
The Verkhovna Rada, officially the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, is the unicameral parliament of Ukraine.

Anatoliy Kyrylovych Kinakh is a Ukrainian politician and honorary professor at the Mykolaiv Government Humanitarian University. Kinakh is a former People's Deputy of Ukraine. Kinakh currently serves as the leader of Party of Industrialists and Entrepreneurs of Ukraine.
The judicial system of Ukraine is outlined in the 1996 Constitution of Ukraine. Before this there was no notion of judicial review nor any Supreme court since 1991's Ukrainian independence when it started being slowly restructured.

The prime minister of Ukraine is the head of government of Ukraine. The prime minister presides over the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, which is the highest body of the executive branch of the Ukrainian government. Following the 1991 Declaration of Independence of Ukraine the position replaced the Soviet post of chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR, which was established on March 25, 1946.
The Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, commonly referred to as the Government of Ukraine, is the highest body of state executive power in Ukraine. As the Cabinet of Ministers of the Ukrainian SSR, it was formed on 18 April 1991, by the Law of Ukrainian SSR No.980-XII. Vitold Fokin was approved as the first Prime Minister of Ukraine.
Holos Ukrayiny is a Ukrainian daily newspaper published in Kyiv. Laws adopted by the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine are published in Holos Ukrayiny when they come into force the next day.
The State Council of Crimea is the parliament of the Russia-administered Republic of Crimea. It claims to be a continuation of the 'Supreme Council of Crimea' following a vote by the Ukrainian parliament to dissolve the Supreme Council of Crimea. The Parliament is housed in the Parliament building in the centre of Simferopol.
Imperative mandate commonly refers to a provision in the Constitution of Ukraine in which members of the Verkhovna Rada are bound by the constitution and laws of Ukraine to remain members of the parliamentary faction or bloc in which they were elected. Imperative mandate provisions were defined in the Constitution in articles Articles 78 and 81.
The legal system of Ukraine is based on civil law, and belongs to the Romano-Germanic legal tradition. The main source of legal information is codified law. Customary law and case law are not as common, though case law is often used in support of the written law, as in many other legal systems. Historically, the Ukrainian legal system is primarily influenced by the French civil code, Roman Law, and traditional Ukrainian customary law. The new civil law books were heavily influenced by the German Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch.

The president of Ukraine is the head of state of Ukraine. The president represents the nation in international relations, administers the foreign political activity of the state, conducts negotiations and concludes international treaties. The president is directly elected by the citizens of Ukraine for a five-year term of office, limited to two terms consecutively.
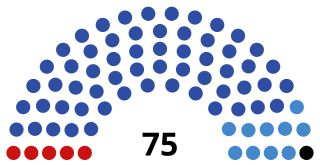
The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine of the 7th convocation was a convocation of the legislative branch of the Verkhovna Rada, Ukraine's unicameral parliament. Its composition was based on the results of the 2012 parliamentary election. Half of the seats in the parliament were apportioned between the five winning parties based on the popular vote, while the other half was apportioned between 4 parties and 44 independents between 225 constituencies throughout the country. It first met in the capital Kyiv on December 12, 2012, and ended its session on November 27, 2014, after the 8th Verkhovna Rada began its first session.

A button pusher is a term in Ukrainian politics and society related to a member of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine who votes on a motion by using their own identity card as well as ones belonging to other deputies.

The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine of the 8th convocation was a convocation of the legislative branch of the Verkhovna Rada, Ukraine's unicameral parliament. The 8th convocation met at the Verkhovna Rada building in Kyiv, having begun its term on 27 November 2014 following the last session of the 7th Verkhovna Rada. Its five-year term came to an end on July 24, 2019, marking the end of its tenth session.

Civil–military administrations are temporary local government units in Ukraine. They are concentrated in the Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts of eastern Ukraine, due to the ongoing War in Donbas. They are created under the aegis of the Anti-Terrorist Center of the Security Service of Ukraine.
Ukrainian decommunization laws were passed in 2015, in the early stages of the Russo-Ukrainian War. These laws relate to decommunization as well as commemoration of Ukrainian history, and have been referred to as "memory laws". They outlawed the public display of Soviet communist symbols and propaganda, and outlawed the public display of Nazi symbols and propaganda. These laws have also restricted the public display of militarism and fascism symbols, including rising sun flag.

The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine of the 9th convocation is the current convocation of the legislative branch of the Verkhovna Rada, Ukraine's unicameral parliament. The 9th convocation meets at the Verkhovna Rada building in Kyiv, having begun its term on 29 August 2019 following the last session of the 8th Verkhovna Rada.

The State Migration Service of Ukraine (SMS) is a government agency of Ukraine that administers policy in the areas of immigration, emigration, and citizenship, as well as the resident registration system. It is part of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Ukraine and was established in 2010.
The Civil Code of Ukraine is a Ukrainian codification of private law, basic normative legal act. It regulates personal non-property and property relations, based on legal equality, free will, property independence of their participants. It was adopted by the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine on 16 January 2003.

Justice is a parliamentary faction in the Verkhovna Rada, founded by 11 deputies of the Holos party who disagree with the actions of the party leadership.

Pavlo Riabikin is a Ukrainian statesman, politician and diplomat. On 26 April 2023, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy appointed him Ambassador of Ukraine to China.













