Rail transport in Switzerland is noteworthy for the density of its network, its coordination between services, its integration with other modes of transport, timeliness and a thriving domestic and trans-Alp freight system. It is made necessary by strong regulations on truck transport, and is enabled by properly coordinated intermodal logistics.

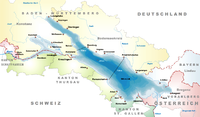
The Alpine Rhine Valley is a glacial alpine valley, formed by the Alpine Rhine, the part of the Rhine between the confluence of the Anterior Rhine and Posterior Rhine at Reichenau and Lake Constance. It covers three countries, with sections of the river demarcating the borders between Austria and Switzerland and between Liechtenstein and Switzerland. The full length of the Alpine Rhine is 93.5 km.

Lustenau is a town in the westernmost Austrian state of Vorarlberg in the district of Dornbirn. It lies on the river Rhine, which forms the border with Switzerland. Lustenau is Vorarlberg's fourth largest town.

High Rhine is the name of the part of the Rhine between Lake Constance and the city of Basel, flowing in a general east-to-west direction and forming mostly the Germany–Switzerland border. It is the first of four named sections of the Rhine between Lake Constance and the river delta at the North Sea.

Köln Hauptbahnhof is the central railway station of Cologne, Germany. The station is an important local, national and international transport hub, with many ICE, Eurostar and Intercity trains calling there, as well as regional Regional-Express, RegionalBahn and local S-Bahn trains. EuroNight and Nightjet night services also call at the station. It has frequent connections to Frankfurt by way of the Cologne–Frankfurt high-speed rail line, which starts in southern Cologne. On an average day, about 280,000 travellers frequent the station, making it the fifth busiest station in Germany.

Bingen (Rhein) Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the German city of Bingen am Rhein on the West Rhine Railway. It is located in the borough of Bingerbrück. The station that serves central Bingen is called Bingen Stadt.
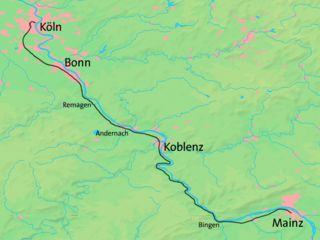
The West Rhine railway is a famously picturesque, double-track electrified railway line running for 185 km from Cologne via Bonn, Koblenz, and Bingen to Mainz. It is situated close to the western (left) bank of the river Rhine and mostly aligned to allow 160 km/h operation between Cologne and Koblenz and between Bingen and Mainz. Line speed between Koblenz and Bingen is restricted by the meandering nature of the Rhine Gorge, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The East Rhine Railway is a major, double-track, electrified railway line, running along the right bank of the Rhine from Cologne to Wiesbaden. The 179-kilometer (111.2 mi)-long line forms two Deutsche Bahn routes. Route 465 extends from Cologne to Koblenz, via Troisdorf, Bonn-Beuel, Unkel, and Neuwied. From Koblenz, Route 466 extends to Wiesbaden, via Rüdesheim am Rhein. Together with the Taunus railway, the line is used by Stadt-Express line SE-10 of the Rhine-Main Transport Association, which runs from Frankfurt to Koblenz and Neuwied.

The Main-Neckar Railway is a main line railway west of the Odenwald in the Upper Rhine Plain of Germany that connects Frankfurt am Main to Heidelberg via Darmstadt, Bensheim and Weinheim. It was opened in 1846 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany.
The Rhine-Main Railway, is a railway line in southern Germany from Mainz via Darmstadt to Aschaffenburg. It was built by the Hessian Ludwig Railway and opened on 1 August 1858 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany. Until 1862, when the railway bridge over the Rhine river constructed and assembled by MAN-Werk Gustavsburg was finished, a train ferry operated on the river.

The Oberhausen–Arnhem railway is a two-track, electrified main line railway running close to the lower Rhine from Oberhausen via Wesel, Emmerich and the German–Dutch border to Arnhem and forms part of the line between the Ruhr and Amsterdam. The line was opened by the Cologne-Minden Railway Company in 1856 and is one of the oldest lines in Germany.

The Lahntal railway or Lahn Valley Railway is a railway line between Niederlahnstein in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate to Wetzlar in Hesse, partly following the Lahn valley (Lahntal). Its western terminus was originally in Oberlahnstein. Trains now mostly operate between Koblenz and Gießen. The line was opened by the Nassau Rhine and Lahn Railway Company and the Nassau State Railway between 1858 and 1863 and is one of the oldest railways in Germany.

The Alter Rhein is the old river bed of the Alpine Rhine in St. Gallen and Vorarlberg in the Alpine Rhine Valley, which was cut off when the Rhine was straightened during the 20th century. These cut-off arms have become valuable recreational areas and a nature reserve.

The Mainz bypass railway is a bypass around the Mainz Hauptbahnhof node primarily used for freight in the German states of Hesse and Rhineland Palatinate.

Frankfurt-Sindlingen station is a suburban station on the network of the Rhine-Main S-Bahn in the district of Sindlingen in the German city of Frankfurt. The station is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 5 station.
A number of narrow-gauge lines survive, largely as a consequence of German reunification, in the former East Germany where some of them form part of the public transport system as active commercial carriers. Most extensive of those still employing steam traction is the Harz mountain group of metre-gauge lines, the Harzer Schmalspurbahnen. Other notable lines are the Zittau–Oybin–Jonsdorf line in Saxony, the Mollibahn and the Rügensche Kleinbahn on the Isle of Rügen on the Baltic coast and the Radebeul-Radeburg line, Weisseritztalbahn in the suburbs of Dresden. Although most rely on the tourist trade, in some areas they provide significant employment as steam traction is particularly labour-intensive.

The Regulation of the Rhine or Rhine Correction, refers to the canalisation of the Alpine Rhine on the border between Austria and Switzerland in the late 19th/early 20th century. Its aim was to reduce the risk of flooding and to re-route the international border which ran along the old course of the Rhine.

The St. Margrethen–Lauterach line is a 9.580-kilometre (5.953 mi) long, part single part double tracked, electrified railway line in the Alpine Rhine Valley, near Lake Constance. The route is owned and operated by Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB) and is mainly used by the border station in St. Margrethen.