Related Research Articles
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), also known as matrix metallopeptidases or matrixins, are metalloproteinases that are calcium-dependent zinc-containing endopeptidases; other family members are adamalysins, serralysins, and astacins. The MMPs belong to a larger family of proteases known as the metzincin superfamily.
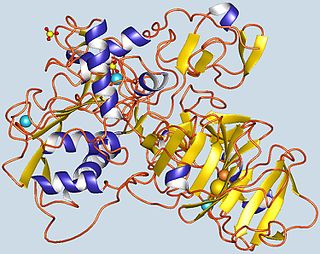
Gelatinase A, also known as MMP2 is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Gelatinase B is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as Clostridium. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of gas gangrene. They normally target the connective tissue in muscle cells and other body organs.
Neutrophil collagenase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Clostripain is a proteinase that cleaves proteins on the carboxyl peptide bond of arginine. It was isolated from Clostridium histolyticum. The isoelectric point of the enzyme is 4.8-4.9, and optimum pH is 7.4~7.8. The composition of the enzyme is indicated to be of two chains of relative molecular mass 45,000 and 12,500.

Matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9), also known as 92 kDa type IV collagenase, 92 kDa gelatinase or gelatinase B (GELB), is a matrixin, a class of enzymes that belong to the zinc-metalloproteinases family involved in the degradation of the extracellular matrix. In humans the MMP9 gene encodes for a signal peptide, a propeptide, a catalytic domain with inserted three repeats of fibronectin type II domain followed by a C-terminal hemopexin-like domain.

72 kDa type IV collagenase also known as matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and gelatinase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP2 gene. The MMP2 gene is located on chromosome 16 at position 12.2.
Interstitial collagenase, also known as fibroblast collagenase, and matrix metalloproteinase-1(MMP-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP1 gene. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. MMP-1 was the first vertebrate collagenase both purified to homogeneity as a protein, and cloned as a cDNA. MMP-1 has an estimated molecular mass of 54 kDa.

Matrilysin also known as matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP-7), pump-1 protease (PUMP-1), or uterine metalloproteinase is an enzyme in humans that is encoded by the MMP7 gene. The enzyme has also been known as matrin, putative metalloproteinase-1, matrix metalloproteinase pump 1, PUMP-1 proteinase, PUMP, metalloproteinase pump-1, putative metalloproteinase, MMP). Human MMP-7 has a molecular weight around 30 kDa.

Stromelysin-2 also known as matrix metalloproteinase-10 (MMP-10) or transin-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP10 gene.

Collagenase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMP13 gene. It is a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family. Like most MMPs, it is secreted as an inactive pro-form. MMP-13 has an predicted molecular weight around 54 kDa. It is activated once the pro-domain is cleaved, leaving an active enzyme composed of the catalytic domain and the hemopexin-like domain PDB: 1PEX. Although the actual mechanism has not been described, the hemopexin domain participates in collagen degradation, the catalytic domain alone being particularly inefficient in collagen degradation. During embryonic development, MMP-13 is expressed in the skeleton as required for restructuring the collagen matrix for bone mineralization. In pathological situations it is highly overexpressed; this occurs in human carcinomas, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.

Neutrophil collagenase, also known as matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) or PMNL collagenase (MNL-CL), is a collagen cleaving enzyme which is present in the connective tissue of most mammals. In humans, the MMP-8 protein is encoded by the MMP8 gene. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. Most MMP's are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. However, the enzyme encoded by this gene is stored in secondary granules within neutrophils and is activated by autolytic cleavage.
Collagenase clostridium histolyticum is an enzyme produced by the bacterium Clostridium histolyticum that dismantles collagen. It is used as a powder-and-solvent injection kit for the treatment of Dupuytren's contracture, a condition where the fingers bend towards the palm and cannot be fully straightened, and Peyronie's disease, a connective tissue disorder involving the growth of fibrous plaques in the soft tissue of the penis. BioSpecifics Technologies developed the preparation, which is manufactured and marketed by Endo Pharmaceuticals as Xiaflex in the US and by Sobi as Xiapex in Europe.
Plant matrix metalloproteinases are metalloproteins and zinc enzymes found in plants.
Hathewaya histolytica is a species of bacteria found in feces and the soil. It is a motile, gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobe. H. histolytica is pathogenic in many species, including guinea pigs, mice, and rabbits, and humans. H. histolytica has been shown to cause gas gangrene, often in association with other bacteria species.
Brachyurin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the Hydrolysis of proteins, with broad specificity for peptide bonds. Native collagen is cleaved about 75% of the length of the molecule from the N-terminus.
Leishmanolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Deuterolysin is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Atrolysin C is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Hanada, K.; Mizutani, T.; Yamagishi, M.; Tsuji, H.; Misaki, T.; Sawada, J. (1973). "The isolation of collagenase and its enzymological and physico-chemical properties". Agric. Biol. Chem. 37 (8): 1771–1781. doi:10.1271/bbb1961.37.1771.
- ↑ Merkel JR, Dreisbach JH (July 1978). "Purification and characterization of a marine bacterial collagenase". Biochemistry. 17 (14): 2857–63. doi:10.1021/bi00607a025. PMID 210785.
- ↑ Heindl MC, Fermandjian S, Keil B (July 1980). "Circular dichroism comparative studies of two bacterial collagenases and thermolysin". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Protein Structure. 624 (1): 51–9. doi:10.1016/0005-2795(80)90224-x. PMID 6250633.
- ↑ Labadie J, Montel MC (January 1982). "[Purification and study of some properties of a collagenase produced by Empedobacter collagenolyticum]". Biochimie. 64 (1): 49–53. doi:10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80609-3. PMID 6279175.
- ↑ Bond MD, Van Wart HE (June 1984). "Characterization of the individual collagenases from Clostridium histolyticum". Biochemistry. 23 (13): 3085–91. doi:10.1021/bi00308a036. PMID 6087888.
- ↑ Bond MD, Van Wart HE (June 1984). "Relationship between the individual collagenases of Clostridium histolyticum: evidence for evolution by gene duplication". Biochemistry. 23 (13): 3092–9. doi:10.1021/bi00308a037. PMID 6087889.
- ↑ Van Wart HE, Steinbrink DR (November 1985). "Complementary substrate specificities of class I and class II collagenases from Clostridium histolyticum". Biochemistry. 24 (23): 6520–6. doi:10.1021/bi00344a032. PMID 3002445.
- ↑ Tong, N.T.; Tsugita, A.; Keil-Dlouha, V. (1986). "Purification and characterization of two high-molecular-mass forms of Achromobacter collagenase". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 874 (3): 296–304. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(86)90028-2.
- ↑ Endo A, Murakawa S, Shimizu H, Shiraishi Y (July 1987). "Purification and properties of collagenase from a Streptomyces species". Journal of Biochemistry. 102 (1): 163–70. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122028. PMID 2822678.
- ↑ Makinen KK, Makinen PL (September 1987). "Purification and properties of an extracellular collagenolytic protease produced by the human oral bacterium Bacillus cereus (strain Soc 67)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 262 (26): 12488–95. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)45232-5 . PMID 3040751.