
This is intended to be a complete list of properties and districts listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Orleans County, New York. The locations of National Register properties and districts may be seen in a map by clicking on "Map of all coordinates". Two listings, the New York State Barge Canal and the Cobblestone Historic District, are further designated a National Historic Landmark.

The Lake McDonald Lodge Historic District is a historic district in Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. It comprises the Lake McDonald Lodge and surrounding structures on the shores of Lake McDonald. It is centered on the main lodge, which was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1987, as well as surrounding guest cabins, dormitory buildings, employee residences, utility buildings, and retail structures. The district includes several privately owned inholding structures that are contributing structures, as well as a number of non-contributing buildings.

Gales Ferry is a census-designated place and village in the town of Ledyard, Connecticut, United States. It is located along the eastern bank of the Thames River. The community developed as a result of having a ferry to Uncasville located at this site, and from which the village was named. Gales Ferry was listed as a census-designated place for the 2010 Census, with a population of 1,162.

Fort Benjamin Harrison was a U.S. Army post located in suburban Lawrence Township, Marion County, Indiana, northeast of Indianapolis, between 1906 and 1991. It is named for the 23rd United States president, Benjamin Harrison.
William Augustus Edwards, also known as William A. Edwards was an Atlanta-based American architect renowned for the educational buildings, courthouses and other public and private buildings that he designed in Florida, Georgia and his native South Carolina. More than 25 of his works have been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Walworth County, Wisconsin. It is intended to provide a comprehensive listing of entries in the National Register of Historic Places that are located in Walworth County, Wisconsin. The locations of National Register properties for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below may be seen in a map.

The Pennsylvania School for the Deaf is the third-oldest school of its kind in the United States. Its founder, David G. Seixas (1788–1864), was a Philadelphia crockery maker-dealer who became concerned with the plight of impoverished deaf children who he observed on the city's streets. The current school building is listed by the National Register of Historic Places, and two former campuses are similarly recognized.
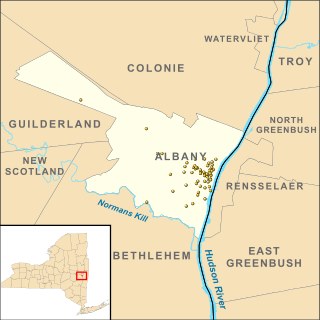
There are 77 properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York, United States. Six are additionally designated as National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), the most of any city in the state after New York City. Another 14 are historic districts, for which 20 of the listings are also contributing properties. Two properties, both buildings, that had been listed in the past but have since been demolished have been delisted; one building that is also no longer extant remains listed.

The Commercial Historic District in Potlatch, Idaho was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986. In 1986, it included seven contributing buildings and a contributing object. It includes work by architect C. Ferris White and work by A.M. Homes.

The Terry's Plain Historic District is a 325-acre (132 ha) historic district in the town of Simsbury, Connecticut that was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1993. The district is significant as a preserved rural landscape. It included 27 contributing buildings of various architectural styles, including Greek Revival, Federal and Late Victorian architecture, and 17 non-contributing buildings.

Kemper Hall is placed on a Kenosha County park with 17.5 acres in Kenosha, Wisconsin, United States. Kemper Hall overlooks Lake Michigan with a historic chapel, observatory, the Anderson Arts Center, and the Durkee Mansion.

The Jacksonville Historic District is a historic district encompassing 696 buildings in Jacksonville, Illinois. The buildings in the district were mainly constructed from 1829 to the 1930s and represent nearly every popular architectural style from the period. The Greek Revival, Italianate, and Queen Anne styles are especially prevalent in the district. The district includes the campuses of two prominent Jacksonville educational institutions: Illinois College and the Illinois School for the Deaf. Illinois College, the first college in Illinois to grant a degree, was founded in 1829; its first building, Beecher Hall, is the oldest building in the district. The Illinois School for the Deaf was established in 1839 by the Illinois Legislature for the education of hearing-impaired students. Aside from these two institutions, the majority of the district is residential and includes many of Jacksonville's most historically and architecturally significant homes. The district is considered to have retained its historic character well, as 650 of its buildings are considered contributing buildings and the number of recent buildings in the district has been called "remarkably low".

The Rock Crest–Rock Glen Historic District is a nationally recognized historic district located in Mason City, Iowa, United States. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. At the time of its nomination it contained 10 resources, which included eight contributing buildings, one contributing site, and one non-contributing building. All of the buildings are houses designed in the Prairie School style, and are a part of a planned development. Joshua Melson, a local developer, bought the property along Willow Creek between 1902 and 1908. Initially, there were only going to be 10 houses built, but the number grew to 16. While only half the houses planned were actually constructed, it is still the largest cluster of Prairie School houses in the country. The one non-contributing house is the 1959 McNider House, a Modern movement structure that was built where one of the planned houses was to be built, but never was. The architects who contributed to the district include Walter Burley Griffin, who provided the initial plan for the development; Barry Byrne, who took over from Griffin; Marion Mahony Griffin, Walter Griffin's wife and an architect in her own right; and Einar Broaten. Frank Lloyd Wright had a design that was never built here. The plans were used to build the Isabel Roberts House in River Forest, Illinois instead.

The Merrill Avenue Historic District in Glendive, Montana is a historic district which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1988. The district includes 28 contributing buildings and a contributing site on 2.5 acres (1.0 ha). It includes Classical Revival, Late Gothic Revival, and Italianate architecture.

The Griffin Commercial Historic District, in Griffin, Georgia, is a 28 acres (11 ha) historic district which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1988. It included 93 contributing buildings, two contributing structures, and a contributing site. The district is roughly bounded by Central Alley, Sixth, Taylor and Eighth Streets.

The Little Campus is a historic district and part of the University of Texas at Austin campus in Austin, Texas. Originally built in 1856 as the Texas Asylum for the Blind, the complex was used for a variety of purposes through the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. It was acquired by the University of Texas after World War I and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.

Haralson Bleckley was an American architect who designed many buildings in his hometown of Atlanta, Georgia. Several of his works are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). His office was in the Flatiron Building. He also proposed the Bleckley Plaza Plan, a largescale architectural project that would have seen the creation of a large plaza in downtown Atlanta.

The Griffin City Hall, in Griffin, Georgia, was built around 1910. It was designed by Atlanta architect Haralson Bleckley. It has become known as Old City Hall or Historic City Hall, and is located on the northeast corner of E. Solomon St. at N. 6th St. in Griffin.

The Grantville Historic District, in Grantville, Georgia, is a historic district which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991. The listing included 225 contributing buildings, a contributing structure, and a contributing site on 192 acres (0.78 km2).



















