Aesthetics is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of beauty and the nature of taste and, in a broad sense, incorporates the philosophy of art. Aesthetics examines the philosophy of aesthetic value, which is determined by critical judgments of artistic taste; thus, the function of aesthetics is the "critical reflection on art, culture and nature".

The history of mathematics deals with the origin of discoveries in mathematics and the mathematical methods and notation of the past. Before the modern age and the worldwide spread of knowledge, written examples of new mathematical developments have come to light only in a few locales. From 3000 BC the Mesopotamian states of Sumer, Akkad and Assyria, followed closely by Ancient Egypt and the Levantine state of Ebla began using arithmetic, algebra and geometry for purposes of taxation, commerce, trade and also in the field of astronomy to record time and formulate calendars.
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory, algebra, geometry, analysis, and set theory.

In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement that has been proven, or can be proven. The proof of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to establish that the theorem is a logical consequence of the axioms and previously proved theorems.
Philosophy of mathematics is the branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of mathematics and its relationship with other human activities.

A mathematical proof is a deductive argument for a mathematical statement, showing that the stated assumptions logically guarantee the conclusion. The argument may use other previously established statements, such as theorems; but every proof can, in principle, be constructed using only certain basic or original assumptions known as axioms, along with the accepted rules of inference. Proofs are examples of exhaustive deductive reasoning which establish logical certainty, to be distinguished from empirical arguments or non-exhaustive inductive reasoning which establish "reasonable expectation". Presenting many cases in which the statement holds is not enough for a proof, which must demonstrate that the statement is true in all possible cases. A proposition that has not been proved but is believed to be true is known as a conjecture, or a hypothesis if frequently used as an assumption for further mathematical work.
Ramsey theory, named after the British mathematician and philosopher Frank P. Ramsey, is a branch of the mathematical field of combinatorics that focuses on the appearance of order in a substructure given a structure of a known size. Problems in Ramsey theory typically ask a question of the form: "how big must some structure be to guarantee that a particular property holds?"
In common mathematical parlance, a mathematical result is called folklore if it is an unpublished result with no clear originator, but which is well-circulated and believed to be true among the specialists. More specifically, folk mathematics, or mathematical folklore, is the body of theorems, definitions, proofs, facts or techniques that circulate among mathematicians by word of mouth, but have not yet appeared in print, either in books or in scholarly journals.
Low-complexity art, first described by Jürgen Schmidhuber in 1997 and now established as a seminal topic within the larger field of computer science, is art that can be described by a short computer program.

Pure mathematics is the study of mathematical concepts independently of any application outside mathematics. These concepts may originate in real-world concerns, and the results obtained may later turn out to be useful for practical applications, but pure mathematicians are not primarily motivated by such applications. Instead, the appeal is attributed to the intellectual challenge and aesthetic beauty of working out the logical consequences of basic principles.

Paul Erdős was a Hungarian mathematician. He was one of the most prolific mathematicians and producers of mathematical conjectures of the 20th century. Erdős pursued and proposed problems in discrete mathematics, graph theory, number theory, mathematical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory. Much of his work centered around discrete mathematics, cracking many previously unsolved problems in the field. He championed and contributed to Ramsey theory, which studies the conditions in which order necessarily appears. Overall, his work leaned towards solving previously open problems, rather than developing or exploring new areas of mathematics.
In mathematics, Hilbert's program, formulated by German mathematician David Hilbert in the early 1920s, was a proposed solution to the foundational crisis of mathematics, when early attempts to clarify the foundations of mathematics were found to suffer from paradoxes and inconsistencies. As a solution, Hilbert proposed to ground all existing theories to a finite, complete set of axioms, and provide a proof that these axioms were consistent. Hilbert proposed that the consistency of more complicated systems, such as real analysis, could be proven in terms of simpler systems. Ultimately, the consistency of all of mathematics could be reduced to basic arithmetic.

Neuroesthetics is a recent sub-discipline of applied aesthetics. Empirical aesthetics takes a scientific approach to the study of aesthetic experience of art, music, or any object that can give rise to aesthetic judgments. Neuroesthetics is a term coined by Semir Zeki in 1999 and received its formal definition in 2002 as the scientific study of the neural bases for the contemplation and creation of a work of art. Anthropologists and evolutionary biologists alike have accumulated evidence suggesting that human interest in, and creation of, art evolved as an evolutionarily necessary mechanism for survival across cultures and throughout history. Neuroesthetics uses neuroscience to explain and understand the aesthetic experiences at the neurological level. The topic attracts scholars from many disciplines including neuroscientists, art historians, artists, art therapists and psychologists.
The language of mathematics has a wide vocabulary of specialist and technical terms. It also has a certain amount of jargon: commonly used phrases which are part of the culture of mathematics, rather than of the subject. Jargon often appears in lectures, and sometimes in print, as informal shorthand for rigorous arguments or precise ideas. Much of this uses common English words, but with a specific non-obvious meaning when used in a mathematical sense.

A Mathematician's Apology is a 1940 essay by British mathematician G. H. Hardy which defends the pursuit of mathematics for its own sake. Central to Hardy's "apology" – in the sense of a formal justification or defence – is an argument that mathematics has value independent of its applications. Hardy located this value in what he called the beauty of mathematics and gave some examples of and criteria for mathematical beauty. The book also includes a brief autobiography which gives insight into the mind of a working mathematician.
In physics and cosmology, the mathematical universe hypothesis (MUH), also known as the ultimate ensemble theory, is a speculative "theory of everything" (TOE) proposed by cosmologist Max Tegmark. According to the hypothesis, the universe is a mathematical object in and of itself. Tegmark extends this idea to hypothesize that all mathematical objects exist, which he describes as a form of Platonism or Modal realism.
Applied aesthetics is the application of the branch of philosophy of aesthetics to cultural constructs. In a variety of fields, artifacts are created that have both practical functionality and aesthetic affectation. In some cases, aesthetics is primary, and in others, functionality is primary. At best, the two needs are synergistic, in which "beauty" makes an artifact work better, or in which more functional artifacts are appreciated as aesthetically pleasing. This achievement of form and function, of art and science, of beauty and usefulness, is the primary goal of design, in all of its domains.

Mathematics and art are related in a variety of ways. Mathematics has itself been described as an art motivated by beauty. Mathematics can be discerned in arts such as music, dance, painting, architecture, sculpture, and textiles. This article focuses, however, on mathematics in the visual arts.
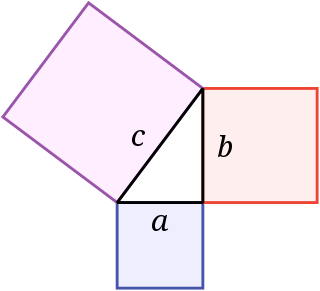
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.

A Pythagorean tiling or two squares tessellation is a tiling of a Euclidean plane by squares of two different sizes, in which each square touches four squares of the other size on its four sides. Many proofs of the Pythagorean theorem are based on it, explaining its name. It is commonly used as a pattern for floor tiles. When used for this, it is also known as a hopscotch pattern or pinwheel pattern, but it should not be confused with the mathematical pinwheel tiling, an unrelated pattern.
















