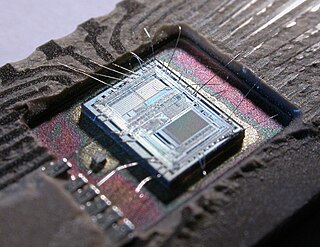
A microcontroller or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, restaurants, hotels, libraries, and airports.
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included microcontrollers radio-frequency (RF) devices including Wi-Fi, EEPROM, and flash memory devices, symmetric and asymmetric security chips, touch sensors and controllers, and application-specific products. Atmel supplies its devices as standard products, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), or application-specific standard product (ASSPs) depending on the requirements of its customers.

Nordic Semiconductor ASA was founded in 1983 and is a Norwegian fabless technology company with its headquarters in Trondheim, Norway. The company specializes in designing ultra-low-power wireless communication semiconductors and supporting software for engineers developing and manufacturing Internet of Things (IoT) products.
Atmel ARM-based processors are microcontrollers and microprocessors integrated circuits, by Microchip Technology, that are based on various 32-bit ARM processor cores, with in-house designed peripherals and tool support.
A Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP) is a communication peripheral in digital signal processor (DSP) and microcontroller unit (MCU) components from Texas Instruments.
ASIX Electronics Corp. is a fabless semiconductor supplier with a focus on networking, communication, and connectivity applications. ASIX Electronics specializes in Ethernet-centric silicon products such as non-PCI Ethernet controller, USB 2.0 to LAN controller, and network SoC for embedded networking applications.
MiWi is a proprietary wireless protocol supporting peer-to-peer, star network connectivity. It was designed by Microchip Technology. MiWi uses small, low-power digital radios based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, and is designed for low-power, cost-constrained networks, such as industrial monitoring and control, home and building automation, remote control, wireless sensors, lighting control, and automated meter reading.
EFM32 Gecko MCUs are a family of mixed-signal 32-bit microcontroller integrated circuits from Energy Micro based on ARM Cortex-M CPUs, including the Cortex-M0+, Cortex-M3, and Cortex-M4.

Silicon Laboratories, Inc., commonly referred to as Silicon Labs, is a fabless global technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductors, other silicon devices and software, which it sells to electronics design engineers and manufacturers in Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure worldwide.

An RF module is a (usually) small electronic device used to transmit and/or receive radio signals between two devices. In an embedded system it is often desirable to communicate with another device wirelessly. This wireless communication may be accomplished through optical communication or through radio-frequency (RF) communication. For many applications, the medium of choice is RF since it does not require line of sight. RF communications incorporate a transmitter and a receiver. They are of various types and ranges. Some can transmit up to 500 feet. RF modules are typically fabricated using RF CMOS technology.
OpenPicus was an Italian hardware company launched in 2011 that designed and produced Internet of Things system on modules called Flyport. Flyport is open hardware and the openPicus framework and IDE are open software.
Flyport is a stand-alone system on module, no external processor is needed to create IoT applications. The company ceased operations in 2018.

Redpine Signals was a fabless semiconductor company founded in 2001. The company made chipsets and system-level products for wireless networks. It served the Internet of Things and wireless embedded systems market, enabling all volume levels of chipsets and modules.

Intel Quark is a line of 32-bit x86 SoCs and microcontrollers by Intel, designed for small size and low power consumption, and targeted at new markets including wearable devices. The line was introduced at Intel Developer Forum in 2013, and discontinued in January 2019.

The Arduino Uno is an open-source microcontroller board based on the Microchip ATmega328P microcontroller (MCU) and developed by Arduino.cc and initially released in 2010. The microcontroller board is equipped with sets of digital and analog input/output (I/O) pins that may be interfaced to various expansion boards (shields) and other circuits. The board has 14 digital I/O pins, 6 analog I/O pins, and is programmable with the Arduino IDE, via a type B USB cable. It can be powered by a USB cable or a barrel connector that accepts voltages between 7 and 20 volts, such as a rectangular 9-volt battery. It has the same microcontroller as the Arduino Nano board, and the same headers as the Leonardo board. The hardware reference design is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike 2.5 license and is available on the Arduino website. Layout and production files for some versions of the hardware are also available.

The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microcontroller, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontroller capability, produced by Espressif Systems in Shanghai, China.
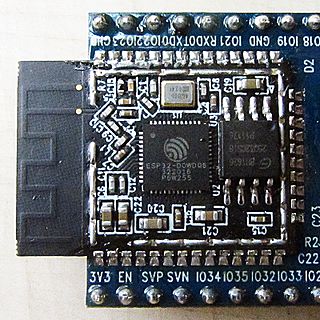
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system-on-chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, an Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor, or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. It is commonly found either on device-specific PCBs or on a range of development boards with GPIO pins and various connectors depending on the model and manufacturer of the board.
ESP Easy is a free and open source MCU firmware for the Internet of things (IoT). and originally developed by the LetsControlIt.com community. It runs on ESP8266 Wi-Fi based MCU platforms for IoT from Espressif Systems. The name "ESP Easy," by default, refers to the firmware rather than the hardware on which it runs. At a low level, the ESP Easy firmware works the same as the NodeMCU firmware and also provides a very simple operating system on the ESP8266. The main difference between ESP Easy firmware and NodeMCU firmware is that the former is designed as a high-level toolbox that just works out-of-the-box for a pre-defined set of sensors and actuators. Users simply hook up and read/control over simple web requests without having to write any code at all themselves, including firmware upgrades using OTA updates.

RP2040 is a 32-bit dual ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller integrated circuit by Raspberry Pi Ltd. In January 2021, it was released as part of the Raspberry Pi Pico board. Its successor is the RP2350 series.








