
Rambutan is a medium-sized tropical tree in the family Sapindaceae. The name also refers to the edible fruit produced by this tree. The rambutan is native to Southeast Asia. It is closely related to several other edible tropical fruits, including the lychee, longan, pulasan, and quenepa.

Ponce is a city and a municipality on the southern coast of Puerto Rico. The most populated city outside the San Juan metropolitan area, was founded on August 12, 1692 and is named after Juan Ponce de León y Loayza, the great-grandson of Spanish conquistador Juan Ponce de León. Ponce is often referred to as La Perla del Sur, La Ciudad Señorial, and La Ciudad de las Quenepas.

Genipa americana is a species of trees in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to the tropical forests of North and South America, as well as the Caribbean.

The Sapindaceae are a family of flowering plants in the order Sapindales known as the soapberry family. It contains 138 genera and 1,858 accepted species. Examples include horse chestnut, maples, ackee and lychee.
Honeyberry or honey berry is a common name for the edible fruits of several plants and may refer to:

Melicoccus is a genus of ten species of flowering plants in the family Sapindaceae, native to tropical regions of northern and western South America.

Sapindus is a genus of about thirteen species of shrubs and small trees in the lychee family, Sapindaceae and tribe Sapindeae. It is native to warm temperate to tropical regions of the world. The genus includes both deciduous and evergreen species. Members of the genus are commonly known as soapberries or soapnuts because the fruit pulp is used to make soap. The generic name is derived from the Latin words sapo, meaning "soap", and indicus, meaning "of India".

Malpighia is a genus of flowering plants in the nance family, Malpighiaceae. It contains 108 species of shrubs or small trees, all of which are native to the American tropics, ranging from Texas through Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean to Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. The generic name honours Marcello Malpighi, a 17th-century Italian physician and botanist. The species grow to 1–6 m (3.3–19.7 ft) tall, with a dense, often thorny crown. The leaves are evergreen, simple, 0.5–15 cm (0.20–5.91 in) long, with an entire or serrated margin. The flowers are solitary or in umbels of two to several together, each flower 1–2 cm (0.39–0.79 in) diameter, with five white, pink, red, or purple petals. The fruit is a red, orange, or purple drupe, containing two or three hard seeds. M. emarginata is cultivated for its sweet and juicy fruits, which are very rich in vitamin C.

Talisia is a genus of 52 species of flowering plants in the family Sapindaceae, native to tropical regions of the Americas. The genus is closely related to Melicoccus, with some species sometimes included in that genus.

Nephelium ramboutan-ake, the pulasan, is a tropical fruit in the soapberry family Sapindaceae. It is closely related to the rambutan and sometimes confused with it. Other related soapberry family fruits include lychee and longan. Usually eaten fresh, it is sweeter than the rambutan and lychee, but very rare outside Southeast Asia.

Plaza del Mercado de Ponce or, formally, Plaza del Mercado Isabel Segunda, is a historic marketplace building in Ponce, Puerto Rico. It was inaugurated in 1863 by Ponce Mayor Don Luis de Quixano. Designed by famed engineer Timoteo Luberza, it occupies a city block in the Ponce Historic Zone at the grid formed by Calle Atocha, Estrella, Leon, and Castillo streets. It has room for 65 kiosks. It was originally called Plaza del Capá.
The Vía Verde project, also known as Gasoducto del Norte, was a pipeline project proposed by the administration of Governor Luis Fortuño intended to supply natural gas to northern Puerto Rico from Puerto Rico's southern region. The pipeline would have run from Peñuelas, on Puerto Rico's southern coast, to electricity-generating plants in Arecibo, Cataño and San Juan, crossing the island's Cordillera Central. The project aimed to supply 71% of Puerto Rico's electrical energy needs, while lowering the cost of electricity in the island. A project of Governor Luis Fortuño, it was called the "crown jewel" project of his administration. The project was also supported by former governor of Puerto Rico Rafael Hernández Colón. The pipeline was called "the centerpiece of [Governor Fortuño]'s efforts to kick-start Puerto Rico's dormant economy."
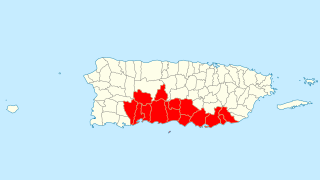
Porta Caribe is a tourism region in southern Puerto Rico. It was established in 2003 by the Puerto Rico Tourism Company, an agency of the Government of Puerto Rico. When created in 2003 it consisted of 14 municipalities in the south central zone. With the creation of the neighboring Porta Cordillera zone in July 2012, the municipalities of Adjuntas and Jayuya were transferred to the newly created Porta Cordillera zone and Porta Caribe became a 12-municipality tourism region. The name Porta Caribe translates to "Doorway to the Caribbean." Its executive director is Maritza W. Ruiz Cabán.

