
A potter's field, paupers' grave or common grave is a place for the burial of unknown, unclaimed or indigent people. "Potter's field" is of Biblical origin, referring to Akeldama, stated to have been purchased after Judas Iscariot's suicide by the chief priests of Jerusalem with the coins that had been paid to Judas for his identification of Jesus. The priests are stated to have acquired it for the burial of strangers, criminals, and the poor, the coins paid to Judas being considered blood money. Prior to Akeldama's use as a burial ground, it had been a site where potters collected high-quality, deeply red clay for the production of ceramics, thus the name potters' field.

Matthew 1 is the first chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It contains two distinct sections. The first lists the genealogy of Jesus from Abraham to his legal father Joseph, husband of Mary, his mother. The second part, beginning at verse 18, provides an account of the virgin birth of Jesus Christ.

Matthew 1:3 is the third verse of the first chapter in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The verse is part of the section where the genealogy of Joseph, the legal father of Jesus, is listed.

Matthew 1:2 is the second verse of the first chapter in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The verse is the first part of the section where the genealogy of Joseph, the legal father of Jesus, is listed.

Matthew 1:1 is the opening verse in the first chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. Since Matthew is traditionally placed as the first of the four Gospels, this verse commonly serves as the opening to the entire New Testament.

Matthew 1:20 is the twentieth verse of the first chapter in the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. Previously Joseph had found Mary to be pregnant and had considered leaving her. In this verse an angel comes to him in a dream and reassures him.

Matthew 2:3 is the third verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. In the previous verse the magi had informed King Herod that they had seen portents showing the birth of the King of the Jews. In this verse he reacts to this news.

Matthew 2:4 is the fourth verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The magi have informed King Herod that they had seen portents showing the birth of the King of the Jews. In this verse he calls together leading figures of Jerusalem to find out where Jesus was to be born.

Matthew 2:5 is the fifth verse of the second chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. The magi have informed King Herod that they had seen portents showing the birth of the King of the Jews. Herod has asked the leading Jewish religious figures about how to find out where Jesus was to be born. In this verse they tell him.

Matthew 4:13 is the thirteenth verse of the fourth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. In the previous verse, Jesus returned to Galilee after hearing of the arrest of John the Baptist. In this verse, he leaves from Nazareth to Capernaum.
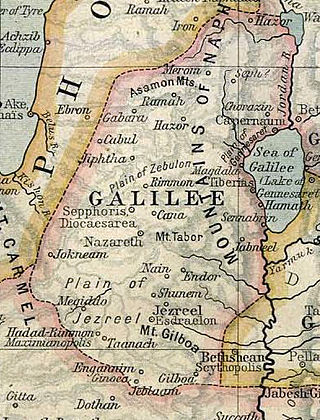
Matthew 4:14–15 are the fourteenth and fifteenth verses of the fourth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. In the previous verses Jesus returned to Galilee after hearing of the arrest of John the Baptist and then left Nazareth for Capernaum. These introduce and then contain the first portion of a quote from the Book of Isaiah showing how these movements were preordained by scripture.

Matthew 27:3 is the third verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse returns to the story of Judas Iscariot who, in the previous chapter, had accepted payment to betray Jesus to the Jewish authorities. This verse opens the story of Judas' remorse and death, interrupting the Gospel's narrative regarding the trials of Jesus.
Matthew 28:12 is the twelfth verse of the twenty-eighth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse is part of the resurrection narrative. In this verse the guards of the tomb, after being present for an angel hearkening the resurrection, are bribed by the priests to lie about what they saw.

Matthew 27:59 is the fifty-ninth verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse describes Joseph of Arimathea gathering Jesus' body after the crucifixion.

Matthew 27:57 is the fifty-seventh verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse begins a discussion of the burial of Jesus and introduces Joseph of Arimathea.

Matthew 27:11 is the eleventh verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse brings the narrative back to Pilate's Court, and the final trial of Jesus.

Matthew 27:8 is the eighth verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse continues the final story of Judas Iscariot. In the previous verses, Judas has killed himself, but not before casting the thirty pieces of silver into the Temple. The priests used them to buy a potter's field and make a cemetery, which is known as the Field of Blood.

Matthew 27:5 is the fifth verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse continues the final story of Judas Iscariot. In the earlier verse Judas had regretted his decision to betray Jesus, but is met with disinterest from the Jewish leaders. In this verse his response is to return the blood money and then commit suicide.

Matthew 27:6 is the sixth verse of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. This verse continues the final story of Judas Iscariot. In the previous verse Judas had cast into the temple the thirty pieces of silver he'd been paid for betraying Jesus. In this verse the priests discuss what to do with them.
Matthew 27:9-10 are the ninth and tenth verses of the twenty-seventh chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. These verses end the final story of Judas Iscariot, with a quotation from scripture showing how the events around his final days were predicted.


















