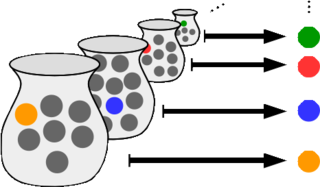
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, abbreviated AC or AoC, is an axiom of set theory equivalent to the statement that a Cartesian product of a collection of non-empty sets is non-empty. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of sets, each containing at least one element, it is possible to construct a new set by arbitrarily choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family of nonempty sets, there exists an indexed set such that for every . The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem.
An axiom, postulate, or assumption is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The word comes from the Ancient Greek word ἀξίωμα (axíōma), meaning 'that which is thought worthy or fit' or 'that which commends itself as evident'.
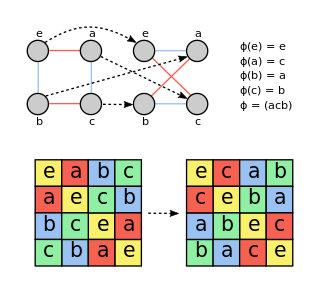
In mathematics, an automorphism is an isomorphism from a mathematical object to itself. It is, in some sense, a symmetry of the object, and a way of mapping the object to itself while preserving all of its structure. The set of all automorphisms of an object forms a group, called the automorphism group. It is, loosely speaking, the symmetry group of the object.
In mathematics and computer science, currying is the technique of translating the evaluation of a function that takes multiple arguments into evaluating a sequence of functions, each with a single argument. For example, currying a function that takes three arguments creates a nested unary function , so that the code
In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers do. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics.
First-order logic—also known as predicate logic, quantificational logic, and first-order predicate calculus—is a collection of formal systems used in mathematics, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science. First-order logic uses quantified variables over non-logical objects, and allows the use of sentences that contain variables, so that rather than propositions such as "Socrates is a man", one can have expressions in the form "there exists x such that x is Socrates and x is a man", where "there exists" is a quantifier, while x is a variable. This distinguishes it from propositional logic, which does not use quantifiers or relations; in this sense, propositional logic is the foundation of first-order logic.

In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word isomorphism is derived from the Ancient Greek: ἴσοςisos "equal", and μορφήmorphe "form" or "shape".
Mathematical logic is the study of formal logic within mathematics. Major subareas include model theory, proof theory, set theory, and recursion theory. Research in mathematical logic commonly addresses the mathematical properties of formal systems of logic such as their expressive or deductive power. However, it can also include uses of logic to characterize correct mathematical reasoning or to establish foundations of mathematics.
In mathematics, a complete lattice is a partially ordered set in which all subsets have both a supremum (join) and an infimum (meet). A lattice which satisfies at least one of these properties is known as a conditionally complete lattice. Specifically, every non-empty finite lattice is complete. Complete lattices appear in many applications in mathematics and computer science. Being a special instance of lattices, they are studied both in order theory and universal algebra.
Universal algebra is the field of mathematics that studies algebraic structures themselves, not examples ("models") of algebraic structures. For instance, rather than take particular groups as the object of study, in universal algebra one takes the class of groups as an object of study.
In category theory, an epimorphism is a morphism f : X → Y that is right-cancellative in the sense that, for all objects Z and all morphisms g1, g2: Y → Z,

A mathematical proof is a deductive argument for a mathematical statement, showing that the stated assumptions logically guarantee the conclusion. The argument may use other previously established statements, such as theorems; but every proof can, in principle, be constructed using only certain basic or original assumptions known as axioms, along with the accepted rules of inference. Proofs are examples of exhaustive deductive reasoning which establish logical certainty, to be distinguished from empirical arguments or non-exhaustive inductive reasoning which establish "reasonable expectation". Presenting many cases in which the statement holds is not enough for a proof, which must demonstrate that the statement is true in all possible cases. A proposition that has not been proved but is believed to be true is known as a conjecture, or a hypothesis if frequently used as an assumption for further mathematical work.
In mathematics, an algebraic structure consists of a nonempty set A, a collection of operations on A, and a finite set of identities, known as axioms, that these operations must satisfy.
In mathematics, especially in order theory, a Galois connection is a particular correspondence (typically) between two partially ordered sets (posets). Galois connections find applications in various mathematical theories. They generalize the fundamental theorem of Galois theory about the correspondence between subgroups and subfields, discovered by the French mathematician Évariste Galois.
In mathematics, the adjective trivial is often used to refer to a claim or a case which can be readily obtained from context, or an object which possesses a simple structure. The noun triviality usually refers to a simple technical aspect of some proof or definition. The origin of the term in mathematical language comes from the medieval trivium curriculum, which distinguishes from the more difficult quadrivium curriculum. The opposite of trivial is nontrivial, which is commonly used to indicate that an example or a solution is not simple, or that a statement or a theorem is not easy to prove.

In mathematics, when a mathematical phenomenon runs counter to some intuition, then the phenomenon is sometimes called pathological. On the other hand, if a phenomenon does not run counter to intuition, it is sometimes called well-behaved. These terms are sometimes useful in mathematical research and teaching, but there is no strict mathematical definition of pathological or well-behaved.
In mathematics, algebraic geometry and analytic geometry are two closely related subjects. While algebraic geometry studies algebraic varieties, analytic geometry deals with complex manifolds and the more general analytic spaces defined locally by the vanishing of analytic functions of several complex variables. The deep relation between these subjects has numerous applications in which algebraic techniques are applied to analytic spaces and analytic techniques to algebraic varieties.
In mathematics, a characterization of an object is a set of conditions that, while different from the definition of the object, is logically equivalent to it. To say that "Property P characterizes object X" is to say that not only does X have property P, but that X is the only thing that has property P. Similarly, a set of properties P is said to characterize X, when these properties distinguish X from all other objects. Even though a characterization identifies an object in a unique way, several characterizations can exist for a single object. Common mathematical expressions for a characterization of X in terms of P include "P is necessary and sufficient for X", and "X holds if and only if P".
In mathematics, the norm residue isomorphism theorem is a long-sought result relating Milnor K-theory and Galois cohomology. The result has a relatively elementary formulation and at the same time represents the key juncture in the proofs of many seemingly unrelated theorems from abstract algebra, theory of quadratic forms, algebraic K-theory and the theory of motives. The theorem asserts that a certain statement holds true for any prime and any natural number . John Milnor speculated that this theorem might be true for and all , and this question became known as Milnor's conjecture. The general case was conjectured by Spencer Bloch and Kazuya Kato and became known as the Bloch–Kato conjecture or the motivic Bloch–Kato conjecture to distinguish it from the Bloch–Kato conjecture on values of L-functions. The norm residue isomorphism theorem was proved by Vladimir Voevodsky using a number of highly innovative results of Markus Rost.
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values true and false, usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in elementary algebra the values of the variables are numbers. Second, Boolean algebra uses logical operators such as conjunction (and) denoted as ∧, disjunction (or) denoted as ∨, and the negation (not) denoted as ¬. Elementary algebra, on the other hand, uses arithmetic operators such as addition, multiplication, subtraction, and division. Boolean algebra is therefore a formal way of describing logical operations, in the same way that elementary algebra describes numerical operations.



















