Linn counties and is surrounded by the Mount Washington Wilderness area.

Manam, known locally as Manam Motu, is an island located in the Bismarck Sea across the Stephan Strait from Yawar on the northeast coast of mainland Papua New Guinea's Bogia District. The island is 10 kilometers (6.2 mi) wide, and was created by the activity of the Manam Volcano, one of the country’s most active. The island was evacuated in 2004 and its residents resettled elsewhere in Papua New Guinea, but many have begun to return despite concerns of future volcanic activity. Manam is still erupting as of January 2024.
The andesite line is the most significant regional geologic distinction in the Pacific Ocean basin. It separates the mafic basaltic volcanic rocks of the Central Pacific Basin from the partially submerged continental areas of more felsic andesitic volcanic rock on its margins. The andesite line parallels the subduction zones and deep oceanic trenches around the Pacific basin. It is the surface expression of melting within and above the plunging subducting slab. It follows the western edge of the islands off California and passes south of the Aleutian Arc, along the eastern edge of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the Kuril Islands, Japan, the Mariana Islands, Yap, Palau, the Solomon Islands, Fiji, Tonga, and New Zealand's North Island. The dissimilarity continues northeastward along the western edge of the Andes mountains of South America to Mexico, returning then to the islands off California. Indonesia, the Philippines, Japan, New Guinea, and New Zealand lie outside the andesite line.

Mount Price is a small stratovolcano in the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It has an elevation of 2,049 metres and rises above the surrounding landscape on the western side of Garibaldi Lake in New Westminster Land District. The mountain contains a number of subfeatures, including Clinker Peak on its western flank, which was the source of two thick lava flows between 15,000 and 8,000 years ago that ponded against glacial ice. These lava flows are structurally unstable, having produced large landslides as recently as the 1850s. A large provincial park surrounds Mount Price and other volcanoes in its vicinity. It lies within an ecological region that surrounds much of the Pacific Ranges.

The Table, sometimes called Table Mountain, is a 2,021-metre (6,631 ft) high flow-dominated andesite tuya located 4 kilometres (2 mi) south of Garibaldi Lake, 15 kilometres (9 mi) northeast of Cheekye and 5 kilometres (3 mi) north of Mount Garibaldi, British Columbia, Canada. It rises over 530 metres (1,740 ft) above the surface of Garibaldi Lake, which lies less than 1 kilometre (1 mi) to the north.

In volcanology, a pyroclastic shield or ignimbrite shield is an uncommon type of shield volcano. Unlike most shield volcanoes, pyroclastic shields are formed mostly of pyroclastic and highly explosive eruptions rather than relatively fluid basaltic lava issuing from vents or fissures on the surface of the volcano. They typically display low-angle flank slopes and often have a central caldera caused by large eruptions. Lava is commonly extruded after explosive activity has ended. The paucity of associated Plinian fall deposits indicates that pyroclastic shields are characterized by low Plinian columns.

West Crater is a small lava dome with associated lava flows in southern Washington, United States. Located in Skamania County, it rises to an elevation of 4,131 feet (1,259 m), and forms part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It is also part of the Marble Mountain-Trout Creek Hill volcanic field, a little-known Quaternary volcanic field in the southern Cascades of Washington state. The area can be hiked, and can be accessed by roads in the Gifford Pinchot National Forest.
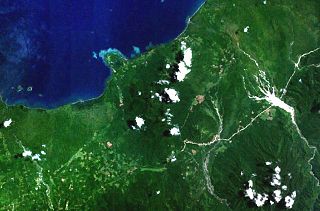
The Sulu Range is a small volcanic mountain range on the Papua New Guinean island of New Britain. It consists of a group of partially overlapping small stratovolcanoes and lava domes, with the highest point being 610 m (2,000 ft) Mount Malopu at the southwestern end of the range. Kaiamu, a maar at the northwestern end of the Sulu Range, forms a peninsula with a small lake extending about 1 km (0.62 mi) into Bangula Bay. Other volcanoes in the range include Mount Ululu, Mount Ruckenberg, Mount Talutu and Mount Ubia.

