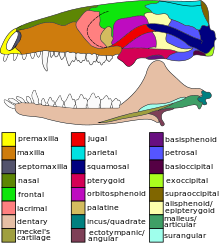
Anatomy
The jugal bone is located on either side of the skull in the circumorbital region. It is the origin of several masticatory muscles in the skull. [1] The jugal and lacrimal bones are the only two remaining from the ancestral circumorbital series: the prefrontal, postfrontal, postorbital, jugal, and lacrimal bones. [2]
During development, the jugal bone originates from dermal bone. [3]
In dinosaurs
This bone is considered key in the determination of general traits in cases in which the entire skull has not been found intact (for instance, as with dinosaurs in paleontology). In some dinosaur genera the jugal also forms part of the lower margin of either the antorbital fenestra or the infratemporal fenestra, or both. Most commonly, this bone articulates with the quadratojugal, the postorbital, the lacrimal, and the maxilla. [4] In horned dinosaurs, like Pentaceratops , the jugal bone is thick and comes to a point, which has led paleontologists to refer to it as the "jugal horn". [5]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.