The International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association (ILGA) is an organization which is committed to advancing human rights to all people, disregarding gender identity, sex characteristics and expression. ILGA participates in a multitude of agendas within the United Nations, such as creating visibility for LGBTI issues by conducting advocacy and outreach at the Human Rights Council, working with members to help their government improve LGBTI rights, ensuring LGBTI members are not forgotten in international law, and advocating for LBTI women's issues at the Commission on the Status of Women.

The Organisation Intersex International (OII) is a global advocacy and support group for people with intersex traits. According to Milton Diamond, it is the world's largest organization of intersex persons. A decentralised network, OII was founded in 2003 by Curtis Hinkle and Sarita Vincent Guillot. Upon Hinkle's retirement, American intersex activist Hida Viloria served as Chairperson/President elect from April 2011 through November 2017, when they resigned in order to focus on OII's American affiliate, OII-USA's transition into the independent American non-profit, the Intersex Campaign for Equality.
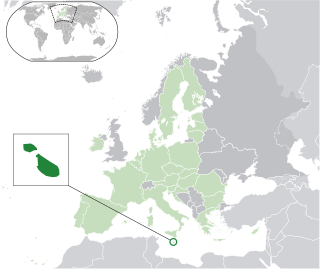
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Malta rank among the highest in the world. Throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the rights of the LGBT community received more awareness and same-sex sexual activity was legalized on 29 January 1973. The prohibition was already dormant by the 1890s.

In law, sex characteristic refers to an attribute defined for the purposes of protecting individuals from discrimination due to their sexual features. The attribute of sex characteristics was first defined in national law in Malta in 2015. The legal term has since been adopted by United Nations, European, and Asia-Pacific institutions, and in a 2017 update to the Yogyakarta Principles on the application of international human rights law in relation to sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression and sex characteristics.

Intersex people are individuals born with any of several sex characteristics including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies".

Intersex Human Rights Australia (IHRA) is a voluntary organisation for intersex people that promotes the human rights and bodily autonomy of intersex people in Australia, and provides education and information services. Established in 2009 and incorporated as a charitable company in 2010, it was formerly known as Organisation Intersex International Australia, or OII Australia. It is recognised as a Public Benevolent Institution.

The International Intersex Forum is an annual event organised, then later supported, by the ILGA and ILGA-Europe that and organisations from multiple regions of the world, and it is believed to be the first and only such intersex event.

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics, such as chromosomes, gonads, or genitals, that, according to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies."
Ruth Baldacchino is an LGBT and intersex activist, former Co-Secretary General of the International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association, and Senior Program Officer for the first intersex human rights fund.

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics, such as chromosomes, gonads, or genitals that, according to the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies".

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics, such as chromosomes, gonads, or genitals that, according to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies". "Because their bodies are seen as different, intersex children and adults are often stigmatized and subjected to multiple human rights violations".

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics that "do not fit the typical definitions for male or female bodies". They are substantially more likely to identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender (LGBT) than endosex people, an estimated 52% identifying as non-heterosexual and 8.5% to 20% experiencing gender dysphoria. Although many intersex people are heterosexual and cisgender, this overlap and "shared experiences of harm arising from dominant societal sex and gender norms" has led to intersex people often being included under the LGBT umbrella, with the acronym sometimes expanded to LGBTI. Some intersex activists and organisations have criticised this inclusion as distracting from intersex-specific issues such as involuntary medical interventions.

The following is a timeline of intersex history.

Intersex rights in Australia are protections and rights afforded to intersex people through statutes, regulations, and international human rights treaties, including through the Sex Discrimination Act 1984 (Cth) which makes it unlawful to discriminate against a person based upon that person's intersex status in contexts such as work, education, provision of services, and accommodation.

The Malta declaration is the statement of the Third International Intersex Forum, which took place in Valletta, Malta, in 2013. The event was supported by the ILGA and ILGA-Europe and brought together 34 people representing 30 organisations from multiple regions of the world.

Intersex people in Germany have legal recognition of their rights to physical integrity and bodily autonomy, with exceptions, but no specific protections from discrimination on the basis of sex characteristics. In response to an inquiry by the German Ethics Council in 2012, the government passed legislation in 2013 designed to classify some intersex infants as a de facto third category. The legislation has been criticized by civil society and human rights organizations as misguided.

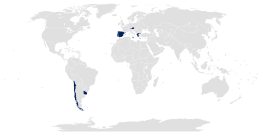
Since November 7, 2023, Chile bans unnecessary and non-consensual surgeries, procedures or medical treatments on intersex newborns, boys, girls and adolescents. Since March 15, 2022, Chile bans discrimination based on "sex characteristics" under Law 21,430 on Guarantees and Integral Protection of the Rights of Children and Adolescents. The country has the most advanced legal protection framework in Latin America.
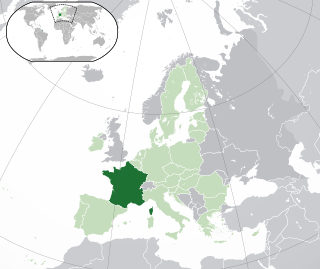
Intersex people in France face significant gaps in protection from non-consensual medical interventions and protection from discrimination. The birth of Abel Barbin, a nineteenth-century intersex woman, is marked in Intersex Day of Remembrance. Barbin may have been the first intersex person to write a memoir, later published by Michel Foucault.

Intersex people are born with sex characteristics, such as chromosomes, gonads, hormones, or genitals that, according to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit the typical definitions for male or female bodies". Such variations may involve genital ambiguity, and combinations of chromosomal genotype and sexual phenotype other than XY-male and XX-female.

Intersex people in Switzerland have no recognition of rights to physical integrity and bodily autonomy, and no specific protections from discrimination on the basis of sex characteristics. In 2012, the Swiss National Advisory Commission on Biomedical Ethics published a report on the medical management of differences of sex development or intersex variations.