Pelican Butte is a steep-sided shield volcano in the Cascade Range of southern Oregon. It is located 28 miles (45 km) due south of Crater Lake and 12 miles (19 km) northeast of Mount McLoughlin. Pelican Butte is the most prominent shield volcano in the southern Oregon Cascades and has a large volume at 4.8 cubic miles (20 km3), making it one of the bigger Quaternary volcanoes in the region, approaching the size of some of the range's stratovolcanoes. While still part of the Cascades, Pelican Butte is disconnected from the main axis, forming above faults along the eastern border of the range. Pelican Butte is part of the Quaternary Mount McLoughlin Reach, a volcanic vent zone that runs from the volcano to Aspen Lake, encompassing 33 vents over an area of 357 square miles (925 km2). Ice age glaciers carved a large cirque into the northeast flank of the mountain, but despite this erosion, its original shape is largely preserved. Several proposals have been made over the last few decades for the development of a ski area on this flank, but none have been implemented.

The Twin Buttes are two volcanic cinder cones located in the Cascade Mountain Range in Shasta County, California. They are part of the Bidwell Spring chain and lie within a region that was active in the Quaternary. Formed during the Pleistocene between 25,000 and 15,000 years ago, the volcanoes erupted lava flows that coursed toward the Burney Mountain lava dome. These lava flows cover an area of 3.9 square miles (10.1 km2) and are made of basalt and dacite. The volcanoes also erupted cinder and volcanic ash that reached eastward.

The Canadian Cascade Arc, also called the Canadian Cascades, is the Canadian segment of the North American Cascade Volcanic Arc. Located entirely within the Canadian province of British Columbia, it extends from the Cascade Mountains in the south to the Coast Mountains in the north. Specifically, the southern end of the Canadian Cascades begin at the Canada–United States border. However, the specific boundaries of the northern end are not precisely known and the geology in this part of the volcanic arc is poorly understood. It is widely accepted by geologists that the Canadian Cascade Arc extends through the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. However, others have expressed concern that the volcanic arc possibly extends further north into the Kitimat Ranges, another subdivision of the Coast Mountains, and even as far north as Haida Gwaii.
Mount Trafalgar is an extinct volcano on the north east coast of Oro Province, Papua New Guinea. The mountain is a major andesite volcano, with the magma known for its high levels of Nickel and Chromium. Captain John Moresby named the mountain after the naval battle of Trafalgar.
Mount Victory is an active volcano on the north east coast of Oro Province, Papua New Guinea with an approximate height of 1,884 metres (6,181 ft) to 1,891 metres (6,204 ft). It is bounded by the Ajova River.

Chipmunk Mountain is a mountain in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located 23 km (14 mi) southwest of Bralorne. It has an elevation of 2,390 m (7,840 ft) and a topographic prominence of 540 m (1,770 ft), making it the highest point on an east-trending screed ridge. This horn-like rocky tower is similar to The Black Tusk in Garibaldi Provincial Park.
Crevasse Crag is a jagged steep-sided prominence on the summit of a glaciated mountain ridge in the Lillooet Ranges of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located about 49 km (30 mi) southeast of the village of Pemberton. Situated on the boundary between New Westminster Land District and Kamloops Division Yale Land District, the peak has a maximum elevation of 2,496 m (8,189 ft) and a topographic prominence of 66 m (217 ft).
The geology of El Salvador is underlain by rocks dating to the Paleozoic. Prior to the Pennsylvanian, sediments deposited and were intensely deformed, intruded by granite rocks and metamorphosed. Northern Central America took shape during uplift in the Triassic, large than its current area and extending east to the Nicaragua Rise. The Cayman Ridge and Bartlet Trough formed from longitudinal faults at the crest of the uplift. Deformation in the Cretaceous brought granite intrusions, particularly in what is now Nicaragua. Much of the terrain and coastline of the country is defined by volcanoes and volcanic deposits produced from the subduction of the Cocos Plate.
The Bearwallow Mountain Andesite or Bearwallow Mountain Formation is a geologic formation exposed in and around the Mogollon Mountains of southwest New Mexico. It has a radiometric age of 27 to 23 million years, corresponding to the late Oligocene to early Miocene epochs.