The Urban Ecological Park, also known as the Ponce Ecological Park, is a passive park in Ponce, Puerto Rico. The park was designed by Bonin Orozco Arquitectos and was inaugurated on 19 September 2012. The park is unique in that it was designed to create a "green lung" in the city by using ecological mindset in its entirety, from the construction materials used to the design and other areas as well. Except for one tree that got relocated within the project, the new park made use of all the existing trees and shrubs as they existed on the site prior to the development of the park.

Martex Farms is a Puerto Rican company based in Santa Isabel, Puerto Rico, an area known as the "Ruta Agrícola". It is the largest banana, avocado and tropical palm grower on the south coast of the island.

Día Mundial de Ponce is a cultural celebration held in Ponce, Puerto Rico, every year during the month of September. The celebration actually starts the Monday before Labor Day with various evening-time cultural festivities. It then culminates with the grand parade that takes place on the Sunday before Labor Day. The celebration started in 2012 and has an estimated attendance of 4,000 people. The week-long event aims to celebrate the cultural heritage of the city by giving tribute to the organizations, the people and "the great sons and daughters of the city of Ponce." The first year of this celebration, the Grand Parade took place on the last Sunday of the celebration, but starting in 2013, the week-long events ended on a Saturday and the Grand Parade was changed to take place the last Saturday. That year the celebration was also changed to occur the last weekend of September, rather than the weekend before Labor Day.
Villa Pesquera is a sea-front fishing village in barrio Playa, in the municipality of Ponce, Puerto Rico. The site is one of the tourist attractions in the municipality of Ponce.

Ponce Servicos, formerly Plaza del Mercado Juan Bigas, is a brutalist municipal building located Ponce, Puerto Rico. It is the largest building in the municipality in terms of footprint area and the only one that occupies an entire city block. The structure was built in 1981 as a way to provide a modern, air-conditioned, structure for the merchants and shoppers of the historic but aging Plaza de Mercado Isabel II building, while the latter underwent restoration. On its opening day it was named Plaza del Mercado Juan Bigas, in honor of Juan Bigas Moulins, the Ponce businessman by that name.

The Fiesta Nacional de la Danza, also known as Semana de la Danza Puertorriqueña, is a cultural celebration that takes place every year in Ponce, Puerto Rico. The festival centers on the danza, a musical genre native from the city of Ponce and oftentimes called "Puerto Rico's classical music" with rhythm, tune, and cadence that are similar to the waltz. The celebration lasts a week and takes place in mid-May. It is sponsored by the Ponce Municipal Government and the Institute of Puerto Rican Culture.

The Feria de Artesanías de Ponce, formally, Feria de Artesanías y Muestra de Arte de Ponce, is an event that takes place every year in Ponce, Puerto Rico, where artists, craftspeople and artisans showcase their products. The products showcased are traditionally hand-made and in small quantities. The fair centers around crafts that highlight the traditional cultural background of Puerto Rico, including Taino, African, and Spanish traditions. The event started in 1974 and is reported to draw "thousands of visitors". It lasts three days and is held over a weekend during the month of April.




















