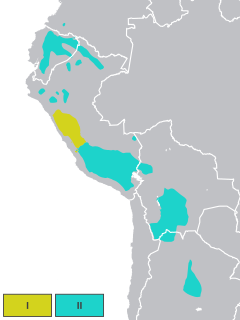
Quechua, usually called Runasimi in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes and highlands of South America. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken language family of indigenous peoples of the Americas, with a total of probably some 8–10 million speakers. Approximately 25% of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish colonisers initially encouraged its use, but from the middle of their reign they suppressed it. However, Quechua ultimately survived and variants are still widely spoken today.

Imbabura is a province located in the Andes of northern Ecuador. The capital is Ibarra. The people of the province speak Spanish and the Imbaburan Quechua language.

Rumiñahui or Rumiñawi is a canton of Pichincha Province in Ecuador. Its seat is Sangolquí. The canton lies southeast of Quito Canton and forms a suburb of Quito.

Utcubamba, in Quechua Utkhupampa, is one of seven provinces of the Amazonas Region, Peru. It was created by Law#-23843 on May 30, 1984. Its capital is Bagua Grande and its principal attraction is the Tourist Corridor of Utcubamba where the valley becomes notably closer forming "the canyon of Utcubamba". These conditions modify the climate in a substantial way and create a radical ecological shift. The area is fresh and fragrant and the orchids that are bountiful are unique in the world. Notably picturesque cascades are observed in the rocky vertical walls that the river has created. There are hot springs a few meters from El Ingenio bridge.

The Casma Province is one of twenty provinces of the Ancash Region of Peru.

Utcubamba or Utkhupampa is a river in the Amazonas Region of Peru, located at 5°32′6″S78°33′9″W. The name is a historical reference to the past agricultural practice of growing cotton in the Utcubamba Valley.
The Chiriaco is a river in Peru. It is a tributary of the Marañón and takes Tuntungos, Shushug and Wawas as principal tributaries.

Chacas is a district of the province Asunción in the Ancash Region of Peru. Its seat is Chacas.

Tambomachay is an archaeological site associated with the Inca Empire, located near Cusco, Peru. An alternate Spanish name is El Baño del Inca.
Chetilla District is one of twelve districts of the province Cajamarca in Peru.

Santa Rosa District is one of nine districts of the province Melgar in Peru.

Alca District is one of eleven districts of the province La Unión in Peru.
Cajay District is one of sixteen districts of the Huari Province in Peru.

Inka Wasi or Inkawasi is an archaeological site in Peru. It is located in the Ayacucho Region, Parinacochas Province, Pullo District.
Tupu Inka is an archaeological site in Peru. It is located in the Puno Region, Yunguyo Province, Unicachi District.

Colcampata is an archaeological site in Peru. It is situated in the Cusco Region, Cusco Province, Cusco District.

Collor is an archaeological site in Peru. It is situated in the Cajamarca Region, Cajamarca Province, Namora District. The site lies at a height of about 2,970 metres (9,744 ft) on a mountain named Coyor, east of Lake San Nicolas.

Wilca is an archaeological site in Peru. It is situated in the Amazonas Region, Utcubamba Province, in the east of the Cajaruro District, near the border with the Bongara Province.

Carachupa is an archaeological site with rock art in Peru. It is located near the village of Carachupa, in Lonya Grande District, region of Amazonas.

Purunllacta or Purum Llacta (possibly from Quechua purum, purun savage, wild / wasteland, llaqta place is an archaeological site in Peru. It is situated in the Amazonas Region, Chachapoyas Province, Soloco District, southwest and near the archaeological site of Purum Llaqta of the Cheto District.














