
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is a hereditary inflammatory disorder. FMF is an autoinflammatory disease caused by mutations in the Mediterranean fever (MEFV) gene, which encodes a 781–amino acid protein called pyrin. While all ethnic groups are susceptible to FMF, it usually occurs in people of Mediterranean origin—including Sephardic Jews, Mizrahi Jews, Ashkenazi Jews, Assyrians, Armenians, Azerbaijanis, Druze, Levantines, Kurds, Greeks, Turks and Italians.

The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones.

HMG-CoA reductase is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia.

Prenylation is the addition of hydrophobic molecules to a protein or a biomolecule. It is usually assumed that prenyl groups (3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) facilitate attachment to cell membranes, similar to lipid anchors like the GPI anchor, though direct evidence of this has not been observed. Prenyl groups have been shown to be important for protein–protein binding through specialized prenyl-binding domains.

Anakinra, sold under the brand name Kineret, is a biopharmaceutical medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes, familial Mediterranean fever, and Still's disease. It is a slightly modified recombinant version of the human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist protein. It is marketed by Swedish Orphan Biovitrum. Anakinra is administered by subcutaneous injection.

Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) also known as leukocytic pyrogen, leukocytic endogenous mediator, mononuclear cell factor, lymphocyte activating factor and other names, is a cytokine protein that in humans is encoded by the IL1B gene. There are two genes for interleukin-1 (IL-1): IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. IL-1β precursor is cleaved by cytosolic caspase 1 to form mature IL-1β.

Muckle–Wells syndrome (MWS) is a rare autosomal dominant disease which causes sensorineural deafness and recurrent hives, and can lead to amyloidosis. Individuals with MWS often have episodic fever, chills, and joint pain. As a result, MWS is considered a type of periodic fever syndrome. MWS is caused by a defect in the CIAS1 gene which creates the protein cryopyrin. MWS is closely related to two other syndromes, familial cold urticaria and neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease—in fact, all three are related to mutations in the same gene and subsumed under the term cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS).
Periodic fever syndromes are a set of disorders characterized by recurrent episodes of systemic and organ-specific inflammation. Unlike autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus, in which the disease is caused by abnormalities of the adaptive immune system, people with autoinflammatory diseases do not produce autoantibodies or antigen-specific T or B cells. Instead, the autoinflammatory diseases are characterized by errors in the innate immune system.
Neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease is a rare genetic periodic fever syndrome which causes uncontrolled inflammation in multiple parts of the body starting in the newborn period. Symptoms include skin rashes, severe arthritis, and chronic meningitis leading to neurologic damage. It is one of the cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes.

Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals. This enzyme catalyzes the following reaction:

Cell division control protein 42 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDC42 gene. Cdc42 is involved in regulation of the cell cycle. It was originally identified in S. cerevisiae (yeast) as a mediator of cell division, and is now known to influence a variety of signaling events and cellular processes in a variety of organisms from yeast to mammals.
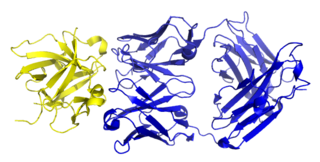
Canakinumab, sold under the brand name Ilaris, is a medication for the treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, active Still's disease, including adult-onset Still's disease, gout flares. It is a human monoclonal antibody targeted at interleukin-1 beta. It has no cross-reactivity with other members of the interleukin-1 family, including interleukin-1 alpha.

Diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.33), most commonly referred to in scientific literature as mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Schnitzler syndrome or Schnitzler's syndrome is a rare disease characterised by onset around middle age of chronic hives (urticaria) and periodic fever, bone and joint pain, weight loss, malaise, fatigue, swollen lymph glands and enlarged spleen and liver.
An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule that is secreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Th) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-12, and IL-18, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interferon gamma (IFNγ), and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and play an important role in mediating the innate immune response. Inflammatory cytokines are predominantly produced by and involved in the upregulation of inflammatory reactions.

Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS) is a group of rare, heterogeneous autoinflammatory disease characterized by interleukin 1β-mediated systemic inflammation and clinical symptoms involving skin, joints, central nervous system, and eyes. It encompasses a spectrum of three clinically overlapping autoinflammatory syndromes including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, the Muckle–Wells syndrome (MWS), and neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease that were originally thought to be distinct entities, but in fact share a single genetic mutation and pathogenic pathway, and keratoendotheliitis fugax hereditaria in which the autoinflammatory symptoms affect only the anterior segment of the eye.

Jos W.M. van der Meer is emeritus professor and former chairman at the department of internal medicine of the Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre in Nijmegen, Netherlands. He is a member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences, of which he was vice president and chairman of the division of natural sciences (2006-2012). He is a member of Academia Europaea. Between 2014 and 2016 he was president of European Academies Science Advisory Council (EASAC). He performs research on cytokines and host defence, chronic fatigue syndrome and hyper-immunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS). He is also active in graphic art and makes cartoons, for example for the Dutch science journal Mediator.

The Interleukin-1 family is a group of 11 cytokines that plays a central role in the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses to infections or sterile insults.
Autoinflammatory diseases (AIDs) are a group of rare disorders caused by dysfunction of the innate immune system. These responses are characterized by periodic or chronic systemic inflammation, usually without the involvement of adaptive immunity.

















