Related Research Articles

Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion.
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer (sacculus) that surrounds the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the N-acetylmuramic acid is an oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Peptidoglycan hydrolysis and synthesis are two processes that must occur in order for cells to grow and multiply, a technique carried out in three stages: clipping of current material, insertion of new material, and re-crosslinking of existing material to new material.

An oligopeptide, is a peptide consisting of two to twenty amino acids, including dipeptides, tripeptides, tetrapeptides, and other polypeptides. Some of the major classes of naturally occurring oligopeptides include aeruginosins, cyanopeptolins, microcystins, microviridins, microginins, anabaenopeptins, and cyclamides. Microcystins are best studied because of their potential toxicity impact in drinking water. A review of some oligopeptides found that the largest class are the cyanopeptolins (40.1%), followed by microcystins (13.4%).

Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria, commonly known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases.

Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they can poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning.
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria inside these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term nonribosomal peptide typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article.
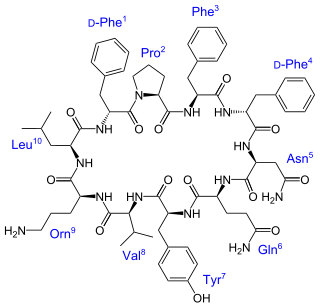
Tyrocidine is a mixture of cyclic decapeptides produced by the bacteria Brevibacillus brevis found in soil. It can be composed of 4 different amino acid sequences, giving tyrocidine A–D. Tyrocidine is the major constituent of tyrothricin, which also contains gramicidin. Tyrocidine was the first commercially available antibiotic, but has been found to be toxic toward human blood and reproductive cells. The function of tyrocidine within its host B. brevis is thought to be regulation of sporulation.

Cyclic peptides are polypeptide chains which contain a circular sequence of bonds. This can be through a connection between the amino and carboxyl ends of the peptide, for example in cyclosporin; a connection between the amino end and a side chain, for example in bacitracin; the carboxyl end and a side chain, for example in colistin; or two side chains or more complicated arrangements, for example in alpha-amanitin. Many cyclic peptides have been discovered in nature and many others have been synthesized in the laboratory. Their length ranges from just two amino acid residues to hundreds. In nature they are frequently antimicrobial or toxic; in medicine they have various applications, for example as antibiotics and immunosuppressive agents. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) is a convenient method to detect cyclic peptides in crude extract from bio-mass.

In enzymology, an L-amino acid oxidase (LAAO) (EC 1.4.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Aryldialkylphosphatase is a metalloenzyme that hydrolyzes the triester linkage found in organophosphate insecticides:

Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena, among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of Nodularia spumigena are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins.

Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxin produced by cyanobacteria. It is the most toxic of the microcystins.
Lambda-carrageenase is an enzyme which breaks down a polysaccharide found in red seaweeds, lambda-carrageenan. This enzyme has only been found in marine bacteria.
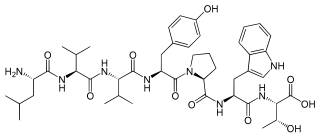
Spinorphin is an endogenous, non-classical opioid peptide of the hemorphin family first isolated from the bovine spinal cord (hence the prefix spin-) and acts as a regulator of the enkephalinases, a class of enzymes that break down endogenous the enkephalin peptides. It does so by inhibiting the enzymes aminopeptidase N (APN), dipeptidyl peptidase III (DPP3), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), and neutral endopeptidase (NEP). Spinorphin is a heptapeptide and has the amino acid sequence Leu-Val-Val-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Thr (LVVYPWT). It has been observed to possess antinociceptive, antiallodynic, and anti-inflammatory properties. The mechanism of action of spinorphin has not been fully elucidated (i.e., how it acts to inhibit the enkephalinases), but it has been found to act as an antagonist of the P2X3 receptor, and as a weak partial agonist/antagonist of the FP1 receptor.

Cyanophycinase (EC 3.4.15.6, cyanophycin degrading enzyme, beta-Asp-Arg hydrolysing enzyme, CGPase, CphB, CphE, cyanophycin granule polypeptidase, extracellular CGPase) is an enzyme. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
Plantazolicin (PZN) is a natural antibiotic produced by the gram-positive soil bacterium Bacillus velezensis FZB42. PZN has specifically been identified as a selective bactericidal agent active against Bacillus anthracis, the causative agent of anthrax. This natural product is a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP); it can be classified further as a thiazole/oxazole-modified microcin (TOMM) or a linear azole-containing peptide (LAP).
CSTX is a name given to a group of closely related neurotoxic peptides present in the venom of the wandering spider Cupiennius salei. There are twenty types so far described for this protein group. However, some are reclassified into cupiennins group of toxin, including CSTX-3, -4, -5, and -6, because of their chemical affinity. The first thirteen were isolated and identified in 1994 by Lucia Kuhn-Nentwig, Johann Schaller, and Wolfgang Nentwig of the Zoological Institute at the University of Bern, Switzerland. The different types are most likely the products of splicing variant of the same gene. They are all L-type calcium channel blockers, and also exhibit cytolytic activity by forming an alpha-helix across the cell membrane in mammalian neurons. They also inhibit voltage-gated calcium channels in insect neurons.
Cupiennins are a group of small cytolytic peptides from the venom of the wandering spider Cupiennius salei. They are known to have high bactericidal, insecticidal and haemolytic activities. They are chemically cationic α-helical peptides. They were isolated and identified in 2002 as a family of peptides called cupiennin 1. The sequence was determined by a process called Edman degradation, and the family consists of cupiennin 1a, cupiennin 1b, cupiennin 1c, and cupiennin 1d. The amino acid sequences of cupiennin 1b, c, and d were obtained by a combination of sequence analysis and mass spectrometric measurements of comparative tryptic peptide mapping. Even though they are not strong toxins, they do enhance the effect of the spider venom by synergistically enhancing other components of the venom, such CSTX.
An isopeptidase is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes isopeptide bonds, or amide bonds that occur outside the main chain in a polypeptide chain.
Hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria are a heterogeneous group of prokaryotes which can degrade and utilize hydrocarbon compounds as source of carbon and energy. Despite being present in most of environments around the world, several of these specialized bacteria live in the sea and have been isolated from polluted seawater.
References
- ↑ Dziga, Dariusz; Wladyka, Benedykt; Zielińska, Gabriela; Meriluoto, Jussi; Wasylewski, Marcin (Apr 2012). "Heterologous expression and characterisation of microcystinase". Toxicon. 59 (5): 578–86. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.01.001. PMID 22326726.
- ↑ Somdee, Theerasak; Thunders, Michelle; Ruck, John; Lys, Isabelle; Allison, Margaret; Page, Rachel (2013). "Degradation of [Dha7]MC-LR by a Microcystin Degrading Bacterium Isolated from Lake Rotoiti, New Zealand". ISRN Microbiology. 2013: 1–8. doi: 10.1155/2013/596429 . PMC 3712209 . PMID 23936728.